Abstract
Background
For patients undergoing oncologic surgery, the quality of life (QoL) is generally accepted as an important outcome parameter in addition to long-term survival, mortality, and complication rates. Our study focused on outcome in terms of QoL in patients with esophageal cancer, comparing the sites of anastomosis (cervical versus thoracic anastomosis).
Methods
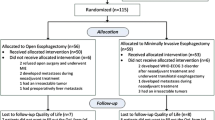
In a prospective longitudinal single-center study from 1998 to 2005, 105 patients underwent surgery for esophageal cancer. To assess QoL the EORTC-QLQ-C-30 and a tumor-specific module were administered before surgery, at discharge, and three, six, 12, and 24 months after surgery. Clinical data were collected prospectively and follow-up was performed every six months.
Results
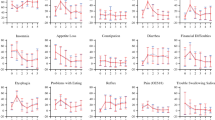
The histological type was squamous cell carcinoma in 51.4% of the cases, adenocarcinoma in 41.9%, and some other type in 6.7%. There was no significant difference between cervical and thoracic anastomosis with regard to morbidity, mortality, and survival rates (30% five-year survival rate), whereas tumor stage was a significant (p < 0.001) prognostic factor. Most QoL scores dropped significantly below baseline in the early postoperative period. Even though they recovered slowly during the follow-up period, they never reached preoperative levels again. There was no statistically significant difference in any of the QoL scales between patients with a cervical or a thoracic anastomosis.
Conclusions
Esophageal resections are associated with significant deterioration of QoL, which persists during the follow-up period. The surgical technique and position of the esophagogastrostomy did not affect QoL deterioration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wijnhoven BP, Tran KT, Esterman A, et al. An evaluation of prognostic factors and tumor staging of resected carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg 2007;245(5):717–25
Hulscher JB, Tijssen JG, Obertop H, van Lanschot JJ. Transthoracic versus transhiatal resection for carcinoma of the esophagus: a meta-analysis. Ann Thorac Surg 2001;72(1):306–13
Sundelof M, Ye W, Dickman PW, Lagergren J. Improved survival in both histologic types of oesophageal cancer in Sweden. Int J Cancer 2002;99(5):751–4
Hulscher JB, van Sandick JW, de Boer AG, et al. Extended transthoracic resection compared with limited transhiatal resection for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. N Engl J Med 2002;347(21):1662–9
Wu PC, Posner MC. The role of surgery in the management of oesophageal cancer. Lancet Oncol 2003;4(8):481–8
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003;349(23):2241–52
Urschel JD. Esophagogastrostomy anastomotic leaks complicating esophagectomy: a review. Am J Surg 1995;169(6):634–40
Walther B, Johansson J, Johnsson F, et al. Cervical or thoracic anastomosis after esophageal resection and gastric tube reconstruction: a prospective randomized trial comparing sutured neck anastomosis with stapled intrathoracic anastomosis. Ann Surg 2003;238(6):803–12; discussion 812–4
Lam TC, Fok M, Cheng SW, Wong J. Anastomotic complications after esophagectomy for cancer. A comparison of neck and chest anastomoses. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1992;104(2):395–400
Muller JM, Erasmi H, Stelzner M, et al. Surgical therapy of oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg 1990;77(8):845–57
Patil PK, Patel SG, Mistry RC, et al. Cancer of the esophagus: esophagogastric anastomotic leak–a retrospective study of predisposing factors. J Surg Oncol 1992;49(3):163–7
Chasseray VM, Kiroff GK, Buard JL, Launois B. Cervical or thoracic anastomosis for esophagectomy for carcinoma. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1989;169(1):55–62
Dewar L, Gelfand G, Finley RJ, et al. Factors affecting cervical anastomotic leak and stricture formation following esophagogastrectomy and gastric tube interposition. Am J Surg 1992;163(5):484–9
Fok M, Law S, Stipa F, et al. A comparison of transhiatal and transthoracic resection for oesophageal carcinoma. Endoscopy 1993;25(9):660–3
Iannettoni MD, Whyte RI, Orringer MB. Catastrophic complications of the cervical esophagogastric anastomosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1995;110(5):1493–500; discussion 1500–1
McLarty AJ, Deschamps C, Trastek VF, et al. Esophageal resection for cancer of the esophagus: long-term function and quality of life. Ann Thorac Surg 1997;63(6):1568–72
Schmidt CE, Bestmann B, Kuchler T, et al. Quality of life associated with surgery for esophageal cancer: differences between collar and intrathoracic anastomoses. World J Surg 2004;28(4):355–60
Blazeby JM, Farndon JR, Donovan J, Alderson D. A prospective longitudinal study examining the quality of life of patients with esophageal carcinoma. Cancer 2000;88(8):1781–7
Brooks JA, Kesler KA, Johnson CS, et al. Prospective analysis of quality of life after surgical resection for esophageal cancer: preliminary results. J Surg Oncol 2002;81(4):185–94
Baba M, Aikou T, Natsugoe S, et al. Appraisal of ten-year survival following esophagectomy for carcinoma of the esophagus with emphasis on quality of life. World J Surg 1997;21(3):282–5; discussion 286
de Boer AG, van Lanschot JJ, van Sandick JW, et al. Quality of life after transhiatal compared with extended transthoracic resection for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol 2004;22(20):4202–8
