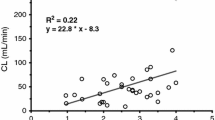
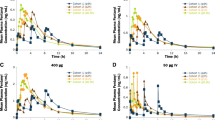
Summary
Alfentanil, fentanyl and sufentanil are synthetic opioid analgesics acting at specific opioid receptors. These opioids are widely used as analgesics to supplement general anaesthesia for various surgical procedures or as primary anaesthetic agents in very high doses during cardiac surgery. Fentanyl and sufentanil especially are administered via infusion for long term analgesia and sedation in intensive care patients.
Opioid analgesics are mainly administered using the intravenous route. However, other techniques of administration, including epidural, intrathecal, transdermal and intranasal applications, have been demonstrated.
Important pharmacokinetic differences between alfentanil, fentanyl and sufentanil have been shown in many reports. Alfentanil has the most rapid analgesic onset and time to peak effect as well as the shortest distribution and elimination half-lives. The volume of distribution and total body clearance of this agent are smaller when compared with those of fentanyl and sufentanil.
The pharmacokinetics of the opioid analgesics can be affected by several factors including patient age, plasma protein content, acid-base status and cardiopulmonary bypass, but not significantly by renal insufficiency or compensated hepatic dysfuntion. In addition, pharmacokinetic properties can be influenced by changes in hepatic blood flow and administration of drug combinations which compete for the same plasma protein carrier or metabolising pathway.
Although comparing specific pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-lives is deeply entrenched in the literature and clinical practice, simply comparing half-lives is not a rational way to select an opioid for specific requirements. Using pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models, computer simulations based on changes in the effect site opioid concentration or context-sensitive half-times seem to be extremely useful for selecting an opioid on a more rational basis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans CJ, Keith DE, Morrison H, et al. Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science 1992; 258: 1952–5
Kiefer BL, Befort K, Gaveriaux-Ruff C, et al. The delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacologic characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 12048–52
Chen Y, Mestek A, Liu J, et al. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a μ-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 1993; 44: 8–12
Fakuda K, Kato S, Mori K, et al. Primary structures and expression from cDNAs of rat opioid receptor delta- and μ-subtypes. FEBS Lett 1993; 327: 311–4
Nishi M, Takeshima H, Fukuda K, et al. cDNA cloning and pharmacological characterization of an opioid receptor with high affinities for kappa-subtype-selective ligands. FEBS Lett 1993; 330: 77–80
Yasuda K, Raynor K, Kong H, et al. Cloning and functioning comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 6736–40
Holaday JW, Tortella FC. Multiple opioid receptors: possible physiological functions of μ and delta binding sites in vivo. In: Genazzini AR, Müller EE, editors. Central and peripheral endorphins: basis and clinical aspects. New York: Raven Press, 1984: 237–50
Pleuvry BJ. Opioid receptors and their ligands: natural and unnatural. Br J Anaesth 1991; 66: 370–80
Pasternak GW. Pharmacological mechanisms of opioid analgesics. Clin Neuropharmacol 1993; 16: 1–18
Soudijn W. The pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of fentanyl. In: Wood TD, editor. Stress-free anaesthesia. London: Royal Society of Medicine, 1978: 4–10
Hug Jr CC. Pharmacokinetics of new synthetic narcotic analgesics. In: Estafanous F, editor. Opioids in anesthesia. Boston: Butterworth, 1984: 55–60
Freye E. Opioide in der Medizin. Wirkung und Einsatzgebiete zentraler Analgetika, 3. Auflage. Berlin: Springer 1995: 181–6
