Abstract
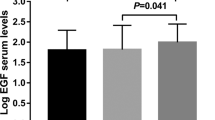
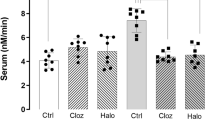
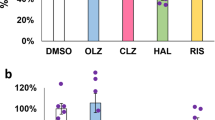
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) comprises a structurally related family of proteins containing heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and transforming growth factor alpha (TGFα) that regulates the development of dopaminergic neurons as well as monoamine metabolism. We assessed the contribution of EGF to schizophrenia by measuring EGF family protein levels in postmortem brains and in fresh serum of schizophrenic patients and control subjects. EGF protein levels were decreased in the prefrontal cortex and striatum of schizophrenic patients, whereas the levels of HB-EGF and TGFα were not significantly different in any of the regions examined. Conversely, EGF receptor expression was elevated in the prefrontal cortex. Serum EGF levels were markedly reduced in schizophrenic patients, even in young, drug-free patients. Chronic treatment of animals with the antipsychotic drug haloperidol had no influence on EGF levels in the brain or serum. These findings suggest that there is abnormal EGF production in various central and peripheral tissues of patients with both acute and chronic schizophrenia. EGF might thus provide a molecular substrate for the pathologic manifestation of the illness, although additional studies are required to determine a potential link between impaired EGF signaling and the pathology/etiology of schizophrenia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Groenen LC, Nice EC, Burgess AW . Structure-function relationships for the EGF/TGFa family of mitogens Growth Factors 1994; 11: 235–257
King LE Jr, Gates RE, Nanney LB, Stoscheck CM . Epidermal growth factor (EGF) regulates non-mitogenic functions in differentiated mammalian tissues In: Bernsttein IA, Hirone T (ed) Processes in Cutaneous Epidermal Differentiation Praeger Scientific: New York 1987; pp 233–251
Xian CJ, Zhou XF . Roles of transforming growth factor-alpha and related molecules in the nervous system Mol Neurobiol 2000; 20: 157–183
Ferrari G, Toffano G, Skaper SD . Epidermal growth factor exerts neuronotrophic effects on dopaminergic and GABAergic CNS neurons: comparison with basic fibroblast growth factor J Neurosci Res 1991; 30: 493–497
Ishiyama J, Saito H, Abe K . Epidermal growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor promote the generation of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anaesthetized rats Neurosci Res 1991; 12: 403–411
Morrison RS, Kornblum HI, Leslie FM, Bradshaw RA . Trophic stimulation of cultured neurons from neonatal rat brain by epidermal growth factor Science 1987; 238: 72–75
Nakagawa T, Sasahara M, Hayase Y, Haneda M, Yasuda H, Kikkawa R et al. Neuronal and glial expression of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in central nervous system of prenatal and early-postnatal rat Dev Brain Res 1998; 108: 263–272
Seroogy KB, Lundgren KH, Lee DC, Guthrie KM, Gall CM . Cellular localization of transforming growth factor-alpha mRNA in rat forebrain J Neurochem 1993; 60: 1777–1782
Scalabrino G, Nicolini G, Buccellato FR, Peracchi M, Tredici G, Manfridi A, Pravettoni G . Epidermal growth factor as a local mediator of the neurotrophic action of vitamin B(12) (cobalamin) in the rat central nervous system FASEB J 1999; 13: 2083–2090
Adamson ED, Meek J . The ontogeny of epidermal growth factor receptors during mouse development Dev Biol 1984; 103: 62–70
Gomez-Pinilla F, Knauer DJ, Nieto-Sampedro M . Epidermal growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in rat brain. Development and cellular localization Brain Res 1988; 438: 385–390
Werner MH, Nanney LB, Stoscheck CM, King LE . Localization of immunoreactive epidermal growth factor receptors in human nervous system J Histochem Cytochem 1988; 36: 81–86
Casper D, Mytilineou C, Blum M . EGF enhances the survival of dopamine neurons in rat embryonic mesencephalon primary cell culture J Neurosci Res 1991; 30: 372–381
Casper D, Blum M . Epidermal growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor protect dopaminergic neurons from glutamate toxicity in culture J Neurochem 1995; 65: 1016–1026
Ventrella LL . Effect of intracerebroventricular infusion of epidermal growth factor in rats hemitransected in the nigro-striatal pathway J Neurosurg Sci 1993; 37: 1–8
Alexi T, Hefti F . Trophic actions of transforming growth factor alpha on mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons developing in culture Neuroscience 1993; 55: 903–918
