Abstract
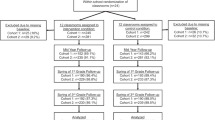
This study evaluated the effectiveness of the Early Risers “Skills for Success” Program when implemented by neighborhood family resource centers available to urban children and their families. Kindergarten and first-grade children (n=327) enrolled in 10 schools were screened for aggressive behavior, and randomized to two model variations of the Early Risers Program or a no-intervention control condition. The full-strength model (CORE + FLEX) included child and parent/family components whereas the partial model (CORE-only) offered only the child component. The intervention was delivered over two continuous years. CORE + FLEX children showed higher levels of program attendance than their CORE-only counterparts but no differences on outcomes measures were observed between models. When both program models were collapsed and compared to controls, program children showed significant gains on measures of school adjustment and social competence, the most aggressive program children showed reductions in disruptive behavior, and program parents reported reduced levels of stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abidin, R. R. (1995). The Parenting Stress Index (2nd ed.). Charlottesville, VA: Pediatric Psychology Press.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Teacher's Report Form and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont.
Achenbach, T. M., McConaughy, S. H., & Howell, C. T. (1987). Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: Implications of cross-informant correlations for situational speci-ficity. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 213-232.
August, G. J., Hektner, J. M., Egan, E. E., Realmuto, G. M., & Bloomquist, M. L. (2002). The Early Risers longitudinal prevention trial: Examination of three year outcomes in aggressive children with intent-to-treat and as-intended analyses. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 16 (Suppl. 4), 27-39.
August, G. J., Realmuto, G. M., Hektner, J. M., & Bloomquist, M. L. (2001a). An intergrated components preventive intervention for aggressive elementary school children: The Early Risers program. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 69, 614-626.
August, G. J., Realmuto, J. M., Winters, K. C., & Hektner, J. M. (2001b). Prevention of adolescent drug abuse: Targeting high-risk children with a multifaceted intervention model—The Early Risers 'Skills for Success' program. Applied and Preventive Psychology, 10, 135-154.
Coie, J. D., & Dodge, K. A. (1988). Multiple sources of data on social behavior and social status in the school: A cross-age comparison. Child Development, 59, 815-829.
Committee for Children (1992). Second Step: A Violence Prevention Curriculum, Grades 1-3. (2nd ed.). Seattle, WA: Committee for Children.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group (1999). Initial impact of the Fast Track prevention trial for conduct problems: I. The high-risk sample. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67, 631-647.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group (2002). Evaluation of the first 3 years of the Fast Track prevention trial with children at high risk for adolescent conduct problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 19-35.
Dumas, J. E., Rollock, D., Prinz, R. J., Hops, H., & Blechman, E. A. (1999). Cultural sensitivity: Problems and solutions in applied and preventive intervention. Applied and Preventive Psychology, 8, 175-196.
Grossman, D. C., Neckerman, H. J., Keopsell, T. D., Liu, P., Asher, K. N., Beland, K., Frey, K., & Rivara, F. P. (1997). Effectiveness of a violence prevention curriculum among children in elementary school. JAMA, 277, 1605-1611.
Guerra, N. G., Eron, L. D., Heusmann, L. R., Tolan, P. H., & Van Acker, R. (1997). A cognitive-ecological approach to the prevention and mitigation of violence and aggression in inner-city youth. In D. P. Fry & K. Bjoerkqvist (Eds.), Cultural variation in conflict resolution: Alternatives to violence (pp. 199-213). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Harter, S., & Pike, R. (1984). The pictorial scale of perceived competence and social acceptance for young children. Child Development, 55, 1969-1982.
Hedeker, D., & Gibson, R. D. (1996). MIXREG: A computer program for mixed-effects regression analysis with autocorrelated errors. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 49, 229-252.
Henggeler, S. W., Schoenwald, S. K., Borduin, C. M., Rowland, M. D., & Cunningham, P. M. (1998). Multisystemic treatment of antisocial behavior in children and adolescents. New York: Guilford Press.
