Abstract
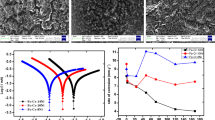
The present work is devoted to the problem of biodegradation of orthopaedic implants manufactured from stainless steel. In vitro simulations of the biocompatibility of two types of stainless steel, AISI 304 and AISI 316L, and their individual metal components, i.e. iron, chromium, nickel and molybdenum, were carried out in simulated physiological solution (Hank's) containing complexing agents. Knowledge of the effects of the chemical and biological complexing agents, EDTA and proteins, respectively, on the corrosion resistance of a metal should provide a better understanding of the processes occurring in vivo on its surface. The behavior of stainless steels and metal components was studied under open circuit and under potentiostatic conditions. The concentration of dissolved corrosion products in the form of released ions was determined by differential pulse polarography (DPP) and atomic emission spectrometry using inductively coupled plasma (ICP-AES). The composition of solid corrosion products formed on the surface was analyzed by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and their morphology was viewed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The addition of EDTA and proteins to physiological solution increased the dissolution of pure metals and stainless steels. The effect of particular protein differs on different metals and alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. M. E. Silva, J. M. Monteiro, M. G. S. Ferreira and J. M. Vieira, Clin. Mater. 12 (1993) 103.
K. Merritt, S. A. Brown and N. A. Sharkey, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 18 (1984) 1005.
P. Kovacs, in “Corrosion '92, The NACE Annual Conference and Corrosion Show” (Paper no. 214).
S. Brown and K. Merritt, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 14 (1980) 173.
M. H. Samitz and S. A. Katz, Br. J. Dermatol. 92 (1975) 287.
J. Yang and J. Black, Biomaterials 15 (1994) 262.
J. L. Woodman, J. Black and S. A. Jiminez, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 18 (1984) 99.
G. C. F. Clark and D. F. Williams, ibid. 16 (1982) 125.
A. Minović, M.Sc. thesis, University of Ljubljana (2000).
M. Pourbaix, “Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions” (NACE, Huston, Texas 1974).
I. Milošev and H.-H. Strehblow J. Biomed. Maters. Res. 52 (2000) 404.
T. Piao and S.-H, Park, J. Electrochem. Soc. 144 (1997) 3371.
Y. Okazaki, T. Tateishi and Y. Ito, Mater. Trans. JIM 38 (1997) 78.
J. Pan, C. Karlen and C. Ulfvin, J. Electrochem. Soc. 147 (2000) 1021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocijan, A., Milošev, I. & Pihlar, B. The influence of complexing agent and proteins on the corrosion of stainless steels and their metal components. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 14, 69–77 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021505621388
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021505621388