Abstract
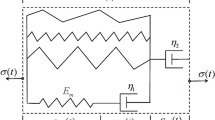
Ligaments display time-dependent behavior, characteristic of a viscoelastic solid, and are nonlinear in their stress–strain response. Recent experiments25 reveal that stress relaxation proceeds more rapidly than creep in medial collateral ligaments, a fact not explained by linear viscoelastic theory but shown by Lakes and Vanderby17 to be consistent with non-linear theory. This study tests the following hypothesis: non-linear viscoelasticity of ligament requires a description more general than the separable quasilinear viscoelasticity (QLV) formulation commonly used. The experimental test for this hypothesis involves performing both creep and relaxation studies at various loads and deformations below the damage threshold. Freshly harvested, rat medial collateral ligaments (MCLs) were used as a model. Results consistently show a nonlinear behavior in which the rate of creep is dependent upon stress level and the rate of relaxation is dependent upon strain level. Furthermore, relaxation proceeds faster than creep; consistent with the experimental observations of Thornton et al.25 The above results from rat MCLs are not consistent with a separable QLV theory. Inclusion of these nonlinearities would require a more general formulation. © 2001 Biomedical Engineering Society.
PAC01: 8719Rr, 8385St, 8360Df
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ambrosio, L., R. De Santis., S. Iannace., P. A. Netti., and L. Nicolais. Viscoelastic behavior of composite ligament prostheses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.42.:6–12., 1998.
Arms, S., J. Boyle., R. Johnson., and M. Pope. Strain measurements in the medial collateral ligament of the human knee: An autopsy study. J. Biomech.16.:491–496., 1983.
Atkinson, T. S., B. J. Ewers., and R. C. Haut. The tensile and stress relaxation responses of human patellar tendon varies with specimen cross-sectional area. J. Biomech.32.:907–914., 1999.
Atkinson, T. S., R. C. Haut, and N. J. Altiero. A microstructural poroelastic model for patellar tendon. Proc. ASME Bioeng. Conf. 35:573, 1997.
Best, T. M., J. McElhaney., W. E. Garret., and B. S. Myers. Characterization of the passive responses of live skeletal muscle using the quasilinear theory of viscoelasticity. J. Biomech.27.:413–419., 1994.
Chelikani, S., and M. M. Panjabi. Biomechanical symmetry of the rabbit ACL. Presented at the 19th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Biomechanics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, 1995 (unpublished).
Chimich, D., N. Shrive., C. Frank., L. Marchuk., and R. Bray. Water content alters viscoelastic behavior of the normal adolescent rabbit medial collateral ligament. J. Biomech.25.:831–837., 1992.
ntFung, Y. C. Stress strain history relations of soft tissues in simple elongation. In: Biomechanics, Its Foundations and Objectives, edited by Y. C. Fung, N. Perrone, and M. Anliker. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1972.
Graf, B., R. Vanderby., M. Ulm., R. Rogalski., and R. Thielke. The effect of preconditioning on the viscoelastic response of primate patellar tendon. Arthroscopy.10.:90–96., 1994.
Hannafin, J. A., and S. P. Arnoczky. Effect of cyclic and static tensile loading on the water content and solute diffusion in canine flexor tendons: An in vitro. study. J. Orthop. Res.12.:350–356., 1994.
Haut, R. C., and R. W. Little. Rheological properties of canine anterior cruciate ligaments. J. Biomech.2.:289–298., 1969.
Haut, R. C., and R. W. Little. A constitutive equation for collagen fibers. J. Biomech.5.:423–430., 1972.
Hull, M. L., G. S. Berns., H. Varma., and H. A. Patterson. Strain in the medial collateral ligament of the human knee under single and combined loads. J. Biomech.2.:199–206., 1996.
Holden, J. P., E. S. Grood., D. L. Korvick., J. F. Cummings., D. L. Butler., and D. I. Bylski-Austrow. In vivo. forces in the anterior cruciate ligament: Direct measurements during walking and trotting in a quadraped. J. Biomech.27.:517–526., 1994.
