Abstract
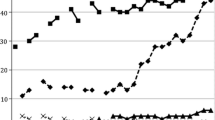
To explore the long-term contributions of perceived peer and parental influences on adolescent risk and protective behaviors (sexual involvement, condom use, and drug use), we assessed self-reported behaviors and perceptions of peer risk involvement and parental supervision and communication among 383 low-income, urban African Americans aged 9 to 15 years at baseline over a 4-year, period. Baseline perceptions of peer sexual involvement were significantly associated with youth sexual behavior at baseline and were predictive of sexual involvement through all 4 years of follow-up. Perceived parental monitoring was inversely correlated with sexual involvement ment through 3 years of follow-up. Perceptions of peer condom use were associated with increased levels of condom use at baseline and through 6 months of follow-up. Positive parental communication was correlated with increased condom use. Drug use was higher among youths who perceived peers or family members to be using drugs and was inversely correlated with increased parental monitoring and supervision. Stepwise regression revealed peer and parental influences for all three behaviors. Perceptions of both peer and parental behaviors influence long-term risk and protective behaviors of adolescents. Therefore, parents should be included in adolescent riskreduction intervention efforts. Inclusion of friends and/or changing youth perceptions of peer involvement may also be effective intervention strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander CN, Campbell EQ. Peer influences on adolescent drinking. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1967;28:444–453.
Jessor R, Graves TD, Hanson RC, Jessor SL. Society, Personality and Deviant Behavior: a Study of a Tri-ethnic Community. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston; 1968.
DeLamnter J, MacCorquodale P. Premarital Sexuality: Attitudes, Relationships Behavior. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press; 1979.
Walsh RH, Ferrell MZ, Tolone WL. Selection of reference group, perceived reference group permissiveness, and personal permissiveness, attitudes and behavior: a study of two consecutive panels (1967–1971; 1970–1974). J. Marriage Fam. 1976;38:495–507.
Jessor SL, Jessor R. Maternal ideology and adolescent problem behavior. Dev Psychol. 1974;10:246–254.
Jessor R, Costa F, Jessor SL, Donovan JE. Time of first intercourse: a prospective study. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1983;44:608–626.
Jaccard J, Dittus P. Parent-Teen Communication: Toward the Prevention of Unintended Pregnancies. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1991:2.
Stanton BF, Li X, Galbraith J, et al. Parental underestimates of adolescent risk behavior: a randomized, controlled trial of parental monitoring intervention. J Adolesc Health. 2002;26:18–26.
Ianazu J, Fox G. Maternal influence on the sexual behavior of teenage daughters. J Fam Issues. 1980;1:81–102.
Steinberg L, Mounts NS, Lamborn S. Authoritative parenting and adolescent adjustment across varied ecological niches. J Res Adolesc. 1991;1:19–36.
Steinberg L, Dornbusch SM, Brown BB. Ethnic differences in adolescent achievement: an ecological peespective. Am Psychol. 1992;47:723–729.
Romer D, Black M, Ricardo I, et al. Social influences on the sexual behavior of youth at risk for HIV exposure. Am J Public Health. 1994;84:977–985.
Dinges MM, Oetting ER. Similarity in drug use patterns between adolescents and their friends. Adolescence. 1993;28:253–266.
Rodgers JL, Billy JOG, Udry JR. A model of friendship similarity in mildly deviant behaviors. J Appl Soc Psychol. 1984;14:413–425.
Steinberg L, Fletcher A, Darling N. Parental monitoring and peer influences on adolescent substance use. Pediatrics. 1994;93:1060–1064.
Dombusch SM, Ritter PL, Leiderman PH, Roberts DF, Fraleigh MJ. The relation of parenting style to adolescent school performance. Child Development. 1987;58:1244–1257.
Giordano PG, Cernkovick SA, Pugh MD. Friendship and delinquency. Am J Social. 1986;91:1170–1202.
Ennett ST, Bauman KE. The contribution of influence and selection to adolescent peer group homogeneity: the case of adolescent cigarette smoking. J Personality Soc Psychol. 1994;67:653–663.
Billy JOG, Udry JR. The influence of male and female best friends on adolescent sexual behavior. Adolescence. 1985;20:21–32.
Romer D, Stanton BF, Galbraith J, et al. Parental monitoring and communication as influences on adolescent sexual behavior in high-risk urban settings. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:1055–1062.
Baumrind D. The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. J Early Adolesc. 1991;11:56–95.
Crouter AC, MacDenid SM, McHale SM, Perry-Jenkins M. Parental monitoring and perceptions of children's school performance and conduct in dual-and single-earner families. Dev Psychol. 1990;26:649–657.
Goldfarb JL, Mumford DM, Schum DA, Smith PB, Flowers C, Schum C. An attempt to detect “pregnancy susceptibility” in indigent adolescent girls. J Youth Adolesc. 1997;6:127–144.
Stanton BF, Li X, Ricardo I, Galbraith J, Feigelman S, Kaljee L. A randomized controlled effectiveness trial of an AIDS prevention program for low-income African-American youth. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1996;150:363–372.
Galbraith J, Ricardo I, Stanton BF, Black M, Feigelman S, Kaljee L. Challenges and rewards of involving community in research: an overview of the “Focus on Kids” AIDS-prevention program. Health Educ Q. 1996;23:383–394.
Stanton BF, Black M, Feigelman S, et al. Development of a culturally, theoretically and developmentally based survey instrument for assessing risk behaviors among African-American early adolescents living in urban low-income neighborhoods. AIDS Educ Prev. 1995;7:160–177.
Silverberg SB, Small SA. Parental monitoring, family structure and adolescent substance use. Paper presented at: Meeting of the Society of Research in Child Development; April 18–20, 1991; Seattle, WA.
McCubbin HI, Thompson AI. Family Assessment Inventories for Research and Practice. Madison: University of Wisconsin; 1987.
Li X, Stanton B, Feigelman S. Impact of perceived parental monitoring on adolescent risk behavior over 4 years. J Adolesc Health. 2000;27:49–56.
DiClemente R. Psychosocial determinants of condom use among adolescents. In: DiClemente R, ed. Adolescents and AIDS: a Generation at Risk. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1992:34–51.
Jessor R, Jessor SL, Finney J. A social psychology of marijuana use: longitudinal studies of high school and college youth. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1973;26:1–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanton, B., Li, X., Pack, R. et al. Longitudinal influence of perceptions of peer and parental factors on African American adolescent risk involvement. J Urban Health 79, 536–548 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1093/jurban/79.4.536
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jurban/79.4.536