Abstract
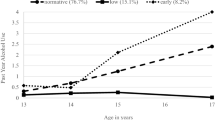
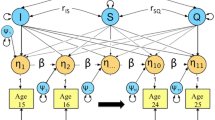
Genetic and environmental determinants of self-reported alcohol consumption were investigated in a sample of 2513 twin pairs who were first assessed at age 16 and were followed-up at age 17. At age 16, 77% of the sample was drinking, and 65% of drinkers reported drinking to intoxication. Both drinking and drinking to intoxication increased at the 1-year follow-up. Model fitting indicated that most of the variance in drinking initiation was due to shared environmental effects but that shared environmental effects were less important, and additive genetic effects were more important, in explaining frequency of drinking among subjects who had already initiated drinking. Similarly, shared environmental effects explained most of the variation in initiation of drinking to intoxication but were less important in explaining frequency of intoxication among subjects who had already initiated drinking to intoxication. The magnitude of genetic and environmental estimates for males and females did not differ significantly, but it was clear that either different genetic factors or different shared environmental factors were influencing males and females. For all drinking variables studied, shared environmental effects decreased from age 16 to age 17, while additive genetic effects increased from age 16 to age 17.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Han, C., McGue, M. K., and Iacono, W. G. Lifetime tobacco, alcohol and other substance use in adolescents Minnesota twins: Univariate and multivariate behavioral genetic analyses. Addiction 94:981-993.
Heath, A. C. (1995). Genetic influences on drinking behavior in humans. In Begleiter, H., and Kissin, B. (eds.), The Genetics of Alcoholism, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 82-121.
Heath, A. C., Meyer, J., Jardine, R., and Martin, N. G. (1991). The inheritance of alcohol consumption patterns in a general population twin sample: II. Determinants of consumption frequency and quantity consumed. J. Stud. Alcohol 52(4):425-433.
Jöreskog, K. G., and Sörbom, D. (1993). PRELIS 2 User's Reference Guide, Scientific Software, Chicago.
Kaprio, J., Viken, R., Koskenvuo, M., Romanov, K., and Rose, R. J. (1992). Consistency and change in patterns of social drinking: A 6-year follow-up of the Finnish Twin Cohort. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 16(2):234-240.
Kaprio, J., Rimpelä, A., Winter, T., Viken, R. J., Rimpelä, M., and Rose, R. J. (1995). Common genetic influences on BMI and age at menarche. Hum. Biol. 67:739-753.
Karvonen, S. (1995). Regional differences in drinking among Finnish adolescents. Addiction 90:57-64.
Koopmans, J. R., and Boomsma, D. I. (1996). Familial resemblances in alcohol use: Genetic or cultural transmission. J. Stud. Alcohol 57:19-28.
Koopmans, J. R., van Doornen, L. J. P., and Boomsma, D. I. (1994). Smoking and sports participation. In Goldbourt, U., DeFairre, U., and Berg, K. (eds.), Genetic Factors in Coronary Heart Disease, Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 217-235.
Maes, H. H., Woodard, C. E., Murrelle, L., Meyer, J. M., Silberg, J. L., Hewitt, J. K., Rutter, M., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Carbonneau, R., Neale, M. C., and Eaves, L. J. (1999). Tobacco, alcohol and drug use in eight-to sixteen-year-old twins: The Virginia Twin Study of Adolescent Behavioral Development. J. Stud. Alcohol 60:293-305.
Neale, M. C. (1999). Mx: Statistical Modeling, 5th ed., Department of Psychiatry, Medical College of Virginia, Richmond.
Neale, M. C., and Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families, Kluwer Academic, Boston.
Rose, R. J., Kaprio, J., Winter, T., Koskenvuo, M., and Viken, R. J. (1999). Familial and socioregional environmental effects on abstinence from alcohol at age sixteen. J. Stud. Alcohol Suppl. 13:63-74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viken, R.J., Kaprio, J., Koskenvuo, M. et al. Longitudinal Analyses of the Determinants of Drinking and of Drinking to Intoxication in Adolescent Twins. Behav Genet 29, 455–461 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021631122461
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021631122461