Sibilia M, Steinbach JP, Stingl L, Aguzzi A, Wagner EF . A strain-independent postnatal neurodegeneration in mice lacking the EGF receptor EMBO J 1998; 17: 719–731
Blum M . A null mutation in TGF-alpha leads to a reduction in midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra Nat Neurosci 1998; 1: 374–377
Hilakivi-Clarke LA, Goldberg R . Effects of tryptophan and serotonin uptake inhibitors on behavior in male transgenic transforming growth factor alpha mice Eur J Pharmacol 1993; 237: 101–108
Hilakivi-Clarke LA, Corduban TD, Taira T, Hitri A, Deutsch S, Korpi ER et al. Alterations in brain monoamines and GABAA receptors in transgenic mice overexpressing TGF alpha Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1995; 50: 593–600
Cirulli F, Alleva E . Effects of repeated administrations of EGF and TGF-alpha on mouse neurobehavioral development Neurotoxicology 1994; 15: 819–825
Kubota N, Kiuchi Y, Nemoto M, Oyamada H, Ohno M, Funahashi H et al. Regulation of serotonin transporter gene expression in human glial cells by growth factors Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 417: 69–76
Van Setten GB, Edstrom L, Stibler H, Rasmussen S, Schultz G . Levels of transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha) in human cerebrospinal fluid Int J Dev Neurosci 1999; 17: 131–134
Mogi M, Harada M, Kondo T, Riederer P, Inagaki H, Minami M et al. Interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha are elevated in the brain from Parkinsonian patients Neurosci Lett 1994; 180: 147–150
Muller N, Ackenheil M . Psychoneuroimmunology and the cytokine action in the CNS: implications for psychiatric disorders Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1998; 22: 1–33
Prolo P, Licinio J . Cytokines in affective disorders and schizophrenia: new clinical and genetic findings Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 396
Licinio J, Wong ML . The role of inflammatory mediators in the biology of major depression: central nervous system cytokines modulate the biological substrate of depressive symptoms, regulate stress-responsive systems, and contribute to neurotoxicity and neuroprotection Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 317–327
Jankowsky JL, Patterson PH . Cytokine and growth factor involvement in long-term potentiation Mol Cell Neurosci 1999; 14: 273–286
Nawa H, Takahashi M, Patterson PH . Cytokine and growth factor involvement in schizophrenia—support for the developmental model Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 594–603
Takei N, Sasaoka K, Inoue K, Takahashi M, Endo Y, Hatanaka H . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases the stimulation-evoked release of glutamate and the levels of exocytosis-associated proteins in cultured cortical neurons from embryonic rats J Neurochem 1997; 68: 370–375
Narisawa-Saito M, Silva AJ, Yamaguchi T, Hayashi T, Yamamoto T, Nawa H . Growth factor-mediated Fyn signaling regulates alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor expression in rodent neocortical neurons Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 2461–2466
Xiong H, Narisawa-Saito M, Jourdi H, Nawa H . The glutamate receptor-mediated regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor production by cytokines in central nervous system Soc Neurosci Abst 1999; 25: 407.10
Namba H, Nagana T, Xiong H, Futamura T, Otsu Y, Takei N et al. Neurotrophins and cytokines positively and negatively regulate expression of glutamate receptor on forebrain inhibitory neurons Soc Neurosci Abst 2000; 26: 223.15
Wakabayashi K, Narisawa-Saito M, Iwakura Y, Arai T, Ikeda K, Takahashi H et al. Phenotypic down-regulation of glutamate receptor subunit GluR1 in Alzheimer's disease Neurobiol Aging 1999; 20: 287–295
Nieuwenhunhuys R, Voogd J, van Huijzen Chr . The Human Central Nervous System—A Synopsis and Atlas Springer-Verlag: Berlin 1988
Takahashi M, Shirakawa O, Toyooka K, Kitamura N, Hashimoto T, Maeda K et al. Abnormal expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor in the corticolimbic system of schizophrenic patients Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 293–300
Yamada A, Kawata S, Tamura S, Kiso S, Higashiyama S, Umeshita K et al. Plasma heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor levels in patients after partial hepatectomy as determined with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 246: 783–787
Ozaki M, Kishigami S, Yano R . Expression of receptors for neuregulins, ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4, in developing mouse cerebellum Neurosci Res 1998; 30: 351–354