Olkkola KT, Hamunen K, Maunuksela EL. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of opioid analgesics in infants and children. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995; 28: 385–404
Freye E. Opioide — Zentrale Analgetika. Ihre Wirkweise beim Menschen. DIAGM 1991; 12: 1105–18
Yun CH, Wood M, Wood AJ, et al. Identification of the pharmacogenetic determinants of alfentanil metabolism: cytochrome P-450 3A4. An explanation of the variable elimination clearance. Anesthesiolgy 1992; 77: 467–74
Kharasch ED, Thummel KE. Human alfentanil metabolism by cytochrome P450 3A3/4: an explanation for the interindividual variability in alfentanil clearance? Anesth Analg 1993; 76: 1033–9
McClain DA, Hug Jr CC. Intravenous fentanyl kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1980; 28: 106–14
Meuldermans W, Hendrick J, Lauwers W. Excretion and biotransformation of alfentanil and sufentanil in rats and dogs. Drug Metab Dispos 1987; 15: 905–13
Gupta SK, Southam MA, Hwang SS. Evaluation of diurnal variation in fentanyl clearance. J Clin Pharmacol 1995; 35: 159–62
Lehmann KA, Sipakis K, Gasparini R, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in general surgical patients under different conditions of anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1993; 37: 176–80
Burm AGL, Ausems MEM, Spierdijk J, et al. Pharmacokinetics of alfentanil administered at a variable rate during three types of surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol 1993; 10: 241–51
Scholz J, Bause H, Schulz M, et al. Pharmacokinetics and effects on intracranial pressure of sufentanil in head trauma patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1994; 38: 369–72
Monk JP, Beresford R, Ward A. Sufentanil: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1988; 36: 286–313
Clotz MA, Nahata MC. Clinical uses of fentanyl, sufentanil, and alfentanil. Clin Pharm 1991; 10: 581–93
Bovill JG, Sebel PS, Blackborn CL, et al. The pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in surgical patients. Anesthesiology 1984; 61: 502–6
Davis JP, Cook DR, Stiller PL, et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of high-dose sufentanil in infants and children undergoing cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg 1987; 66: 203–8
Greeley WJ, de Bruijn NP, Davis DP. Sufentanil pharmacokinetics in pediatric cardiovascular patients. Anesth Analg 1987; 66: 1067–72
Hudson RJ, Bergstrom RG, Thomson IR, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in patients undergoing abdominal aortic surgery. Anesthesiology 1989; 70: 426–31
Davis JP, Stiller RL, Cook DR, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in adolescent patients with chronic renal failure. Anesth Analg 1988; 67: 268–71
Fyman PN, Reynolds JR, Moser F, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in patients undergoing renal transplantation. Can J Anaesth 1988; 35: 312–5
Matteo RS, Schwartz AE, Ornstein E, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in the elderly surgical patient. Can J Anaesth 1990; 37: 852–6
Guay J, Gaudreault P, Tang A, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in normal children. Can J Anaesth 1992; 39: 14–20
Alazia M, Albanese J, Martin C, et al. Pharmacokinetics of long-term sufentanil infusion (72 hours) used for sedation in ICU patients [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1992; 77: A364
Bodenham A, Park GR. Alfentanil infusions in patients requiring intensive care. Clin Pharmacokinet 1988; 15: 216–26
Willens JS, Myslinski NR. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and clinical uses of fentanyl, sufentanil, and alfentanil. Heart Lung 1993; 22: 239–51
Sawchuk CWT, Ong B, Unruh HW, et al. Thoracic versus lumbar epidural fentanyl for postthoracotomy pain. Ann Thorac Surg 1993; 55: 1472–6
Baxter AD, Laganiere S, Samon B, et al. A comparison of lumbar epidural and intravenous fentanyl infusions for post-thoracotomy analgesia. Can J Anaesth 1994; 41: 184–91
