Abstract
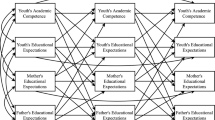
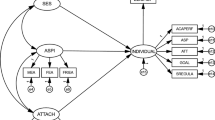
In this study a mediational model was constructed to examine relationships between refined measures of childhood and adolescent social capital and the aspirations of adolescents with varying academic capital and from differing social status and ethnic backgrounds. Longitudinal data were collected from 460 16-year-old Australians and their parents from Anglo-Australian, Greek, and Southern Italian groups. Using partial least squares path modeling the findings suggest: (a) family background, childhood social and academic capital, and adolescents' social capital combine to have medium to large associations with adolescents' aspirations, and that the associations are larger for educational aspirations than for occupational aspirations and stronger for males than for females; (b) the mediational model is more successful in explaining family background differences in educational aspirations than variations in occupational aspirations; and (c) after taking into account social and academic capital, Greek males continue to have higher occupational aspirations than do Anglo-Australian and Southern Italian males, and sons of fathers with high social status continue to have higher occupational aspirations than do other male adolescents. The investigation indicates that within encompassing family backgrounds, differences in educational outcomes should be examined in relation to children's and parents' perceptions of social and cultural capital and to variations in children's academic capital.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer, Melanie & Blau, Judith R. (1993). Class formation in the nineteenth century: The case of the middle class. In J. Blake & J. Hagen (Eds.), Annual review of sociology (Vol. 19). Palo Alto, CA: Annual Reviews, pp. 17–41.
Australian Council for Educational Research (1976). Classroom achievement test in mathematics. Melbourne: Author.
Australian Council for Educational Research (1976). Primary reading survey tests. Melbourne: Author.
Bernstein, Basil B. (1977). Class, codes and control. Towards a theory of educational transmissions (Vol. 3). London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Bourdieu, Pierre (1984). Distinction: A social critique of the judgement of taste. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Bourdieu, Pierre (1988). Homo academicus. Cambridge, U.K.: Polity Press.
Broaded, C. Montgomery (1997). The limits and possibilities of tracking: Some evidence from Taiwan. Sociology of Education, 70, 36–53.
Bronfenbrenner, Urie & Ceci, Stephen J. (1994). Nature-nurture reconceptualization in development perspective: A bioecological model. Psychological Review, 101, 568–586.
Carr, Rhoda V., Wright, James D.,& Brody, Charles J. (1996). Effects of high school work experience a decade later: Evidence from the National Longitudinal Survey. Sociology of Education, 69, 66–81.
Clifton, Rodney A. (1994). Race and ethnicity in education. In T. Husén & T. N. Postlethwaite (Eds.), The international encyclopedia of education. Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon, pp. 4891–4896.
Clifton, Rodney A., Williams, Trevor, & Clancy, Jeff (1991). The academic attainmentof ethnic groups in Australia: A social psychological model. Sociology of Education, 64, 111–126.
Cohen, Jacob (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 155–159.
Coleman, James S. (1988). Social capital in the creation of human capital. American Journal of Sociology, 94, 95–120.
Coleman, James S. (1993). The rational reconstruction of society. American Sociological Review, 58, 1–15.
Darling, Nancy & Steinberg, Laurence (1993). Parenting style as context: An integrative model. Psychological Bulletin, 113, 487–496.
Davies, Scott (1995). Reproduction and resistance in Canadian high schools: An empirical analysis. British Journal of Sociology, 46, 662–687.
Entwisle, Doris R. & Astone, Nan M. (1994). Some practical guidelines for measuring youth's race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status. Child Development, 65, 1520–1540.
Fejgin, Naomi (1995). Factors contributing to the academic excellence of American Jewish and Asian students. Sociology of Education, 68, 18–30.
Fletcher, Anne C., Darling, Nancy E., Steinberg, Laurence, & Dornbusch, Sanford M.(1995). The company they keep: Relation of adolescents' adjustment and behavior to their friends' perceptions of authoritative parenting in the social network. Developmental Psychology, 31, 300–310.
Hanson, Sandra L. (1994). Lost talent: Unrealized educational aspirations and expectations among U.S. youths. Sociology of Education, 67, 159–183.
Hauser, Robert M. & Anderson, Douglas K. (1991). Post-high school plans and aspirations of Black and White high school seniors: 1976–86. Sociology of Education, 64, 263–277.
Hossler, Don & Stage, Frances K. (1992). Family and high school experience influences on the postsecondary educational plans of ninth-grade students. American Educational Research Journal, 29, 425–451.
Jones, F. Lancaster (1989). Occupational prestige in Australia: A new scale. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Sociology, 25, 187–199.