Godfrey D, Pearlson M, Laura M . Structural brain imaging in schizophrenia: a selective review Biol Psychiatry 1999; 46: 627–649
Canesi L, Malatesta M, Battistelli S, Ciacci C, Gallo G, Gazzanelli G . Immunoelectron microscope analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in isolated Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam.) digestive gland cells: evidence for ligand-induced changes in EGFR intracellular distribution J Exp Zool 2000; 286: 690–698
Walker RA . The erbB/HER type 1 tyrosine kinase receptor family J Pathol 1998; 185: 234–235
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J . Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity Cell 1990; 61: 202–212
Earp HS, Dawson TL, Li X, Yu H . Heterodimerization and functional interaction between EGF receptor family members: a new signaling paradigm with implications for breast cancer research Breast Cancer Res Treat 1995; 35: 115–132
Yamada M, Ikeuchi T, Hatanaka H . The neurotrophic action and signalling of epidermal growth factor Prog Neurobiol 1997; 51: 19–37
Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick JS, Dull TJ, Gray A, Tam AW et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells Nature 1984; 309: 418–425
Fries G, Perneczky A, Kempski O . Glioblastoma-associated circulating monocytes and the release of epidermal growth factor J Neurosurg 1996; 85: 642–647
Sokolov BP . Expression of NMDAR1, GluR1, GluR7, and KA1 glutamate receptor mRNAs is decreased in frontal cortex of ‘neuroleptic-free’ schizophrenics: evidence on reversible up-regulation by typical neuroleptics J Neurochem 1998; 71: 2454–2464
McAllister CG, van Kammen DP, Rehn TJ, Miller AL, Gurklis J, Kelley ME et al. Increases in CSF levels of interleukin-2 in schizophrenia: effects of recurrence of psychosis and medication status Am J Psychiatry 1995; 152: 1291–1297
Harrison PJ . The neuropathology of schizophrenia. A critical review of the data and their interpretation Brain 1999; 122: 593–624
Tokumaru S, Higashiyama S, Endo T, Nakagawa T, Miyagawa Ji, Yamamori K et al. Ectodomain shedding of epidermal growth factor receptor ligands is required for keratinocyte migration in cutaneous wound healing J Cell Biol 2000; 151: 209–220
Subramanian SV, Fitzgerald ML, Bernfield M . Regulated shedding of syndecan-1 and -4 ectodomains by thrombin and growth factor receptor activation J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 14713–14720
Waksal HW . Role of an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor in treating cancer Cancer Metastasis Rev 1999; 18: 427–436
Catts VS, Catts SV . Apoptosis and schizophrenia: is the tumour suppressor gene, p53, a candidate susceptibility gene? Schizophr Res 2000; 41: 405–415
Kerwin RW . Glutamate receptors, microtubule associated proteins and developmental anomaly in schizophrenia: an hypothesis Psychol Med 1993; 23: 547–551
Weinberger DR . The biological basis of schizophrenia J Clin Psychiatry Monograph 1997; 15: 4–6
Seeman P . Schizophrenia as a brain disease. The dopamine receptor story Arch Neurol 1993; 50: 1093–1095
Goldstein M, Deutch AY . Dopaminergic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia FASEB J 1992; 6: 2413–2421
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms E Higuchi for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (RFTF-96L00203), the Targeted Research Grant for Brain Science, and grants-in-aid for Creative Scientific Research and for Basic Scientific Research (B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Futamura, T., Toyooka, K., Iritani, S. et al. Abnormal expression of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in the forebrain and serum of schizophrenic patients. Mol Psychiatry 7, 673–682 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001081
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001081
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Suppresses the Development of GABAergic Neurons Via the Modulation of Perineuronal Net Formation in the Neocortex of Developing Rodent Brains
Neurochemical Research (2024)
-
Elevation of EGR1/zif268, a Neural Activity Marker, in the Auditory Cortex of Patients with Schizophrenia and its Animal Model
Neurochemical Research (2022)
-
Decreased Serum EGF in First-episode and Chronic Schizophrenia Patients: Negative Correlation with Psychopathology
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Clozapine-dependent inhibition of EGF/neuregulin receptor (ErbB) kinases
Translational Psychiatry (2019)
-
Correlation of Plasma EGF with Striatal Dopamine Transporter Availability in Healthy Subjects
Scientific Reports (2017)