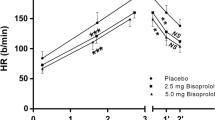
Summary
β-Adrenoceptor blockers (β-blockers) are common first-choice drugs in the treatment of various cardiovascular disorders. Physical exercise performed during single-dose administration of β-blockers, however, is associated with an increased rate of perceived exertion; an effect which appears to be partly reduced with long term treatment. Although clinical doses of β-blockade may reduce heart rate by 30 to 35%, during maximal exercise cardiac output is not equally reduced. Accordingly, most studies have demonstrated increased stroke volume after β-blockade. This reduction in heart rate is typically accompanied by a decreased VO2max (5 to 15%) in both patients and healthy, trained subjects. This smaller reduction in VO2 max, as compared with the decrease in cardiac output, is the result of a partly compensating increased arteriovenous O2 difference. Work capacity as reflected by the ability to perform intense short term or more prolonged steady-state exercise is also impaired following β-blockade. β-Adrenoceptors can be subdivided into types β1- and β2. Blockers which are specific for either β1-receptors (β-selective blockers) or both β1- and β2 receptors (non-selective blockers) differ with regard to their effect on exercise performance. Exercise performance ability, irrespective of exercise intensity and duration, is impaired to a greater extent following non-selective than β-selective blockade at equal reductions in heart rate. This response stems from a decreased energy flux through glycogenolysis during non-selective blockade treatment. Individuals receiving β-blockade medication therefore show greater adaptive response to physical conditioning during treatment with β1-selective than non-selective blockade probably because of greater training intensity with the former therapy. Neither psychomotor performance nor muscular strength and power is negatively affected by β-blockade. Nevertheless, the ability to perform athletic events requiring high levels of motor control under emotional stress but not high levels of aerobic or anaerobic energy release, is probably increased during β-blockade.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlquist, R.P.: A study of the adrenotropic receptors. American Journal of Physiology 153: 586–600 (1948).
Aigner, A.; Muss, N.; Krempler, F.; Fenninger, H. and Sandhofer, F.: Einfluss einer akuten β1- und β1/β2-Rezeptorenblockade auf den Kohlen-hydrat- und Fettstoffwechsel unter Belastungsbedingungen. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 108: 293–298 (1983).
Anderson, S.D.; Bye, P.T.P.; Perry, C.P.; Hamor, G.P.; Theobald, G. and Nyberg, G.: Limitation of work performance in normal adult males in the presence of beta-adrenergic blockade. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 9: 515–520 (1979).
Antal, L.C. and Good, C.S.: Effects of oxpranolol or pistol shooting under stress. The Practitioner 224: 755–760 (1980).
Arnold, A.; McAuliff, J.P.; Colella, D.F.; O’Connor, W.V. and Brown Jr, T.H.G.: The β2-receptor mediated glycogenolytic responses to catecholamines in the dog. Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamic et de Thérapie 176: 451–457 (1968).
Arnold, A. and Selberis, W.H.: Activities of catecholamines on the rat muscle glycogenolytic (β-2) receptor. Experientia 24: 1010–1011 (1968).
Åström, H.: Haemodynamic effects of beta-adrenergic blockade. British Heart Journal 30: 44–49 (1968).
Åström, H and Jonsson, B.: Haemodynamic effects of different beta blockers in angina pectoris. Scottish Medical Journal 22: 64–68 (1977).
Björntorp, P.: Hypertension and Exercise. Hypertension 4 (Suppl. 3): 56–59 (1982).
Borg, G.: Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scandinavian Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2: 92–98 (1970).
Bowman, W.C. and Nott, M.W.: Actions of sympathomimetic amines and their antagonists on skeletal muscle. Pharmacological Reviews 21: 27–72 (1969).
Brantigan, T.A.; Brantigan, C.O. and Joseph, N.H.: Beta-blockade and musical performance. Lancet 2: 896 (1978).
Brewer, C: Beneficial effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on ‘exam, nerves’. Lancet, Aug 26: 435 (1972).
Brown, H.C.; Carruthers, S.G.; Johnston, G.D.; Kelly, J.G.; McAinsh, J.; McDevitt, D.G. and Shanks, R.G.: Clinical pharmacologic observations on atenolol, a beta-adrenoceptor blocker. Clinical Pharmacology Therapy 20: 524–534 (1976).
Bruce, R.A.; Hossack, K.F.; Kusumi, F. and Clarke, L.J.: Acute effects of oral propranolol on hemodynamic responses to upright exercise. American Journal of Cardiology 44: 132–140 (1979).
Brundin, T.; Edhag, O. and Lundman, T.: Effects remaining after withdrawal of long-term beta-receptor blockade. British Heart Journal 38: 1065–1072 (1976).
Burke, R.E. and Edgerton, V.R.: Motor unit properties and selective involvement in movement; in Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, pp. 31–81, Vol. 3 (Academic Press, New York 1975).