Kalmijn, Matthijs & Kraaykamp, Gerbert (1996). Race, cultural capital, and schooling:An analysis of trends in the United States. Sociology of Education, 69, 22–34.
Kellaghan, Thomas, Sloane, K., Alvarez, B., & Bloom, Benjamin S. (1993). The home environment and school learning: Promoting parental involvement in the education of children. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Kim, U., Triandis, H. C., Kagitcibasi, C., Choi, S-C., & Yoon, G. (1994). Individualism and collectivism: Theory, method and applications. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Lamb, Stephen, Polesel, John, & Teese, Richard (1995). Where do they go? An evaluation of sources of data used for the monitoring of students' destinations and other educational outcomes in Australia. Canberra: Australian Government Printing Service.
Lubinski, David & Humphreys, Lloyd G. (1990). Assessing spurious "moderator effects": Illustrated substantively with the hypothesized ("synergistic") relation between spatial and mathematical ability. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 385–393.
Marini, Margaret M., Fan, Pi-Ling Fan, Finley, Erica, & Beutel, Ann M. (1996). Gender and job values. Sociology of Education, 69, 49–65.
Marjoribanks, Kevin (1994). Families, schools and children's learning: A study of children's learning environments. International Journal of Educational Research, 21, 439–555.
McCarthy, Cameron (1988). Rethinking liberal and radical perspectives on racial inequality in schooling: Making the case for nonsynchrony. Harvard Educational Review, 58, 265–279.
Meade, Phil (1983). The educational experience of Sydney high school students.Canberra: Australian Government Printing Service.
Merton, Robert K. (1968). Social theory and social structure. New York: Free Press.
Merton, Robert K. (1976). Sociological ambivalence and other essays. New York: Free Press.
Morgan, Stephen L. (1996). Trends in Black-White differences in educational expectations: 1980–92. Sociology of Education, 69, 308–319.
Plomin, Robert (1995). Genetics and children's experiences in the family. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 36, 33–68.
Raven, J. (1989). The Raven Progressive Matrices: A review of national norming studies and ethnic and socioeconomic variation in the United States. Journal of Educational Measurement, 26, 1–16.
Rumberger, Russell W. (1995). Dropping out of middle school: A multilevel analysis of students and schools. American Educational Research Journal, 32, 583–625.
Saha, Lawrence J. (1985). The legitimacy of early school learning: Occupational orientations, vocational training plans, and educational attainment among urban Australian youth. Sociology of Education, 58, 228–240.
Saha, Lawrence J. (1994). Aspirations and expectations of students. In T. Husén & T. N. Postlethwaite (Eds.), International encyclopedia of education. Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon, pp. 354–358.
Sellin, Norbert & Keeves, John P. (1997). Path analysis with latent variables. In J. P. Keeves (Ed.), Educational research, methodology, and measurement: An international handbook (2nd. ed.).Oxford, U.K.: Pergamon, pp. 633–640.
Singh, Kusum & Hernandez-Gantes, Victor M. (1996). The relation of English language proficiency to educational aspirations of Mexican-American eighth graders. Journal of Early Adolescence, 16, 253–273.
Smetana, Judith G. (1995). Parenting styles and conceptions of parental authority during adolescence. Child Development, 66, 299–316.
Strodtbeck, Fred L. (1961). Family integration, values and achievement. In A. H. Halsey, J. Floud, & C. A. Anderson (Eds.), Education, economy and society. New York: Free Press, pp. 315–347.
Taft, Ronald (1976). Secondary school children of immigrant families in Victoria. In R.K. Browne & D. J. Magin (Eds.), Sociology of education. Melbourne: Macmillan, pp. 303–307.
Teachman, Jay D. (1996). Intellectual skill and academic performance: Do families bias the relationship? Sociology of Education, 69, 35–48.
Tsai, Shu-Ling, Gates, Hill, & Chiu, Hei-Yuan (1994). Schooling Taiwan's women:Educational attainment in the mid-20th century. Sociology of Education, 67, 243–263.
Wang, Margaret C., Haertel, Geneva D., & Walberg, Herbert J. (1993). Toward a knowledge theory of school learning. Review of Educational Research, 63, 249–294.
Wells, Amy S. & Serna, Irene (1996). The politics of culture: Understanding local political resistance to detracking in racially mixed schools. Harvard Educational Review, 66, 93–118.
Wentzel, Kathryn R. (1994). Family functioning and academic achievement in middle school: A socio-emotional perspective. Journal of Early Adolescence, 14, 268–291.
Williams, Trevor, Long, Michael, Carpenter, Peter, & Hayden, Martin (1993). Entering higher education in the 1980s. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marjoribanks, K. Family Background, Social and Academic Capital, and Adolescents' Aspirations: A Mediational Analysis. Social Psychology of Education 2, 177–197 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009602307141
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009602307141