Salomaki TE, Laitinen JO, Nuutinen LS. A randomized double-blind comparison of epidural versus intravenous fentanyl infusion for analgesia after thoracotomy. Anesthesiology 1991; 75: 790–5
Sandier AN, Stringer D, Panos L, et al. A randomized double-blind comparison of lumbar epidural and intravenous fentanyl infusions for post-thoracotomy pain relief. Anesthesiology 1992; 77: 626–34
Guinard JP, Mavrocordatos P, Chiolero R, et al. A randomized comparison of intravenous versus lumbar and thoracic epidural fentanyl for analgesia after thoracotomy. Anesthesiology 1992; 77: 1108–15
Camu F, Debucquoy F. Alfentanil infusion for postoperative pain: a comparison of epidural and intravenous routes. Anesthesiology 1991; 75: 171–8
Chauvin M, Hongnat JM, Mourgeon E, et al. Equivalence of postoperative analgesia with patient-controlled intravenous or epidural alfentanil. Anesth Analg 1993; 76: 1251–8
Taverne RHT, Ionescu TI, Nuyten STM. Comparative absorption and distribution pharmacokinetics of intravenous and epidural sufentanil for major abdominal surgery. Clin Pharmacokinet 1992; 23: 231–7
Geller E, Chrubasik J, Graf R, et al. A randomized double-blind comparison of epidural sufentanil versus intravenous sufentanil or epidural fentanyl analgesia after major abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg 1993; 76: 1243–50
Camann WR, Denney RA, Holby ED, et al. A comparison of intrathecal, epidural, and intravenous sufentanil for labor analgesia. Anesthesiology 1992; 77: 884–7
Naulty JS, Barnes D, Becker R, Pate A. Continuous subarachnoid sufentanil for labor analgesia [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1990; 73: A964
Honet JE, Arkoosh VA, Huffnagle HJ, et al. Comparison of fentanyl, meperidine, and sufentanil for labor analgesia [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1991; 75: A839
Coda BA, Brown MC, Schaffer R, et al. Pharmacology of epidural fentanyl, alfentanil, and sufentanil in volunteers. Anesthesiology 1994; 81: 1149–61
Cooper DW, Ryall DM, Desira WR. Extradural fentanyl for postoperative analgesia: predominant spinal or systemic action? Br J Anaesth 1995; 74: 184–7
Hansdottir V, Woestenborghs R, Nordberg G. The cerebrospinal fluid and plasma pharmacokinetics of sufentanil after thoracic or lumbar epidural administration. Anesth Analg 1995; 80: 724–9
Swenson JD, Hullander M, Bready RJ. A comparison of patient controlled epidural analgesia with sufentanil by the lumbar versus thoracic route after thoracotomy. Anesth Analg 1994; 78: 215–8
Verborgh C, Claeys M, Vanlersberghs C, et al. Postoperative pain treatment after cholecystectomy with epidural sufentanil at lumbar or thoracic level. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1994; 38: 218–22
Sandler AN. Transdermal fentanyl: acute analgesic studies. J Pain Symptom Manage 1992; 7: S27–S35
Sandier AN, Baxter AD, Samson B, et al. Postoperative analgesia with transdermal fentanyl: analgesic and respiratory effects [abstract]. Can J Anaesth 1993; 40: A51
Fiset P, Cohane C, Browne S, et al. Biopharmaceutics of a transdermal fentanyl device. Anesthesiology 1995; 83: 459–69
Varvel JR, Shafer SL, Hwang S, et al. Bioavailability and absorption of transdermal fentanyl. Anesthesiology 1989; 70: 928–34
Sebel PS, Barrett CW, Kirk CJC, et al. Transdermal absorption of fentanyl and sufentanil in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1987; 32: 529–31
Calis KA, Kohler DR, Corso DM. Transdermally administered fentanyl for pain management. Clin Pharm 1992; 11: 22–36
Haynes G, Brahen NH, Hill HF. Plasma sufentanil concentration after intranasal administration in paediatric outpatients [letter]. Can J Anaesth 1993; 40: 286
Davis JP, Stiller RL, Cook DR, et al. Effects of cholestatic hepatic disease and chronic renal failure on alfentanil pharmacokinetics in children. Anesth Analg 1989; 68: 579–83
Davis PJ, Killian A, Stiller RL, et al. Alfentanil pharmacokinetics in premature infants and older children [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1988; 69: A758