Camus, G.; Scheen, A.; Cession-Fossion, A.; Juchmes, J.; Mylle, P. and Dreezen, E.: Endurance aprés propranolol chez l’Homme effectuant un exercise dynamique général. Comptes Rendus des Seances de la Societe de Biologie et de ses Filiates: 919–924 (1980).
Carlson, L.A.; Ekelund, L.G. and Fröberg, S.: Concentration of triglycerides, phospholipids and glycogen in skeletal muscles and of free fatty acids and β-hydroxybutyric acid in blood in man in response to exercise. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 1: 248–254 (1971).
Cerretelli, P.; Shindell, D.; Pendergast, D.P.; diPrampero, P.E. and Rennie, D.W.: Oxygen uptake transients at the onset and offset of arm and leg work. Respiration Physiology 30: 81–97 (1977).
Chasiotis, D.; Brandt, R.; Harris, R.C. and Hultman, E.: Effects of β-blockade on glycogen metabolism in human subjects during exercise. American Journal of Physiology 245: E166–E170 (1983).
Close, R.I.: Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiological Reviews 52: 129–197 (1972).
Conolly, M.E.; Kersting, F. and Dollery, C.T.: The clinical pharmacology of beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases 29: 203–234 (1976).
Conway, J.; Wheeler, R. and Sannerstedt, R.: Sympathetic nervous activity in relation to age. Cardiovascular Research 5: 577–581 (1971).
Cumming, G.R. and Carr, W.: Hemodynamic response to exercise after propranolol in normal subjects. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 44: 465–474 (1966).
Davis, C.T.M. and Sargeant, A.J.: The effects of atropine and practolol on the perception of exertion during treadmill exercise. Ergonomics 22: 1141–1146 (1979).
Day, J.L.; Metcalfe, J. and Simpson, C.N.: Adrenergic mechanisms in control of plasma lipid concentrations. British Medical Journal 284: 1145–1148 (1982).
Deacon, S.P.: The effects of atenolol and propranolol upon lipolysis. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 5: 123–125 (1978).
De Plaen, J.F.; Amery, A. and Reybrouck, T.: Comparative potency of atenolol and propranolol as beta-adrenergic blocking agents in man. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 10: 297–303 (1976).
Donald, D.E.; Milburn, S.E. and Shepherd, J.T.: Effect of cardiac denervation on the maximal capacity for exercise in the racing greyhound. Journal of Applied Physiology 19: 844–852 (1964).
Donaldson, E.; Grant-Thomson, J.; Morwood, P.; O’Connor, N. and Tippett, R.: Pilot study on the value of a beta-blocking drug in initial helicopter training. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine 51: 926–929 (1980).
Ekblom, B. and Goldbarg, A.N.: The influence of physical training and other factors on the subjective rating of perceived exertion. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 83: 399–406 (1971).
Ekblom, B.; Goldbarg, A.N.; Kilbom, Å. and Åstrand, P.-O.: Effects of atropine and propranolol on the oxygen transport system during exercise in man. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 30: 35–42 (1972).
Ekblom, B.; Kilbom, Å. and Soltysiak, J.: Physical training, bradycardia, and autonomic nervous system. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 32: 251–256 (1973).
Eklund, B. and Kaijser, L.: Effect of regional and β-adrenergic blockade on blood flow in the resting forearm during contralateral isometric handgrip. Journal of Physiology 262: 39–50 (1976).
Eliasch, H.; Rosen, A. and Scott, H.M.: Systemic circulatory response to stress of simulated flight and to physical exercise before and after propranolol blockade. British Heart Journal 29:671–683 (1967).
Epstein, S.E.; Robinson, B.F.; Kahler, R.L. and Braunwald, E.: Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on the cardiac response to maximal and submaximal exercise in man. Journal of Clinical Investigation 44: 1745–1753 (1965).
Erikssen, J.; Thaulow, E.; Mundal, R.; Opstad, P. and Nitter-Hauge, S.: Comparison of β-adrenoceptor blockers under maximal exercise (pindolol vs metoprolol vs atenolol). British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 13: 201–209 (1982).
Essén, B.: Studies on the regulation of metabolism in human skeletal muscle using intermittent exercise as an experimental model. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl.): 454 (1978).
Ewy, G.A.; Wilmore, J.H.; Morton, A.R.; Stanforth, P.R.; Constable, S.H.; Buono, M.J.; Conrad, K.A.; Miller, H. and Gatewood, C.F.: The effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on obtaining a trained exercise state. Journal of Cardiac Rehabilitation 3: 25–29 (1983).
Fagard, R.; Reybrouck, T.; Lijner, P.; Amery, A.; Moerman, E. and de Schaepdryver, A.: Alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor blockade does not affect ventilation during exercise in man. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 12: 375–379 (1980).
