Abstract
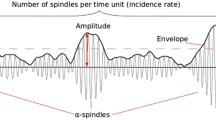
To estimate the EEG predictors of successful training in the voluntary control of psychomotor reactivity, 29 healthy young (aged 22.3 ± 1.5 years) musical performers were examined. The estimation was carried out in terms of segmental α-activity analysis using a biofeedback session as an example, simultaneously stimulating the EEG α rhythm and decreasing the muscle tone. On the first day of the study, the musicians followed instructions for the voluntary control of comfortable finger motor activity when performing musical passages for the right hand during a standard performance practice (without any use of an adaptive feedback). On the second day, the muscle tone and the power of the EEG α rhythm were voluntarily controlled in the context of a biofeedback technology. The analysis of the unsteady EEG segmentation showed that the dynamics of changes in the coherence and segmental characteristics of the α activity were the same for both effective biofeedback training and the standard successful performance practice: an increase in the α-rhythm coherence, an increase in the lifetime of α spindles, and a decrease in their amplitude variability. The results obtained are discussed in terms of the formation and dissociation of neuron ensembles in central mechanisms of optimal psychomotor functioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodenshtain, G. and Pretorius, Kh.M., Extraction of Characteristics from EEG Recordings Using the Adaptive Segmentation Method, Tr. Inst. Inzh. Elektrotekhn. Radioelektron., 1977, vol. 65, no. 5, p. 59.
McEven, J. and Anderson, G.B., Modeling the Stationarity and Gaussianity of Spontaneous Electroencephalographic Activity, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 1975, vol. 22, p. 361.
Rusinov, V.S., Grindel, O.M., Boldyreva, G.N., and Vakar, E.M., Biopotentsialy mozga cheloveka: matematicheskiy analiz (Human Brain Bioelectric Potentials: Mathematical Analysis), Moscow: Meditsina, 1987.
Creutzfeldt, O.-D., Bodenstein, G., and Barlow, J.S., Computerized EEG Pattern Classification by Adaptive Segmentation and Probability Density Function Classification. Clinical Evaluation, EEG Clin. Neurophysiol., 1985, vol. 60, no. 5, p. 373.
Lehmann D., Fluctuation of Functional State: EEG Patterns and Perceptual and Cognitive Strategies, in Functional States of the Brain: Their Determinants, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1980.
Kaplan, A.Ya., The Problem of Segmental Description of Human Electroencephalogram, Fiziol. Chel., 1999, vol. 25, no. 1, p. 125 [Hum. Phys., 1999, vol. 25, no. 1, p. 107].
Bazanova, O.M. and Shtark, M.B., Biofeedback in Optimizing Psychomotor Reactivity: I. Comparison of Biofeedback and Common Performance Practice, Fiziol. Chel., 2007, vol. 33, no. 4, p. 24 [Hum. Phys., 2007, vol. 33, no. 4, p. 400].
Dzhafarova, O.A. and Shtark, M.B., Computer-aided Biofeedback Systems: Trends of Development, Med. Tekhn., 2002, vol. 1, p. 34.
Kaplan, A.Ya., Borisov, S.V., Shishkin, S.L., and Ermolaev, V.A., Analysis of the Segmental Structure of α Activity of Human Electroencephalogram, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2002, vol. 88, no. 4, p. 432.
Singer, W., Engel, A.K., and Kreiter, A.S., Neuronal Assemblies: Necessity, Signature and Detectability, Trends in Cogn. Sci., 1989, vol. 1, p. 252.
Nase, G., Singer, W., Monyer, H., and Engel, A.K., Features of Neuronal Synchrony in Mouse Visual Cortex, J. Neurophysiol., 2003, vol. 90, no. 2, p. 1115.
Wespatat, V., Tennigkeit, F., and Singer, W., Phase Sensitivity of Synaptic Modifications in Oscillating Cells of Rat Visual Cortex, J. Neurosci., 2004, vol. 13,issue 24, no. 41, p. 9067.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.M. Bazanova, E.G. Verevkin, M.B. Shtark, 2007, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2007, Vol. 33, No. 6, pp. 44–49.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bazanova, O.M., Verevkin, E.G. & Shtark, M.B. Biofeedback in optimizing psychomotor reactivity: II. The dynamics of segmental α-activity characteristics. Hum Physiol 33, 695–700 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119707060059
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119707060059