Johnson, G. A., G. A. Livesay., S. L-Y. Woo., and K. R. Rajagopal. A single integral finite strain viscoelastic model of ligaments and tendons. ASME J. Biomech. Eng.118.:221–226., 1996.
King, G. J., P. Edwards., R. F. Brant., N. G. Shrive., and C. B. Frank. Intraoperative graft tensioning alters viscoelastic but not failure behaviors of rabbit medial collateral ligament autografts. J. Orthop. Res.13.:915–922., 1995.
Lakes, R. S., and R. Vanderby. Interrelation of creep and relaxation: A modeling approach for ligaments. ASME J. Biomech. Eng.121.:612–615., 1999.
Lakes, R. S., J. L. Katz., and S. S. Sternstein. Viscoelastic properties of wet cortical bone: Part I, torsional and biaxial studies. J. Biomech.12.:657–678., 1979.
Lakes, R. S., and J. L. Katz. Viscoelastic properties of wet cortical bone: Part III, a nonlinear constitutive equation. J. Biomech.12.:689–698., 1979.
Panjabi, M. M., P. Moy., T. R. Oxland., and J. Cholewicki. Subfailure injury affects the relaxation behavior of rabbit ACL. Clin. Biomech.14.:24–31., 1999.
Provenzano, P. P., D. Heisey, K. Haysashi, R. S. Lakes, and R. Vanderby, Jr. Subfailure damage in ligament: A structural and cellular evaluation. J. Appl. Physiol., in press.
Rousseau, E. P. M., A. A. H. J. Sauren., M. C. van Hout., and A. A. van Steenhoven. Elastic and viscoelastic material behavior of fresh and glutaraldehyde fixed porcine aortic valve tissue. J. Biomech.16.:339–348., 1983.
Sauren, A. A. H. J., M. C. van Hout., A. A. van Steenhoven., F. E. Veldpaus., and J. D. Janssen. The mechanical properties of porcine aortic valve tissues. J. Biomech.16.:327–337., 1983.
Thielke, R. J., R. Vanderby, and E. S. Grood. Volumetric changes in ligaments under tension. Proc. ASME Bioeng. Conf. 29:197, 1995.
Thornton, G. M., A. Oliynyk., C. B. Frank., and N. G. Shrive. Ligament creep cannot be predicted from stress relaxation at low stress: A biomechanical study of the rabbit medial collateral ligament., J. Orthop. Res.15.:652–656., 1997.
Thornton, G. M., C. B. Frank., and N. G. Shrive. Ligament creep behavior can be predicted from stress relaxation by incorporating fiber recruitment. J. Rheol.45.:493–507., 2001.
Thornton, G. M., G. P. Leask., N. G. Shrive., and C. B. Frank. Early medial collateral ligament scars have inferior creep behavior. J. Orthop. Res.18.:238–246., 2000.
urner, S. Creep in glassy polymers. In: The Physics of Glassy Polymers, edited by R. H. Howard. New York: Wiley, 1973.
Viidi, A..A rheological model for uncalcified parallel-fibered collagenous tissue. J. Biomech.1.:3–11., 1968.
Viidik, A..Simultaneous mechanical and light microscopic studies of collagen fibers. Z. Anat. Entwick. Gesch.136.:204–212., 1972.
Woo, S. L-Y., M. A. Gomez., and W. H. Akeso. Quasilinear viscoelastic property of normal articular cartilage. J. Biomech. Eng.102.:85–90., 1980.
Woo, S. L-Y., M. A. Gomez., and W. H. Akeson. The time and history-dependent viscoelastic properties of the canine medial collateral ligament. J. Biomech. Eng.103.:293–298., 1981.
Woo, S. L-Y..Mechanical properties of tendons and ligaments. I. Quasistatic and nonlinear viscoelastic properties. Biorheology.19.:385–396., 1982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Provenzano, P., Lakes, R., Keenan, T. et al. Nonlinear Ligament Viscoelasticity. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 29, 908–914 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1408926
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1408926