Fischer, E.H.; Heilmeyer, L.M.G. and Haschke, R.H.: Phosphorylase and the control of glycogen degradation. Current Topics in Cellular Regulation 4: 211–251 (1971).
Folgering, H. and van Bussel, M.: Maximal exercise power after a single dose of metoprolol and of slow-release metoprolol. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 225–229 (1980).
Franciosa, J.A.; Johnson, S.M. and Tobian, L.J.: Exercise performance in mildly hypertensive patients. Chest 78: 291–299 (1980).
Franz, I.-W. and Lohmann, F.W.: Der Einfluss einer chronischen sog. kardioselektiven und nichtkardioselektiven β-Rezeptoren-Blockade auf den Blutdruck, die O2-Aufnahme und den Kohlenhydratstoffwechsel. Zeitschrift für Kardiologie 68: 503–509 (1979).
Franz, I.-W. and Lohmann, F.W.: Unterschiedlicher einfluss einer chronischen überwiegend β1-selectiven und β1-β2-Rezeptoren-blockade auf der Kohlenhydratstoffwechsel. Ergometrische Undersuchungen bei hochdruckkranken. Klinische Wochenschrift 58: 1155–1161 (1980).
Franz, I.-W.; Lohmann, F.W. and Koch, G.: Effects of chronic antihypertensive treatment with acebutolol and pindolol on blood pressure, plasma catecholamines, and oxygen uptake at rest and during submaximal and maximal exercise. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 4: 180–186 (1982).
Franz, I.-W.; Lohmann, F.W. and Koch, G.: Oxygen uptake and plasma catecholamines during submaximal and maximal exercise after long-term β-receptor blockade. International Journal of Sports Medicine 6: 202–206 (1985).
Franz, I.-W.; Lohmann, F.W.; Koch, G. and Quabbe, H.-J.: Aspects of hormonal regulation of lipolysis during exercise: Effects of chronic β-receptor blockade. International Journal of Sports Medicine 4: 14–20 (1983).
Frick, M.H.; Elovainio, R.O. and Somer, T.: The mechanism of bradycardia evoked by physical training. Cardiologia 51: 46–54 (1967).
Frisk-Holmberg, M.; Jorfeldt, L. and Juhlin-Dannfelt, A.: Influence of alprenolol on hemodynamic and metabolic responses to prolonged exercise in subjects with hypertension. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 6: 675–685 (1977).
Frisk-Holmberg, M.; Jorfeldt, L. and Juhlin-Dannfelt, A.: Metabolic effects in muscle during antihypertensive therapy with β1, and β1/β-adrenoceptor blockers. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 30: 611–618 (1981).
Frisk-Holmberg, M.; Jorfeldt, L.; Juhlin-Dannfelt, A. and Karlsson, J.: Metabolic changes in muscle on long-term alprenolol therapy. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 26: 566–571 (1979).
Frisk-Holmberg, M. and Östman, J.: Differential inhibition of lipolysis in human adipose tissue by adrenergic beta receptor blocking drugs. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 200: 598–605 (1977).
Furberg, C.: Adrenergic beta-blockade and physical working capacity. Acta Medica Scandinavica 182: 119–127 (1967).
Galbo, H.; Holst, J.J.; Christensen, N.J. and Hilsted, J.: Glucagon and plasma catecholamines during beta-receptor blockade in exercising man. Journal of Applied Physiology 40: 855–863 (1976).
Gibson, D.G.: Pharmacodynamic properties of β-adrenergic receptor blocking drugs in man. Drugs 7: 8–38 (1974).
Glaister, D.H.: Effects of beta blockers on psychomotor performance. A Review. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine 52:23–30 (1981).
Gollnick, P.D.; Soule, R.G.; Taylor, A.W.; Williams, C. and Ianuzzo, C.D.: Exercise-induced glycogenosis and lipolysis in the rat: hormonal influence. American Journal of Physiology 219: 729–733 (1970).
Górski, J. and Pietrzyk, K.: The effect of beta-adrenergic receptor blockade on intramuscular glycogen mobilization during exercise in the rat. European Journal of Applied Physiology 48: 201–205 (1982).
Grimby, G. and Smith, U.: Beta-blockade and muscle function. Lancet Dec 16: 1318–1319 (1978).
Hamer, J. and Sowton, E.: Cardiac output after β-adrenergic blockade in ischaemic heart disease. British Heart Journal 27: 892–895 (1965).
Hansson, B.-G.; Dymling, J.-F.; Hedeland, H. and Hulthén, U.L.: Long term treatment of moderate hypertension with the beta1-receptor blocking agent metoprolol. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 11: 239–245 (1977).
Harris, R.C.; Bergström, J. and Hultman, E.: The effect of propranolol on glycogen metabolism during exercise; In Pernow and Saltin (Eds), Muscle Metabolism during Exercise, pp. 301–305 (Plenum Press, New York 1971).