Hoagwood, K., Hibbs, E., Brent, D., & Jensen, P. (1995). Introduction to the special section: Efficacy and effectiveness in studies of child and adolescent psychotherapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 63, 683-687.
Hollingshead, A. (1975). Four factor index of social status. Unpublished working paper.
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (1990). Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test: Manual. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Kellam, S. G., Rebok, G.W., Ialongo, N., & Mayer, L. S. (1994). The course and malleability of aggressive behavior from early first grade into middle school: Results of a developmental epidemiologically-based prevention trial. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35, 359-381.
Moos, R. H., & Moos, B. S. (1986). Family Environment Scale: Manual. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologist Press.
Pelham, W. E., Gnagy, E. M., Greiner, A. R., Hoza, B., Hinshaw, S. P., Swanson, J. M., Simpson, S., Shapiro, C., Bukstein, O., Baron-Myak, C., & McBurnett, K. (2000). Behavioral versus behavioral and pharmacological treatment in ADHD children attending a summer treatment program. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 507-525.
Pelham, W. E., Greiner, A. R., & Gnagy, E. M. (1997). Summer treatment program manual. Buffalo, NY: Comprehensive Treatment of Attention Deficit Disorders, Inc.
Pelham, W. E., & Hoza, B. (1996). Intensive Treatment: A summer treatment program for children with ADHD. In E. D. Hibbs & P. S. Jensen (Eds.), Psychosocial treatment research of child and adolescent disorders: Empirically based strategies for clinical practice (pp. 311-340). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Reid, J. B., Eddy, J. M., Fetrow, R. A., & Stoolmiller, M. (1999). Description and immediate impact of a preventive intervention for conduct problems. American Journal of Community Psychology, 27, 483-517.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (1992). BASC—Behavioral Assessment System for Children: Manual. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Shelton, K. K., Frick, P. J., & Wooton, J. (1996). Assessment of parenting practices in families of elementary school-age children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 25, 317-329.
Sinclair, M. F., Christenson, S. L., Evelo, D. L., & Hurley, C. M. (1998). Dropout prevention for youth with disabilities: Efficacy of a sustained school engagement procedure. Exceptional Children, 65, 7-21.
Sue, S., & Zane, N. (1987). The role of culture and cultural techniques in psychotherapy: A critique and reformulation. American Psychologist, 42, 37-45.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (1996). Using multivariate statistics (3rd ed.). New York: HarperCollins.
Tharp, R. G. (1991). Cultural diversity and treatment of children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 59, 799-812.
Tremblay, R. E., Masse, L. C., Pagani, L., & Vitaro, F. (1996). From childhood physical aggression to adolescent maladjustment: The Montreal prevention experiment. In R. D. Peters & R. J. McMahon (Eds.), Banff international behavioral science series: Vol. 3. Preventing childhood disorders, substance abuse, and delinquency (pp. 268-298). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Walker, H. M., & McConnell, S. R. (1995). Walker-McConnell Scale of Social Competence and School Adjustment: Elementary version. San Diego, CA: Singular.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1996). Early intervention with videotaped modeling: Programs for families of children with oppositional defiant or conduct disorder. In E. D. Hibbs & P. S. Jensen (Eds.), Psychosocial treatments for child and adolescent disorders: Empirically based strategies for clinical practice (pp. 435-474). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Webster-Stratton, C. (1998). Preventing conduct problems in Head Start children: Strengthening parent competencies. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66, 715-730.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Hammond, M. (1997). Treating children with early-onset conduct problems: A comparison of child and parent training interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 93-109.
Woodcock, R. W., & Johnson, M. B. (1990). Woodcock-Johnson Psychoeducational Battery-Revised: Tests of achievement. Allen, TX: DML Teaching Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
August, G.J., Lee, S.S., Bloomquist, M.L. et al. Dissemination of an Evidence-Based Prevention Innovation for Aggressive Children Living in Culturally Diverse, Urban Neighborhoods: The Early Risers Effectiveness Study. Prev Sci 4, 271–286 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026072316380
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026072316380