Abstract
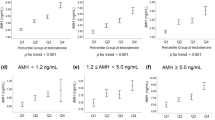
Our objective was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of clomiphene citrate (CC) in infertile and hypoandrogenic men through a retrospective study between September 2013 and May 2014. We identified 47 men between 18 and 55 years placed on 50 mg CC every other day. We evaluated the effect of CC on testosterone after 2 weeks, rates of adverse effects and predictors of CC response. Mean baseline testosterone, bioavailable testosterone and estradiol were 246.8 ng dl−1, 125.5 ng dl−1 and 20.8 pg dl−1, respectively. At 2 weeks, mean testosterone, bioavailable testosterone and estradiol increased to 527.6 ng dl−1, 281.8 ng dl−1 and 32.0 pg dl−1 (all P<0.001). Two patients at 2 weeks and one patient at 3 months had a paradoxical decrease in testosterone. Mean total motile count (TMC) and concentration increased from 59.7 million (s.e.m.: 16.5) and 50.7 millions ml−1 (s.e.m.: 11.1) at baseline to 90.9 million (s.e.m.: 25.9) and 72.5 millions ml−1 (s.e.m.: 17.5), respectively, at 3 months, although this was nonsignificant (P=0.09, 0.09). No patient on CC experienced a paradoxical decrease in TMC or sperm concentration. On age-adjusted regression analysis, age, BMI, longitudinal testis axis, baseline follicle-stimulating hormone, LH and estradiol did not correlate with improvement in bioavailable testosterone at 2 weeks. CC improves testosterone and may improve semen parameters, although a small percentage of men may not demonstrate improvement in testosterone.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moskovic DJ, Katz DJ, Akhavan A, Park K, Mulhall JP . Clomiphene citrate is safe and effective for long-term management of hypogonadism. BJU Int 2012; 110: 1524–1528.
Katz DJ, Nabulsi O, Tal R, Mulhall JP . Outcomes of clomiphene citrate treatment in young hypogonadal men. BJU Int 2012; 110: 573–578.
Ko EY, Siddiqi K, Brannigan RE, Sabanegh ES Jr . Empirical medical therapy for idiopathic male infertility: a survey of the American Urological Association. J Urol 2012; 187: 973–978.
Kim ED, Crosnoe L, Bar-Chama N, Khera M, Lipshultz LI . The treatment of hypogonadism in men of reproductive age. Fertil Steril 2013; 99: 718–724.
Willets AE, Corbo JM, Brown JN . Clomiphene for the treatment of male infertility. Reprod Sci (Thousand Oaks, CA) 2013; 20: 739–744.
Sanofi-aventis. Product information: Clomid: Clomiphene Citrate. Sanofi-Aventis: Bridgewater, NJ, 2006.
Sorbie PJ, Perez-Marrero R . The use of clomiphene citrate in male infertility. J Urol 1984; 131: 425–429.
Ghanem H, Shaeer O, El-Segini A . Combination clomiphene citrate and antioxidant therapy for idiopathic male infertility: a randomized controlled trial. Fertil Steril 2010; 93: 2232–2235.
Roth LW, Ryan AR, Meacham RB . Clomiphene citrate in the management of male infertility. Semin Reprod Med 2013; 31: 245–250.
Hotaling JM, Patel Z . Male endocrine dysfunction. Urol Clin N Am 2014; 41: 39–53.
Matthews GJ, Goldstein M, Henry JM, Schlegel PN . Nonbacterial pyospermia: a consequence of clomiphene citrate therapy. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud 1995; 40: 187–191.
Pasqualotto FF, Fonseca GP, Pasqualotto EB . Azoospermia after treatment with clomiphene citrate in patients with oligospermia. Fertil Steril 2008; 90: 2014.e2011–2012.
Morley JE, Charlton E, Patrick P, Kaiser FE, Cadeau P, McCready D et al. Validation of a screening questionnaire for androgen deficiency in aging males. Metabolism 2000; 49: 1239–1242.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A . The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997; 49: 822–830.
Cappelleri JC, Siegel RL, Glasser DB, Osterloh IH, Rosen RC . Relationship between patient self-assessment of erectile dysfunction and the sexual health inventory for men. Clin Ther 2001; 23: 1707–1719.
Paduch DA, Brannigan RE, Fuchs EF, Kim ED, Marmar JL, Sandlow JI . The laboratory diagnosis of testosterone deficiency. Urology 2014; 83: 980–988.
Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM . A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 3666–3672.
World Health Organization WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 5th (edn). World Health Organization: : Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
Moradi M, Moradi A, Alemi M, Ahmadnia H, Abdi H, Ahmadi A et al. Safety and efficacy of clomiphene citrate and l-carnitine in idiopathic male infertility: a comparative study. Urol J 2010; 7: 188–193.
World Health Organization. A double-blind trial of clomiphene citrate for the treatment of idiopathic male infertility. Int J Androl 1992; 15: 299–307.
Sokol RZ, Steiner BS, Bustillo M, Petersen G, Swerdloff RS . A controlled comparison of the efficacy of clomiphene citrate in male infertility. Fertil Steril 1988; 49: 865–870.
Ribeiro RS, Abucham J . Clomiphene fails to revert hypogonadism in most male patients with conventionally treated nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2011; 55: 266–271.
Mazzola CR, Katz DJ, Loghmanieh N, Nelson CJ, Mulhall JP . Predicting biochemical response to clomiphene citrate in men with hypogonadism. J Sex Med 2014; 11: 2302–2307.
Guay AT, Jacobson J, Perez JB, Hodge MB, Velasquez E . Clomiphene increases free testosterone levels in men with both secondary hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction: who does and does not benefit? Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 156–165.
Murdter TE, Kerb R, Turpeinen M, Schroth W, Ganchev B, Bohmer GM et al. Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 2D6 determines oestrogen receptor activity of the major infertility drug clomiphene via its active metabolites. Hum Mol Genet 2012; 21: 1145–1154.
Weng L, Ziliak D, Im HK, Gamazon ER, Philips S, Nguyen AT et al. Genome-wide discovery of genetic variants affecting tamoxifen sensitivity and their clinical and functional validation. Ann Oncol 2013; 24: 1867–1873.
Brambilla DJ, O'Donnell AB, Matsumoto AM, McKinlay JB . Intraindividual variation in levels of serum testosterone and other reproductive and adrenal hormones in men. Clin Endocrinol 2007; 67: 853–862.
Ashok S, Sigman M . Bioavailable testosterone should be used for the determination of androgen levels in infertile men. J Urol 2007; 177: 1443–1446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All conflict of interest, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter and materials discussed in this manuscript (employment/affiliation, grants or funding, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, royalties, or patents filed, received or pending), are the following: DPP was supported in part by a generous reconstructive urology educational grant from American Medical Systems (Minnetonka, MN, USA). American Medical Systems had no role in study concept, design, data acquisition and analysis, or manuscript drafting and revision.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, D., Brant, W., Myers, J. et al. The safety and efficacy of clomiphene citrate in hypoandrogenic and subfertile men. Int J Impot Res 27, 221–224 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2015.21
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2015.21
This article is cited by
-
Clomifeencitraat voor hypogonadale klachten: bijna 10 jaar ervaring
Tijdschrift voor Urologie (2022)
-
Clomifene
Reactions Weekly (2016)