Harris, R.C.; Hultman, E. and Sahlin, K.: Glycolytic intermediates in human muscle after isometric contraction. Pflügers Archives 389: 277–282 (1981).
Harron, D.W.G.; Balnave, K.; Kinney, C.D.; Wilson, R.; Russell, C.J. and Shanks, R.G.: Effects on exercise tachycardia during forty-eight hours of a series of doses of atenolol, sotalol, and metoprolol. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 29: 295–302 (1981).
Hartling, O.J.; Noer, I.; Svendsen, T.L.; Clausen, J.P. and Trap-Jensen, J.: Selective and non-selective β-adrenoceptor blockade in the human forearm. Clinical Science 58: 279–286 (1980).
Herwaarden van, C.L.A.; Binkhorst, R.A.; Fennis, J.F.M. and ’T Laar van, A.: Effects of propranolol and metoprolol on hae-modynamic and respiratory indices and on perceived exertion during exercise in hypertensive patients. British Heart Journal 41: 99–105 (1979).
Hiatt, R.; Fradl, D.C.; Zerbe, G.O.; Bryyny, R. L. and Nies, A.S.: Selective and non-selective β-blockade of the peripheral circulation. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 35: 12–18 (1984).
Holmberg, E. and Waldeck, B.: The effect of insulin on skeletal muscle contractions and its relation to the effect produced by β-adrenoceptor stimulation. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 109: 225–229 (1980).
Horgan, J.H. and Teo, K.K.: Training response in patients with coronary artery disease receiving beta-adrenergic blocking drugs with or without partial agonist activity. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 5: 1019–1024 (1983).
Hughson, R.L.: Alterations in the oxygen deficit-oxygen debt relationships with β-adrenergic receptor blockade in man. Journal of Physiology 349: 375–387 (1984).
Hughson, R.L. and MacFarlane, B.J.: Effect of oral propranolol on the anaerobic threshold maximum exercise performance in normal man. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 59: 567–573 (1981).
Hughson, R.L.; Rouleau, M. and Jones, N.L.: Oxygen uptake kinetics at onset of exercise in man with and without β-blockade. (Abstract.) Federation Proceedings 37: 580 (1978).
Hughson, R.L. and Smyth, G.A.: Slower adaptation of VO2 to steady state of submaximal exercise with β-blockade. European Journal of Applied Physiology 52: 107–110 (1983).
Hunyor, S. and Nyberg, G.: Comparison of intra-arterial and indirect blood pressures at rest and during isometric exercise in hypertensive patients before and after metoprolol. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 6: 109–114 (1978).
Imhof, P.R.; Blatter, K.; Fuccella, L.M. and Turri, M.: Beta-blockade and emotional tachycardia: Radiotelemetric investigations in ski-jumpers. Journal of Applied Physiology 27: 366–369 (1969).
Issekutz Jr, B.: Role of beta-adrenergic receptors in mobilization of energy sources in exercising dogs. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology 44: 869–876 (1978).
James, I.M.; Pearson, R.M.; Griffith, D.N.W. and Newbury, P.: Effect of stage-fright in musicians. Lancet 2: 952–954 (1977).
Jansson, E.; Norman, B.; Kaiser, P.; Tesch, P.A. and Sollevi, A.: Effect of non-selective β-adrenergic blockade on adenine catabolism in thigh muscle during maximal exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Submitted for publication).
Johansson, S.R.; McCall, M.; Wilhelmsson, C. and Vedin, J.A.: Duration of action of beta blockers. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 27: 593–601 (1980).
Juhlin-Dannfelt, A. and Åström, H.: Influence of β-adrenoceptor blockade on leg blood flow and lactate release in man. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 39: 179–183 (1979).
Juhlin-Dannfelt, A.C.; Terblanche, S.E.; Fell, R.D.; Young, J.C and Holloszy, J.O.: Effects of β-adrenergic receptor blockade on glycogenosis during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology 53: 549–554 (1982).
Kaiser, P.: Running performance as a function of the dose-response relationship to β-adrenoceptor blockade. International Journal of Sports Medicine 3: 29–32 (1982).
Kaiser, P.: Physical performance and muscle metabolism during β-adrenergic blockade in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl.): 536 (1984).
Kaiser, P.; Rössner, S. and Karlsson, J.: Effects of β-adrenergic blockade on endurance and short-time performance in respect to individual muscle fiber composition. International Journal of Sports Medicine 2: 37–42 (1981).
Kaiser, P. and Tesch, P.: Perceived exertion and muscle lactate accumulation during exercise following β-adrenergic blockade; in Knuttgen, Vogel and Poortmans (Eds) Biochemistry of Exercise pp. 728–732 (Human Kinetics Publishers, Champaign 1983a).