Collins C, Koren G, Crean P, et al. Fentanyl pharmacokinetics and hemodynamic effects in preterm infants during ligation of patent ductus arteriosus. Anesth Analg 1985; 64: 1078–80
Koehntop DE, Rodman JH, Brundage DM, et al. Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl in neonates. Anesth Analg 1986; 65: 227–32
Mannering FJ. Drug metabolism in the newborn. FASEB J 1985; 44: 2302
Killian A, Davis PJ, Stiller RL, et al. Influence of gestational age on pharmacokinetics of alfentanil in neonates. Dev Pharmacol Ther 1990; 15: 82–6
Roure P, Jean N, Leclerc AC, et al. Pharmacokinetics of alfentanil in children undergoing surgery. Br J Anaesth 1987; 59: 1437–40
Singleton MA, Rosen JI, Fisher DM. Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl for infants and adults [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1984; 61: A440
Meistelman C, Saint-Maurice C, Lepaul M, et al. A comparison of alfentanil pharmacokinetics in children and adults. Anesthesiology 1987; 66: 13–16
Goresky GV, Koren G, Sabourin MA, et al. The pharmacokinetics of alfentanil in children. Anesthesiology 1987; 67: 654–9
Koren G, Goresky G, Crean P, et al. Pediatric fentanyl dosing based on pharmacokinetics during cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg 1984; 63: 577–82
Greeley WJ, de Bruijn NP. Changes in sufentanil pharmacokinetics within the neonatal period. Anesth Analg 1988; 67: 86–90
Scott JC, Stanski DR. Decreased fentanyl and alfentanil dose requirements with age: a simultaneous pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1987; 240: 159–63
Helmers JHJH, van Peer A, Noordiun H, et al. Sufentanil kinetics in the elderly [abstract]. Proceedings of the 7th European Congress of Anaesthesiology: 1986; Vienna, 188
Helmers JHJH, van Leeuwen L, Zuurmond WWM. Sufentanil pharmacokinetics in young adult and elderly surgical patients. Eur J Anaesthesiol 1994; 11: 181–5
Hudson RJ, Thomson IR, Burgess PM, et al. Alfentanil pharmacokinetics in patients undergoing abdominal aortic surgery. Can J Anaesth 1991; 38: 61–67
Helmers JHJH, van Peer A, Woestenborghs R, et al. Alfentanil pharmacokinetics in elderly patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1984; 36: 239–43
Van Beem H, van Peer A, Gasparini R, et al. Pharmacokinetics of alfentanil during and after a fixed rate infusion. Br J Anaesth 1989; 62: 610–5
Bentley JB, Finley JH, Humphrey LR, et al. Obesity and alfentanil pharmacokinetics [abstract]. Anesth Analg 1983; 62: 251
Maitre PO, Ausems ME, Vozeh S, et al. Evaluating the accuracy of using population pharmacokinetic data to predict plasma concentrations of alfentanil. Anesthesiology 1987; 67: 59–67
Bentley JB, Borel JD, Gillespie TJ, et al. Fentanyl pharmacokinetics in obese and nonobese patients [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1981; 55: A177
Schwartz AE, Matteo RS, Ornstein E, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in obese patients. Anesth Analg 1991; 73: 790–3
Meuldermans WEG, Hurkmans RMA, Heykants JJP. Plasma protein binding and distribution of fentanyl, sufentanil, alfentanil and lofentanil in blood. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1982; 257: 4–19
Meistelman C, Toubas F, Levron JC, et al. Plasma protein binding in mother and newborn infant of fentanyl and alfentanil [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1985; 63: A373
Meistelman C, Benhamou D, Barre J, et al. Effects of age on plasma protein binding of sufentanil. Anesthesiology 1990; 72: 470–3
Belpaire FM, Bogaert MG. Binding of alfentanil to human α1-acid glycoprotein, albumin and serum. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 1991; 29: 96–102
Meistelman C, Levron JC, Barre J, et al. Effects of increased alpha 1-acid glycoprotein in cancer patients on pharmacokinetics of alfentanil [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1988; 69: A602
Bailey PL, Stanley TH. Intravenous opioid anesthetics. In: Miller RD, editor. Anesthesia. 4th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1994: 291–388
