Abstract
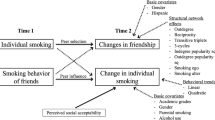
We examined the hypothesis that peer susceptibility would moderate the association between risk-taking and tendency to smoke in adolescents who were primarily African American. Participants were 88 preadolescents recruited from a 6th grade classroom in a public elementary school. We found an interaction of risk-taking and susceptibility to peer influence on smoking tendency. Specifically, a moderator effect was found for peer influence on the association between risk-taking and smoking tendency. The importance of examining peer susceptibility on health promotion and other health behaviors in children and adolescents was supported.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aiken, L. S., & West S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Barkley, R. A. (1998). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford.
Barron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator‐mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (1994). Chronic disease in minority populations. Atlanta: Author.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (1998). Tobacco use amongU.S. racial/ethnic minority groups–African Americans, American Indians and Alaska natives, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders, and Hispanics: A report of the surgeon general. Atlanta: Author.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2000). Youth risk behavior surveillance–United States, 1999. Atlanta: Author, CDC Surveillance Summaries, June 9, 2000. MMWR 2000, 49 (no. SS-5).
Clasen, D. R., & Brown, B. B. (1985). The multidimensionality of peer pressure. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 14, 451–468.
Collins, L. M., Sussman, S., Rauch, J. M., Dent, C. W., Johnson, C. A., Hansen, W. B., et al. (1987). Psychosocial predictors of young adolescent cigarette smoking: A sixteen-month, three wave longitudinal study. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 17554–573.
Flay, B., d'Avernas, J., Best, J. A., Kersell, M., & Ryan, M. (1983). Cigarette smoking: Why young people do it and ways of preventing it. In P. McGreath & P. Firestone (Eds.), Pediatric and adolescent behavior medicine. New York: Springer.
Holmbeck, G. N. (1997). Toward terminological, conceptual, and statistical clarity in the study of mediators and moderators: Examples of the child-clinical and pediatric psychology literatures. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 599–610.
Holmbeck, G. N. (2002). Post-hoc probing of significant moderational and mediational effects in studies of pediatric populations. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 27, 87–96.
Jessor, R. (1984). Adolescent development and behavioral health. In J. D. Matarazzo, S. M. Weiss, J. A. Herd, N. E. Miller, & S. M. Weiss (Eds.), Behavioral health: A handbook of health enhancement and disease prevention. New York: Wiley.
Jessor, R., & Jessor, S. L. (1977). Problem behavior and psychosocial development: A longitudinal study of youth. New York: Academic Press.
Koval, J. J., Pederson, L. L., Mills, C. A., McGrady, G. A., & Carvajal, S. C. (2000). Models of the relationship of stress, depression, and other psychosocial factors to smoking behavior: A comparison of a cohort of students in grades 6 and 8. Preventive Medicine, 30, 463–477.
La Greca, A. M., Bearman, K. J., & Moore, H. (in press). Peer relations. In R. T. Brown (Ed.), Handbook of pediatric psychology in school settings. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Madan-Swain, A., Brown, R. T., Foster, M. A., Vega, R., Byars, K., Rodenberger, W., et al. (2000). Identity in adolescent survivors of childhood cancer. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 25, 105–115.
Mann, S. L., Peterson, A. V., Jr., Marek, P. M., & Kealey, K. A. (2000). The Hutchinson smoking prevention project trial: Design and baseline characteristics. Preventive Medicine, 30, 485–495.
Milich, R., & Kramer, J. (1985). Reflection on impulsivity: An empirical investigation of impulsivity as a construct. In K. Gadow & I. Bialer (Eds.), Advances in learning and behavioral disabilities (Vol. 3, pp. 57–94). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Parker, V., Sussman, S., Crippens, D., Elder, P., & Scholl, D. (1998). The relationship of ethnic identification with cigarette smoking among US urban African American and Latino youth: A pilot study. Ethnicity and Health, 3, 135–143.
Petraitis, J., Flay, B. R., & Miller, T. Q. (1995). Reviewing theories of adolescent substance use: Organizing pieces of the puzzle. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 67–86.
Rivo, M. L., Kofie, V., Schwartz, E., Levy, M. E., & Tuckson, R. V. (1989). Comparisons of Black andWhite smoking-attributable mortality, morbidity, and economic costs in the District of Columbia. Journal of the National Medical Association, 81, 1125–1130.
Skara, S., Sussman, S., & Dent, C. W. (2001). Predicting regular cigarette use among continuation high school students. American Journal of Health Behavior, 25, 147–156.
Stacy, A. W., Flay, B. R., Sussman, S., Brown, S., Santi, S., & Bent, J. A. (1990). Convergent validity of alternative self-report indices of smoking among adolescents. Psychological Assessment, 2442–448.
Stacy, A. W., Sussman, S., Dent, C. W., Burton, D., & Flay, B. R. (1992). Moderators of peer social influence in adolescent smoking. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 18, 163–172.
Sussman, S., Dent, C. W., Burton, D., Stacy, A. W., & Flay, B. R. (1995). Developing school-based tobacco use prevention and cessation programs. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sussman, S., Dent, C. W., Severson, H. H., Burton, D., & Flay, B. R. (1998). Self-initiated quitting among adolescent smokers. Preventive Medicine, 27, A19–A28.
Sussman, S., Dent, C. W., Stacy, A. W., Burciaga, C., Raynor, A., Turner, G. E., et al. (1990). Peer group association and adolescent tobacco use. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 99, 349–352.
Sussman, S., Dent, C. W., Stacy, A. W., Burton, D., & Flay, B. R. (1995). Psychosocial predictors of health risk factors in adolescents. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 20, 91–108.
Tolson, J. M., & Urberg, K.A. (1993). Similarity between adolescent best friends. Journal of Adolescent Research, 8, 274–288.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (1994). Preventing tobacco use among young people: A report of the surgeon general. Atlanta, GA: Author, U.S. Government Printing Office No. 017-001-00491 ‐ 0.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2000). Reducing tobacco use: A report of the surgeon general. Atlanta, GA: Author, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuemmeler, B.F., Taylor, L.A.(., Metz, A.E. et al. Risk-Taking and Smoking Tendency Among Primarily African American School Children: Moderating Influences of Peer Susceptibility. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings 9, 323–330 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020743102967
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020743102967