Abstract
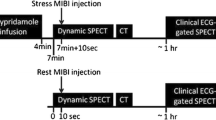
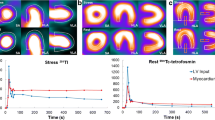
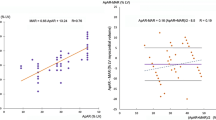
Background: In order to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of the 1-day separate acquisition dual-isotope single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) protocol, using 201Tl for the rest and 99mTc-tetrofosmin for the stress images, a consecutive series of patients with suspected or known coronary artery disease (CAD) was studied that also underwent coronary angiography. Methods: The results of myocardial SPECT, using a semi-quantitative visual analysis, were acquired in 123 patients and compared with the results of coronary angiography. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated, using thresholds of ≥50 and ≥70% stenosis. As an alternative for specificity, the normalcy rate was determined in a separate group of 87 patients with a <5% pre-test likelihood of CAD. Results: The prevalence of CAD using ≥50 and ≥70% stenosis was 88 and 78%, respectively. The sensitivity for detection of patients with ≥50 and ≥70% stenosis was 94 and 97%, respectively while specificity was 62 and 59%, respectively. The high rate of false positive perfusion defects resulting in a low specificity could be explained by specific clinical issues. However, the routine assessment with additional clinical and electrocardiographic data resulted in a correct interpretation of most of the false positive perfusion defects. The positive predictive value was 92 and 85% and the negative predictive value 46 and 77%, using thresholds of ≥50 and ≥70% stenosis, respectively. The normalcy rate was 91%. Conclusion: The one-day separate acquisition rest 201Tl/stress 99mTc-tetrofosmin SPECT protocol is an efficient procedure for myocardial perfusion scintigraphy with high sensitivity for detection of CAD. Specific clinical issues caused a low value for specificity. Therefore, clinical information and knowledge of the electrocardiogram is essential for a correct interpretation of SPECT images.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verani MS. Thallium-201 single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in the assessment of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1992; 70: 3E–9E.
Kiat H, Maddahi J, Roy LT, Van Train K, Friedman J, Resser K. Comparison of technetium 99m methoxy isobutyl isonitrile and thallium 201 for evaluation of coronary artery disease by planar and tomographic methods. Am Heart J 1989; 117: 1–11.
Kahn JK, McGhie I, Akers MS, Sills MN, Faber TL, Kulkarni PV. Quantitative rotational tomography with 201Tl and 99mTc 2–methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile. A direct comparison in normal individuals and patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 1989; 79: 1282–1293.
Iskandrian AS, Heo J, Kong B, Lyons E, Marsch S. Use of technetium-99m isonitrile (RP-30A) in assessing left ventricular perfusion and function at rest and during exercise in coronary artery disease, and comparison with coronary arteriography and exercise thallium-201 SPECT imaging. Am J Cardiol 1989; 64: 270–275.
Wackers FJ. Comparison of thallium-201 and technetium-99m methoxyisobutyl isonitrile. Am J Cardiol 1992; 70: 30E–34E.
Munch G, Neverve J, Matsunari I, Schroter G, Schwaiger M. Myocardial technetium-99m-tetrofosmin and technetium-99m-sestamibi kinetics in normal subjects and patients with coronary artery disease. J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 428–432.
Jain D, Wackers FJ, Mattera J, McMahon M, Sinusas AJ, Zaret BL. Biokinetics of technetium-99m-tetrofosmin: myocardial perfusion imaging agent: implications for a one day imaging protocol. J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 1254–1259.
Flamen P, Bossuyt A, Franken PR. Technetium-99m-tetrofosmin in dipyridamole-stress myocardial SPECT imaging: intraindividual comparison with technetium-99msestamibi. J Nucl Med 1995; 36: 2009–2015.
Acampa W, Cuocolo A, Sullo P, Varrone A, Nicolai E, Pace L. Direct comparison of technetium 99m-sestamibi and technetium 99m-tetrofosmin cardiac single photon emission computed tomography in patients with coronary artery disease. J Nucl Cardiol 1998; 5: 265–274.
Berman DS, Kiat H, Friedman JD, Wang FP, Van Train K, Matzer L. Separate acquisition rest thallium-201/stress technetium-99m sestamibi dual-isotope myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography: a clinical validation study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 22: 1455–1464.
Hendel RC, Parker MA, Wackers FJ, Rigo P, Lahiri A, Zaret BL. Reduced variability of interpretation and improved image quality with a technetium 99m myocardial perfusion agent: comparison of thallium 201 and technetium 99m-labeled tetrofosmin. J Nucl Cardiol 1994; 1: 509–514.