Velanovich V. The quality of quality of life studies in general surgical journals. J Am Coll Surg 2001;193(3):288–96
Bonnetain F, Bouche O, Michel P, et al. A comparative longitudinal quality of life study using the Spitzer quality of life index in a randomized multicenter phase III trial (FFCD 9102): chemoradiation followed by surgery compared with chemoradiation alone in locally advanced squamous resectable thoracic esophageal cancer. Ann Oncol 2006;17(5):827–34
Blazeby JM, Williams MH, Brookes ST, et al. Quality of life measurement in patients with oesophageal cancer. Gut 1995;37(4):505–8
Lipscomb J, Donaldson MS, Arora NK, et al. Cancer outcomes research. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2004;33:178–97
Beitz J, Gnecco C, Justice R. Quality-of-life end points in cancer clinical trials: the U.S. Food and Drug Administration perspective. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 1996;20:7–9
Johnson JR, Temple R. Food and Drug Administration requirements for approval of new anticancer drugs. Cancer Treat Rep 1985;69(10):1155–9
Siewert JR, Stein HJ. Classification of adenocarcinoma of the oesophagogastric junction. Br J Surg 1998;85(11):1457–9
Kuechler T. Quality of life research in oncology. Quality of life and health: concepts, methods and applications. Vienna: Blackwell Wissenschafts-Verlag, 1995:89–96
Fayers B, Curran D, Groenvold M. EORTC QLQ-C30 Scoring manual. 2nd ed.1999
Schwarz R, Hinz A. Reference data for the quality of life questionnaire EORTC QLQ-C30 in the general German population. Eur J Cancer 2001;37(11):1345–51
Osoba D, Rodrigues G, Myles J, et al. Interpreting the significance of changes in health-related quality-of-life scores. J Clin Oncol 1998;16(1):139–44
Blazeby JM. Measurement of outcome. Surg Oncol 2001;10(3):127–33
Blazeby JM, Conroy T, Hammerlid E, et al. Clinical and psychometric validation of an EORTC questionnaire module, the EORTC QLQ-OES18, to assess quality of life in patients with oesophageal cancer. Eur J Cancer 2003;39(10):1384–94
Stein HJ, von Rahden BH, Siewert JR. Survival after oesophagectomy for cancer of the oesophagus. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2005;390(4):280–5
Zieren HU, Jacobi CA, Zieren J, Muller JM. Quality of life following resection of oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg 1996;83(12):1772–5
Viklund P, Wengstrom Y, Rouvelas I, et al. Quality of life and persisting symptoms after oesophageal cancer surgery. Eur J Cancer 2006;42(10):1407–14
van Knippenberg FC, Out JJ, Tilanus HW, et al. Quality of Life in patients with resected oesophageal cancer. Soc Sci Med 1992;35(2):139–45
Blazeby JM, Brookes ST, Alderson D. The prognostic value of quality of life scores during treatment for oesophageal cancer. Gut 2001;49(2):227–30
Urschel JD. Esophagogastric anastomotic leaks: the importance of gastric ischemia and therapeutic applications of gastric conditioning. J Invest Surg 1998;11(4):245–50
Blewett CJ, Miller JD, Young JE, et al. Anastomotic leaks after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer: a comparison of thoracic and cervical anastomoses. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2001;7(2):75–8
Deschamps C, Nichols FC 3rd, Cassivi SD, et al. Long-term function and quality of life after esophageal resection for cancer and Barrett’s. Surg Clin North Am 2005;85(3):649–56, xi
Schniewind B, Bestmann B, Kurdow R, et al. Bypass surgery versus palliative pancreaticoduodenectomy in patients with advanced ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head, with an emphasis on quality of life analyses. Ann Surg Oncol 2006;13(11):1403–11
Schmidt CE, Bestmann B, Kuchler T, et al. Prospective evaluation of quality of life of patients receiving either abdominoperineal resection or sphincter-preserving procedure for rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2005;12(2):117–23
Kahlke V, Bestmann B, Schmid A, et al. Palliation of metastatic gastric cancer: impact of preoperative symptoms and the type of operation on survival and quality of life. World J Surg 2004;28(4):369–75
Sprangers MA, Van Dam FS, Broersen J, et al. Revealing response shift in longitudinal research on fatigue–the use of the thentest approach. Acta Oncol 1999;38(6):709–18
de Boer AG, van Lanschot JJ, Stalmeier PF, et al. Is a single-item visual analogue scale as valid, reliable and responsive as multi-item scales in measuring quality of life? Qual Life Res 2004;13(2):311–20
de Haes JC, van Knippenberg FC, Neijt JP. Measuring psychological and physical distress in cancer patients: structure and application of the Rotterdam Symptom Checklist. Br J Cancer 1990;62(6):1034–8
Spitzer WO, Dobson AJ, Hall J, et al. Measuring the quality of life of cancer patients: a concise QL-index for use by physicians. J Chronic Dis 1981;34(12):585–97
Blazeby JM, Alderson D, Winstone K, et al. Development of an EORTC questionnaire module to be used in quality of life assessment for patients with oesophageal cancer. The EORTC Quality of Life Study Group. Eur J Cancer 1996;32A(11):1912–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jan-Hendrik Egberts and Bodo Schniewind contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egberts, JH., Schniewind, B., Bestmann, B. et al. Impact of the Site of Anastomosis after Oncologic Esophagectomy on Quality of Life — A Prospective, Longitudinal Outcome Study. Ann Surg Oncol 15, 566–575 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-007-9615-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-007-9615-1