Abstract
Objective: To examine the effects of the degree of body mass index and weight gain as the risks for hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes in Japanese men, and to compare that to the corresponding effects in a Caucasian population.
Design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting: Cohort of all male employees at a company.
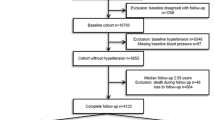
Subjects: A total of 4737 male employees followed until retirement or for 4 y (longest term 4 y).
Results: Increase of body mass index beyond 22 kg/m2 related to an increased risk for hypertension even after being adjusted for possible confounding factors such as age, smoking status, alcohol intake, family history and baseline value of systolic blood pressure. The risks greatly increased in subjects with a body mass index above 27 kg/m2 for hypertension, and 29 kg/m2 for diabetes and hypercholesterolemia. Weight gain (more than 2 kg) was strongly related to an increased risk for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia after being adjusted for possible confounding factors. However, weight gain was not related to diabetes, and weight loss did not decrease the risks for any of the three diseases.
Conclusions: Among Japanese, the degrees of body mass index associated with risks for hypertension, diabetes and hypercholesterolemia were lower than those in Caucasians. The risks for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia were strongly associated with weight gain in a Japanese male population who showed a low prevalence of severe obesity, and the risks were similar to or somewhat higher than those in a Caucasian population with a high prevalence of severe obesity.
Sponsorship: Health Science Research Grant by the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Japan.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Rimm EB, Willett WC, Colditz GA . 1994 Obesity, fat distribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men Diabetes Care 17: 961–969
Colditz GA, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Arky RA, Speizer FE . 1990 Weight as a risk factor for clinical diabetes in women Am. J. Epidemiol. 132: 501–513
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ, Johnson CL . 1998 Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–1994 Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 22: 39–47
Helmrich SP, Ragland DR, Leung RW, Paffenbarger RS . 1991 Physical activity and reduced occurrence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus New Engl. J. Med. 325: 147–152
Huang Z, Willett WC, Manson JE, Rosener B, Stampfer MJ, Speizer FE, Colditz GA . 1998 Body weight, weight change, and risk for hypertension in women Ann. Intern. Med. 128: 81–88
Japan Arteriosclerosis Society. 1997 Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of hyperlipidemia TJ. Jap. Atheroscler. Soc. 25: 1–34
Japan Diabetic Society. 1999 Diagnosis In Guidelines for Treatment of Diabetes ed. Japan Diabetic Society 12–17 Tokyo: Bunkodo
Liu L, Choudhury SR, Okayama A, Hayakawa T, Kita Y, Ueshima H . 1999 Changes in body mass index and its relationships to other cardiovascular risk factors among Japanese population: results from the 1980 and 1990 National Cardiovascular Surveys in Japan J. Epidemiol. 9: 163–174
Manson JE, Nathan DM, Krolewski AS, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Hennekens CH . 1992 A prospective study of exercise and incidence of diabetes among US male physicians J.A.M.A. 268: 63–67
Matsuzawa Y, Inoue S, Ikeda Y, Sakata T, Saitou Y, Satou Y, Sirai K, Ohno M, Miyazaki S, Tokunaga M, Fukagawa K, Yamanouchi K, Nakamura T . 2000 New diagnosis and classification of obesity J. Jap. Soc. Study Obes. 6: 18–28
Ministry of Health and Welfare in Japan. 1996 National Nutrition Survey in 1994 Tokyo: Daiichi Shuppan
Nakayama K, Koyohara Y, Kato I, Iwamoto H, Ueda K, Fujishima M . 1997 Effect of body mass index on morbidity and mortality in a general Japanese population—The Hisayama Study Jpn. J. Geriat. 34: 935–941
Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Ascherio A, Spiegelman D, Colditz GA, Willett WC . 1995 Body size and fat distribution as predictors of coronary heart disease among middle-aged and older US men Am. J. Epidemiol. 141: 1117–1127
Tai T, Chuang L, Wu H, Chen C . 1992 Association of body build with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and hypertension among Chinese adults: a 4-year follow-up study Int. J. Epidemiol. 21: 511–517
The Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. 1997 The sixth report of The Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure Arch. Intern. Med. 157: 2413–2446
Todoroki I, Shinchi K, Kono S, Imanishi K . 1994 Lifestyle and glucose tolerance: a cross-sectional study of Japanese men Ann. Epidemiol. 4: 363–368
Tokunaga K, Matsuzawa Y, Kotani K, Keno Y, Kobatake T, Fujioka, Tarui S . 1991 Ideal body weight estimated from the body mass index with the lowest morbidity Int. J. Obes. 15: 1–5
WHO. 1998 The health consequences of overweight and obesity in adults and children In Obesity, Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic pp 43–72 Geneva: World Health Organization
Willett WC, Dietz WH, Colditz GA . 1999 Guidelines for healthy weight New Engl. J. Med. 341: 427–434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa-Takata, K., Ohta, T., Moritaki, K. et al. Obesity, weight change and risks for hypertension, diabetes and hypercholesterolemia in Japanese men. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 601–607 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601364
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601364
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association of weight status and the risks of diabetes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies
International Journal of Obesity (2022)
-
Gender-specific predictive ability for the risk of hypertension incidence related to baseline level or trajectories of adiposity indices: a cohort study of functional community
International Journal of Obesity (2022)
-
Impacts of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio, sleep efficiency, and conventional risk factors on home hypertension in a general Japanese population
Hypertension Research (2021)
-
Combined effect of weight gain within normal weight range and parental hypertension on the prevalence of hypertension; from the J-MICC Study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2020)
-
Disparities in the impact of overweight on hypertension among Asians: a Japanese and Thai population-based study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2019)