Hug Jr CC, Burm AGL, de Lange S, et al. Alfentanil pharmacokinetics and protein binding before and after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) [abstract]. Proceedings of the 5th Annual Meeting of the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists: 1983; San Diego, 76
Hug Jr CC, Burm AGL, de Lange S. Alfentanil pharmacokinetics in cardiac surgical patients. Anesth Analg 1994; 78: 231–9
Kumar K, Ballantyne J, Bowie D, Laney G. Effect of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) on the plasma protein binding of alfentanil (alf) [abstract]. Pharm Res 1994; 11: S439
Ferner C, Marty J, Bouffard MD, et al. Alfentanil pharmacokinetics in patients with cirrhosis. Anesthesiology 1985; 62: 480–4
Höllt V, Teschemacher H. Hydrophobic interactions responsible for unspecific binding of morphine-like drugs. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 1975; 288: 163–77
Schwartz AE, Matteo RS, Ornstein E, et al. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in neurosurgical patients undergoing hyperventilation. Br J Anaesth 1989; 63: 385–8
Lüllmann H, Martins BS, Peters T. pH-dependent accumulation of fentanyl, lofentanil, alfentanil by beating guinea pig atria. Br J Anaesth 1985; 57: 1012–7
Williams RL. Drug administration in hepatic disease. New Engl J Med 1984; 309: 1616–22
Lemmens HJM. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships for opioids in balanced anaesthesia. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995; 29: 231–42
Marshall JS, Williams S. Serum inhibitors of desialylated glycoprotein binding to hepatocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Acta 1978; 543: 41–52
Williams RL, Benet LZ. Drug pharmacokinetics in cardiac and hepatic disease. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1980; 20: 389–413
Chauvin M, Bonnet F, Montembault C, et al. The influence of hepatic plasma flow on alfentanil plasma concentration plateaus achieved with an infusion model. Anesth Analg 1986; 65: 999–1003
Reitz J, MacKichan JJ, Hoffer L, et al. Reduced plasma clearance of alfentanil associated with prolonged major intra-abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg 1984; 63: 265
Haberer JP, Schoeffler P, Couderc E, et al. Fentanyl pharmacokinetics in anaesthetized patients with cirrhosis. Br J Anaesth 1982; 54: 1267–70
Hug Jr CC, Murphy MR, Sampson JF, et al. Biotransformation of morphine and fentanyl in anhepatic dogs [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1981; 55: A261
Chauvin M, Ferrier C, Haberer JP, et al. Sufentanil pharmacokinetics in patients with cirrhosis. Anesth Analg 1989; 68: 1–4
Hudson RJ, Thomson IR, Cannon JE, et al. Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl in patients undergoing abdominal aortic surgery. Anesthesiology 1986; 64: 334–8
Sjoholm I, Kober A, Odar-Cederlof I, et al. Protein binding of drugs in uremic and normal serum: the role of endogenous binding inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol 1976; 25: 1205–13
Piafsky KM. Disease-induced changes in the plasma binding of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 1980; 5: 246–62
Van Peer A, Vercauteren M, Noorduin H. Alfentanil kinetics in renal insufficiency. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 30: 245–9
Chauvin M, Lebrault C, Levron JC, et al. Pharmacokinetics of alfentanil in chronic renal failure. Anesth Analg 1987; 66: 53–6
Bower S. Plasma protein binding of fentanyl: the effect of hyperlipoproteinaemia and chronic renal failure. J Pharm Pharmacol 1981; 34: 102–6
Bovill JG, Sebel PS. Pharmacokinetics of high dose fentanyl: a study in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 1980; 52: 795–801
Buylaert WA, Herregods LL, Mortier EP, et al. Cardiopulmonary bypass and the pharmacokinetics of drugs: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet 1989; 17: 10–22
Hall R. The pharmacokinetic behaviour of opioids administered during cardiac surgery. Can J Anaesth 1991; 38: 747–56