Kaiser, P. and Tesch, P.A.: Effects of acute-β-adrenergic blockade on lactate metabolism during submaximal exercise. International Journal of Sports Medicine 4: 275–277 (1983b).
Kaiser, P. and Tesch, P.A.: Muscle lactate accumulation during exercise following β-blockade. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 117: 149–151 (1983c).
Kaiser, P.; Tesch, P.; Turner, S.; Karlsson, J. and Kaijser, L.: Oxygen consumption and lactate metabolism during exercise following β-adrenoceptor blockade. Drugs 25: 260–261 (1983d).
Kaiser, P.; Tesch, P.A.; Thorsson, A.; Karlsson, J. and Kaijser, L.: Skeletal muscle glycolysis during submaximal exercise following acute β-adrenergic blockade in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 123: 285–291 (1985a).
Kaiser, P.; Tesch, P.A.; Frisk-Holmberg, M.; Juhlin-Dannfelt, A. and Kaijser, L.: Effect of β1-selective and non-selective β-blockade on work capacity and muscle metabolism. Clinical Physiology (in press, 1985b).
Kaiser, P.; Hylander, B.; Eliasson, K. and Kaijser, L.: Effect of β1-selective and non-selective β-blockade on blood pressure relative to physical performance. American Journal of Cardiology, Vol. 55, 79D–84D (1985c).
Kaplan, N.M.: The present and future use of β-blockers. Drugs 25: 1–4 (1983).
Karlsson, J.; Kjessel, T. and Kaiser, P.: Alpine skiing and acute β-blockade. International Journal of Sports Medicine 4: 190–193 (1983).
Kenney, W.L. and Zambraski, E.J.: Physical activity in human hypertension: A mechanisms approach. Sports Medicine 1: 459–473 (1984).
Keul, J.; Lehmann, M. and Wybitul, K.: Zur Wirkung von Bunitrolol auf Herzfrequenz, metabolische Grössen bei Körperarbeit und Leistungsverhalten. Arzneimittel-Forschung 31: 1948–1953 (1981).
Kindermann, W.; Schmitt, W.M.; Biro, G. and Schnabel, A.: Metabolismus und hormonelles Verhalten bei Körperarbeit unter akuter Betar1-Sympathiko-lyse. Zeitschrift für Kardiologie 70: 406–412 (1981).
Koch, G.; Franz, I.-W.; Grubba, A. and Lohmann, F.W.: β-adrenoceptor blockade and physical activity: Cardiovascular and metabolic aspects. Acta Medica Scandinavica 672: 55–62 (1983).
Krebs, E.G.; DeLange, R.J.; Kemp, R.G. and Riley, W.D.: Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase. Pharmacology Review 18: 163–171 (1966).
Krishnan, G.: Oxprenolol in the treatment of examination stress. Current Medical and Research Opinion 4: 241–243 (1976).
Lands, A.M.; Arnold, A.; McAuliff, J.P.; Luduena, F.P. and Brown Jr, T.G.: Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature 214: 597–598 (1967).
Laslett, L.J.; Paumer, L.; Scott-Baier, P. and Amsterdam, E.A.: Efficacy of exercise training in patients with coronary artery disease who are taking propranolol. Circulation 68: 1029–1034 (1983).
Laustiola, K.; Uusitalo, A.; Koivula, T.; Sovijärvi, A.; Seppälä, E.; Nikkari, T. and Vapaatalo, H.: Divergent effects of atenolol, practolol and propranolol on the peripheral metabolic changes induced by dynamic exercise in healthy men. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 293–297 (1983).
Lawlor, M.R.; Thomas, D.P.; Michele, J.J.; Carey: R.A.; Paolene, A.M. and Bove, A.M.: Effects of chronic β-adrenergic blockade on hemodynamic and metabolic responses to endurance training. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 17: 393–400 (1985).
Leenen, F.H.H.; Coenen, C.H.M.; Zonderland, M. and Maas, A.H.J.: Effects of cardioselective and nonselective β-blockade on dynamic exercise performance in mildly hypertensive men. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 28: 12–21 (1980).
Leitch, A.G.; Hopkin, J.M.; Ellis, D.A.; Clarkson, D.; Merchant, S. and McHardy, G.J.R.: Failure of propranolol and metoprolol to alter ventilatory responses to carbon dioxide and exercise. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 9: 493–498 (1980).
LeWinter, M.M.; Crawford, M.H.; Karliner, J.S. and O’Rourke, R.A.: Effects of oral propranolol in normal subjects. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 17: 709–712 (1975).
Lidén, S. and Gottfries, C.-G.: Beta-blocking agents in the treatment of catecholamine-induced symptoms in musicians. Lancet, Aug 31: 529 (1974).