Eck-Smit BL, van der Wall EE, Kuijper AF, Zwinderman AH, Pauwels EK. Immediate thallium-201 reinjection following stress imaging: a time-saving approach for detection of myocardial viability. J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 737–743.
Matzer L, Kiat H, Wang FP, Van Train K, Germano G, Friedman J. Pharmacologic stress dual-isotope myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography. Am Heart J 1994; 128: 1067–1076.
Amanullah AM, Kiat H, Friedman JD, Berman DS. Adenosine technetium-99m sestamibi myocardial perfusion SPECT in women: diagnostic efficacy in detection of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996; 27: 803–809.
Wang FP, Amanullah AM, Kiat H, Friedman JD, Berman DS. Diagnostic efficacy of stress technetium 99m-labeled sestamibi myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography in detection of coronary artery disease among patients over age 80. J Nucl Cardiol 1995; 2: 380–388.
Mazzanti M, Germano G, Kiat H, Kavanagh PB, Alexanderson E, Friedman JD. Identification of severe and extensive coronary artery disease by automatic measurement of transient ischemic dilation of the left ventricle in dualisotope myocardial perfusion SPECT. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996; 27: 1612–1620.
Mahmood S, Gunning M, Bomanji JB, Gupta NK, Costa DC, Jarritt PH. Combined rest thallium-201/stress technetium-99m-tetrofosmin SPECT: feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of a 90–minute protocol. J Nucl Med 1995; 36: 932–935.
Groutars RG, Verzijlbergen JF, Muller AJ, et al. Prognostic value and quality of life in patients with normal rest thallium-201/stress technetium 99m-tetrofosmin dual-isotope myocardial SPECT. J Nucl Cardiol 2000; 7: 333–341.
Cramer MJ, Verzijlbergen JF, van der Wall EE, Vermeersch PH, Niemeyer MG, Zwinderman AH. Comparison of adenosine and high-dose dipyridamole both combined with low-level exercise stress for 99Tcm-MIBI SPET myocardial perfusion imaging. Nucl Med Commun 1996; 17: 97–104.
Berman DS, Kiat H, Van Train K, Garcia E, Friedman J, Maddahi J. Technetium 99m sestamibi in the assessment of chronic coronary artery disease. Semin Nucl Med 1991; 21: 190–212.
Diamond GA, Forrester JS. Analysis of probability as an aid in the clinical diagnosis of coronary-artery disease. New Engl J Med 1979; 300: 1350–1358.
Jukema JW, van der Wall EE, Vis-Melsen MJ, Kruyswijk HH, Bruschke AV. Dipyridamole thallium-201 scintigraphy for improved detection of left anterior descending coronary artery stenosis in patients with left bundle branch block. Eur Heart J 1993; 14: 53–56.
O'Keefe JH Jr, Bateman TM, Silvestri R, Barnhart C. Safety and diagnostic accuracy of adenosine thallium-201 scintigraphy in patients unable to exercise and those with left bundle branch block. Am Heart J 1992; 124: 614–621.
Lakkis NM, He ZX, Verani MS. Diagnosis of coronary artery disease by exercise thallium-201 tomography in patients with a right ventricular pacemaker. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 29: 1221–1225.
Iskandrian AS, Heo J, Kong B, Lyons E. Effect of exercise level on the ability of thallium-201 tomographic imaging in detecting coronary artery disease: analysis of 461 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 1989; 14: 1477–1486.
Van Train KF, Maddahi J, Berman DS, Kiat H, Areeda J, Prigent F. Quantitative analysis of tomographic stress thallium-201 myocardial scintigrams: a multicenter trial. J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1168–1179.
Weinmann P, Foult JM, Le Guludec D, Tamgac F, Rechtman D, Neuman A. Dual-isotope myocardial imaging: feasibility, advantages and limitations. Preliminary report on 231 consecutive patients. Eur J Nucl Med 1994; 21: 212–215.
Kiat H, Germano G, Friedman J, Van Train K, Silagan G, Wang FP. Comparative feasibility of separate or simultaneous rest thallium-201/stress technetium-99m-sestamibi dual-isotope myocardial perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 542–548.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Groutars, R.G., Verzijlbergen, J.F., Tiel-van Buul, M.M. et al. The accuracy of 1-day dual-isotope myocardial SPECT in a population with high prevalence of coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 19, 229–238 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023637804898
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023637804898