Rosen D, Rosen K, Davidson B, et al. Fentanyl uptake by the Scimed membrane oxygenator. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 1988; 2: 619–22
Durkan W, Lonergan M, Schwartz S, et al. Effect of membrane oxygenators on sufentanil blood levels during cardiopulmonary bypass [abstract]. Anesth Analg 1988; 67: S54
Skacel M, Knott C, Reynolds F, et al. Extracorporeal circuit sequestration of fentanyl and alfentanil. Br J Anaesth 1986; 58: 947–9
Den Hollander J, Hennis PJ, Burm AGL, et al. Pharmacokinetics of alfentanil before and after cardiopulmonary bypass in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery: Part I. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 1992; 6: 308–12
Okutani R, Koski G, Gelb C, et al. High dose sufentanil does not prevent catecholamine responses to hypothermie cardiopulmonary bypass [abstract]. Anesth Analg 1988; 67: S160
Koska III AJ, Romagnoli A, Kramer WG. Effect of cardiopulmonary bypass on fentanyl distribution and elimination. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1981; 29: 100–6
Hug Jr CC, Moldenhauer CC. Pharmacokinetics and dynamics of fentanyl infusions in cardiac surgical patients [abstract]. Anesthesiology 1982; 57: A45
Holley FO, Ponganis KV, Stanski R. Effect of cardiopulmonary bypass on the pharmacokinetics of drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 1982; 7: 234–51
Bentley JB, Cohanan III TJ, Cork RC. Fentanyl sequestration in lungs during cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1983; 34: 703–6
Roerig DL, Kotrly KJ, Ahlf SB, et al. Effect of propranolol on the first pass uptake of fentanyl in the human and rat lung. Anesthesiology 1989; 71: 62–8
Boer F, Bovill JG, Burm AGL, et al. Uptake of sufentanil, alfentanil and morphine in the lungs of patients about to undergo coronary artery surgery. Br J Anaesth 1992; 68: 370–5
Janicki PK, James MF, Erskine WA. Propofol inhibits enzymatic degradation of alfentanil and sufentanil by isolated liver microsomes in vitro. Br J Anaesth 1992; 68: 311–2
Kharasch ED, Hill HF, Eddy AC. Influence of dexmedetomidine and clonidine on human liver microsomal alfentanil metabolism. Anesthesiology 1991; 75: 520–4
Nimmo WS, Thompson PG, Prescott LF. Microsomal enzyme induction after halothane anesthesia. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1981; 12: 433–4
Bartkowski RR, Goldberg ME, Huffnagle S, et al. Sufentanil disposition: is it affected by erythromycin administration? Anesthesiology 1993; 78: 260–5
Sedman AJ. Cimetidine: drug interactions. Am J Med 1984; 76: 109–12
Lee HR, Gaudolfi AJ, Sipes IG, et al. Effect of histamine H2-receptors on fentanyl metabolism [abstract]. Pharmacologist 1982; 24: 145
Klotz U, Kroemer HK. The drug interaction potential of ranitidine: an update. Pharmacol Ther 1991; 50: 233–44
Shafer SL, Varvel JR. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and rational opioid selection. Anesthesiology 1991; 74: 53–63
Shafer SL, Stanski DR. Improving the clinical utility of anesthetic drug pharmacokinetics [editorial]. Anesthesiology 1992; 76: 327–30
Youngs EJ, Shafer SL. Pharmacokinetic parameters relevant to recovery from opioids. Anesthesiology 1994; 81: 833–42
Hughes MA, Glass PSA, Jacobs JR. Context-sensitive half-time in multicompartment pharmacokinetic models for intravenous anesthetic drugs. Anesthesiology 1992; 76: 334–41
Bailey JM. Technique for quantifying the duration of intravenous anesthetic effect. Anesthesiology 1995; 83: 1095–103
Schnider TW, Shafer SL. Evolving clinically useful predictors of recovery from intravenous anesthetics [editorial]. Anesthesiology 1995; 83: 902–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholz, J., Steinfath, M. & Schulz, M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Alfentanil, Fentanyl and Sufentanil. Clin-Pharmacokinet 31, 275–292 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199631040-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199631040-00004