Lundborg, P.; Åström, H.; Bengtsson, C; Fellenius, E.; Von Schenck, H.; Svensson, L. and Smith, U.: Effect of β-adrenoceptor blockade on exercise performance and metabolism. Clinical Science 61: 299–305 (1981).
Lund-Johansen, P.: Haemodynamic long-term effects of a new β-adrenoceptor blocking drug, atenolol (ICI 66082), in essential hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 3: 445–451 (1976).
Lund-Johansen, P.: Hemodynamic consequences of long-term beta-blocker therapy: A 5-year follow-up study of atenolol. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1: 487–495 (1979).
MacDonald, LA.; Bennett, T.; Brown, A.M.; Wilcox, R.G. and Skene, A.M.: The effects of acute or chronic ingestion of propranolol or metoprolol on the metabolic and hormonal responses to prolonged, submaximal exercise in hypertensive men. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 17: 283–293 (1984).
Maksud, M.G.; Coutts, K.D.; Tristani, F.E.; Dorchak, J.R.; Barboriak, J.J. and Hamilton, L.H.: The effects of physical conditioning and propranolol on physical work capacity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 4: 225–229 (1972).
Maksud, M.G.; Tristani, F.E.; Coutts, K.D.; Barboriak, J.J. and Hamilton, L.H.: Effects of propranolol on several physiological responses during orthostatic and exercise stress in healthy male subjects. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 49: 867–872 (1971).
Marsden, CD.; Foley, T.H.; Owen, D.A.L. and McAllister, R.G.: Peripheral β-adrenergic receptors concerned with tremor. Clincal Science 33: 53–65 (1967).
Marsh, R.C; Hiatt, W.R.; Brammell, H.L. and Horwitz, L.D.: Attenuation of exercise conditioning by low dose beta-adrenergic receptor blockade. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2: 551–556 (1983).
McAinsh, J.; Baber, N.S.; Smith, R. and Young, J.: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies with long-acting propranolol. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 6: 115–121 (1978).
McDevitt, D.G.: Clinical significance of cardioselectivity state-of-the-art. Drugs 25: 219–226 (1983).
McDevitt, D.G.; Brown, C; Carruthers, G. and Shanks, R.: Influence of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity and cardioselectivity on beta adrenoceptor blockade. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 21: 556–566 (1977).
McLeod, A.A.; Brown, J.E.; Kuhn, C; Kitchell, B.B.; Sedor, F.A.; Williams, R.S. and Shand, D.G.: Differentiation of hemodynamic, humoral and metabolic responses to β1 and β2-adrenergic stimulation in man using atenolol and propranolol. Circulation 67: 1076–1084 (1983).
McLeod, A.A.; Kraus, W.E. and Williams, R.S.: Effects of beta1-selective and nonselective beta-adrenoceptor blockade during exercise conditioning in healthy adults. American Journal of Cardiology 53: 1656–1661 (1984).
McSorley, P.D. and Warren, D.J.: Effects of propranolol and metoprolol on the peripheral circulation. British Medical Journal 2: 1598–1699 (1978).
Morrison, S.C; Chir, B.; Kumana, C.R.; Rudnick, K.V.; Haynes, B. and Jones, N.L.: Selective and nonselective beta-adrenoceptor blockade in hypertension: Responses to changes in posture, cold and exercise. Circulation 65: 1171–1177 (1982).
Muir, G.G.; Chamberlain, D.A. and Tunstall-Pedoe, D.: Effects of -sympathetic blockade on non-esterified-fatty-acid and carbohydrate metabolism at rest and during exercise. Lancet Oct 31: 930–932 (1964).
Nazar, K.; Brzezinska, Z. and Kowalski, W.: Mechanism of impaired capacity for prolonged muscular work following beta-adrenergic blockade in dogs. Pfluegers Archives: European Journal of Physiology 336: 72–78 (1972).
Nazar, K.; Brzezinska, Z.; Lyszczarz, J. and Danielewicz-Kotowicz, A.: Sympathetic control of the utilization of energy substrates during long-term exercise in dogs. Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamic et de Biochimie 79: 873–879 (1971)
Neil-Dwyer, G.: The clinical importance of lipid solubility in beta blockers. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine 52: 19–22 (1981).
Neil-Dwyer, G.; Bartlett, J.; McAinsh, J. and Cruickshank, J.M.: β-adrenoceptor blockers and the blood-brain barrier. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 11: 549–553 (1981).
Nordenfelt, I.: Blood flow of working muscles during autonomic blockade of the heart. Cardiovascular Research 8: 263–267 (1974).
Pearson, S.B.; Banks, D.C. and Patrick, J.M.: The effect of β-adrenoceptor blockade on factors affecting exercise tolerance in normal man. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 8: 143–148 (1979).
Petersen, E.S.; Whipp, B.J.; Davis, J.A.; Huntsman, D.J.; Brown, H.V. and Wasserman, K.: Effects of β-adrenergic blockade on ventilation and gas exchange during exercise in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology 54: 1306–1313 (1983).
Phillipson, J.: Beta-blockers on the concert platform. British Medical Journal 6: 1209 (1978).
Pine, M.; Favrot, L.; Smith, S.; McDonald, K. and Chidsey, C.A.: Correlation of plasma propranolol concentration with therapeutic response in patients with angina pectoris. Circulation 52: 886–893 (1975).
Pirnay, F.; Delvaux, J.M.; Deroanne, R.; Wittamer, P. and Petit, J.M.: Effet d’un bloqueur bêta-adrénergigue sur la réponse cardiaque pendant l’exercice musculaire. Internationale Zeitschrift für angewanate Physiologie einschliesslich Arbeitphysiologie 29: 88–93 (1970).
Pratt, CM.; Welton, D.E.; Squires, W.G.; Kirby, T.E.; Hartung, G.H. and Miller, R.R.: Demonstration of training effect during chronic beta-adrenergic blockade in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 64: 1125–1129 (1981).
Reybrouck, T.; Amery, A. and Billiet, L.: Hemodynamic response to graded exercise after chronic beta-adrenergic blockade. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology 42: 133–138 (1977a).
Reybrouck, T.; Amery, A.; Fagard, R. and Billiet, L.: Haemodynamic response to graded exercise during chronic beta-adrenergic blockade with bunitrolol, an agent with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 12: 333–339 (1977b).
Richter, E.A.: Influence of the sympatho-adrenal system on some metabolic and hormonal responses to exercise in the rat. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl.): 528 (1984).
Robertson, J.I.S.: State-of-the-art Review: β-blockade and the treatment of hypertension. Drugs 25: 5–11 (1983).
Rowell, L.B.: Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiological Review 54: 75–159 (1974).
Rusko, H.; Kantola, H.; Luhtanen, P.; Pulli, M.; Videman, T. and Viitasalo, J.T.: Effect of beta-blockade on performances requiring force, velocity, coordination and/or anaerobic metabolism. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 20: 139–144 (1980).
Sable, D.L.; Brammell, H.L.; Sheehan, M.W., Nies, A.S.; Gerber, J. and Horwitz, L.D.: Attenuation of exercise conditioning by beta-adrenergic blockade. Circulation 65: 679–684 (1982).
Saltin, B. and Gollnick, P.D.: Skeletal muscle adaptability: Significance for metabolism and performance; in Peachy, Adrian and Geiger (Eds) Handbook of Physiology, section 10, pp. 555–631 Skeletal Muscle (Williams and Wilkins Baltimore 1983).
Schnabel, A.; Kindermann, W.; Salas-Fraire, O.; Cassens, J. and Steinkraus, V.: Effect of β-adrenergic blockade on supramaximal exercise capacity. International Journal of Sports Medicine 4: 278–281 (1983).
Seals, D.R. and Hagberg, J.M.: The effect of exercise training on human hypertension: A review: Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 16: 207–215 (1984).
Shand, D.G.: Comparative pharmacology of the β-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. Drugs 25: 92–99 (1983).
Siitonen, L. and Jänne, J.: Effect of beta-blockade during bowling competitions. Annals of Clinical Research 8: 393–398 (1976).
Siitonen, L.; Sonek, T. and Järre, J.: Effect of beta-blockade on performance: Use of beta-blockade in bowling and in shooting competitions. Journal of International Research 5: 359–366 (1977).
Sjöberg, H.; Frankenhaeuser, M. and Bjurstedt, H.: Interactions between heart rate, psychomotor performance and perceived effort during physical work as influenced by beta-adrenergic blockade. Biological Physiology 8: 31–43 (1979).
Sklar, J.; Johnston, G.D.; Overlie, P.; Gerber, J.G.; Brammell, H.L.; Gal, J. and Nies, A.S.: The effects of a cardioselective (Metoprolol) and a nonselective (Propranolol) beta-adrenergic blocker on the response to dynamic exercise in normal men. Circulation 65: 894–899 (1982).
Smith, R.S. and Warren, D.J.: Effect of acute oral beta adrenergic blockade on muscle blood flow in man. Cardiovascular Research 16: 205–208 (1982).
Sue, D.Y.; van Meber, R.; Hansen, J.E. and Wasserman, K.: Exercise gas exchange in asthmatics after beta-adrenergic blockade. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiration Environmental Exercise Physiology 55: 529–529 (1983).
Svedenhag, J.; Henriksson, J. and Johlin-Oannfelt: β-Adrenergic blockade and training in human subjects. Effects on muscle metabolic capacity. American Journal of Physiology 247 (Endocrinology and Metabolism 10): E305–E311 (1984).
Taggart, P. and Carruthers, M.: Endogenous hyperlipidemia induced by emotional stress of racing driving. Lancet 1: 363–366 (1971).
Taggart, P.; Carruthers, M. and Somerwille, W.: Electrocardiogram, plasma catecholamines and lipids, and their modification by oxprenolol when speaking before an audience. Lancet 2: 341–346 (1973).
Tesch, P.A. and Kaiser, P.: Effects of β-adrenergic blockade on O2 uptake during submaximal and maximal exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology 54: 901–905 (1983).
Tesch, P.A.; Kaiser, P. and Komi, P.V.: Effects of β-adrenergic blockade on EMG signal characteristics during progressive exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 121: 189–191 (1984a).
Tesch, P.A.; Kaiser, P. and Kaijser, L.: Isometric muscle endurance during acute β-adrenergic blockade. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 120: 71–75 (1984b).
Tesch, P.A.; Lindborg, B. and Kaiser, P.: The effect of β1-selective and non-selective blockade on muscle strength. Physician and Sportsmedicine (Submitted for publication).
Thompson, L.J.; Toulson, P.K. and Ragg, K.E.: Effects of oxprenolol and diazepam on psychomotor performance. New Zealand Medical Journal 82: 138 (1975).
Thorén, C: Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on heart rate and blood lactate in children during maximal and submaximal exercise. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica (Suppl.): 115 (1967).
Tipton, CM.: Exercise, training, and hypertension. Exercise and Sports Sciences Reviews 12: 245–306 (1984).
Trap-Jensen, J.; Clausen, J.P.; Noer, I.; Larsen, O.A.; Krogsgaard, A.R. and Christensen, N.J.: The effects of beta-adrenoceptor blockers on cardiac output, liver blood flow and skeletal muscle blood flow in hypertensive patients. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl.): 440 (1976).
Twentyman, O.P.; Disley, A.; Gribbin, H.R.; Alberti, K.G.M.M. and Tattersfield, A.E.: Effect of β-adrenergic blockade on respiratory and metabolic responses to exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology 51: 788–793 (1981).
Vanhees, L.; Fagard, R. and Amery, A.: Influence of beta adrenergic blockade on effects of physical training in patients with ischaemic heart disease. British Heart Journal 48: 33–38 (1982).
Verstappen, F. and von Baak, N.: Exercise tolerance after selective (β-1) and non-selective beta blockade. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 17(2): 255 (1985).
Videman, T.; Sone, T. and Jänne, J.: The effect of beta-blockade in ski-jumpers. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 11: 266–269 (1979).
Walsh, D.A.; Brostrom, CO.; Brostrom, M.A.; Chen, L.; Corbin, J.D.; Reimann, E.; Soderling, T.R. and Krebs, E.G.: Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases from skeletal muscle and liver. Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research 1: 33–45 (1972).
Wilcox, R.G.; Bennett, T.; MacDonald, I.A.; Herbert, M. and Skene, A.M.: The effects of acute or chronic ingestion of pro pranolol or metoprolol on the physiological responses to prolonged, submaximal exercise in hypertensive men. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 17: 273–281 (1984).
William-Olsson, T.; Fellenius, E.; Björntorp, P. and Smith, U.: Differences in metabolic responses to β-adrenergic stimulation after propranolol or metoprolol administration. Acta Medica Scandinavica 205: 201–206 (1979).
Williams, R.S.; Caron, M.G. and Daniel, K.: Skeletal muscle β-adrenergic receptors: Variations due to fiber type and training. American Journal of Physiology 246: E160–E167 (1984).
Wilmore, J.H.; Freund, B.J.; Joyner, M.J.; Hetrick, G.A.; Hartzell, A.A.; Strother, R.T.; Ewy, G.A. and Fans, W.E.: Acute response to submaximal and maximal exercise consequent to beta adrenergic blockade: Implications for the prescription of exercise. American Journal of Cardiology (55: 1D–171D 1985a).
Wilmore, J.H.; Ewy, G.A.; Freund, B.J.; Hartzell, A.A.; Jilka, S.M.; Joyner, M.J.; Todd, C.A.; Kinzer, S.M. and Pepin, E.B.: Cardiorespiratory alterations consequent to endurance exercise training during chronic beta-adrenergic blockade with atenolol and propranolol. American Journal of Cardiology (55: 142D–148D 1985b).
Yorko, J.; Paran, E.; Hare, T.V.; Oort, G.V.; Lowenthal, D.T. and Kendrick, Z.W.: Effect of beta blockade on strength performance, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 17(2): 239 (1985).
Zacharias, F.J.: Patient acceptability of propranolol and occurrence of side effects. Postgraduate Medical Journal (Suppl. 4): 5: 87–89 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tesch, P.A. Exercise Performance and β-Blockade. Sports Medicine 2, 389–412 (1985). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-198502060-00002
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-198502060-00002