Abstract
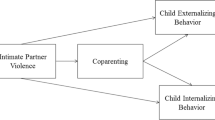
We examined the role of maternal depression and parenting stress in the relationship between intimate partner violence (IPV) and child internalizing and externalizing problems, and explored whether child gender modified these pathways. This secondary analysis used data from the Hawaii Healthy Start Program. Logistic regression models examined the associations between IPV in 1st grade and child internalizing and externalizing behaviors in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd grades. Mediation models used bootstrapping methodology and stratified models examined effect modification. Adjusted models with 214 mothers demonstrated associations between IPV and internalizing (adjusted odds ratios (aOR) = 2.62; 95 % CI 1.11, 6.21) and externalizing (aOR = 4.16; 95 % CI 1.55, 11.19) behaviors. The association with externalizing behaviors was mediated by maternal depression and parenting stress, while internalizing behaviors was mediated by depression only. Stratified models found the association between IPV and externalizing behaviors was significant for girls only. Our results support the importance of multicomponent maternal IPV interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin, R. (1995). Parenting stress index: Professional manual (3rd ed.). Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1981). Behavioral problems and competencies reported by parents of normal and disturbed children aged four through sixteen. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 46(1), 1–82.
Avellar, S., Paulsell, D., Sama-Miller, E., Del Grosso, P., Akers, L., & Kleinman, R. (2014). Home Visiting Evidence of Effectiveness Review: Executive Summary (OPRE Report #2014-59). Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Washington, DC.
Bair-Merritt, M., Jennings, J., Chen, R., Burrell, L., McFarlane, E., Fuddy, L., & Duggan, A. (2010). Reducing maternal intimate partner violence after the birth of a child: a randomized controlled trial of the Hawaii Healthy Start Home Visitation Program. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 164(1), 16–23.
Baldry, A. (2003). Bullying in schools and exposure to domestic violence. Child Abuse & Neglect, 27(7), 713–732.
Cascardi, M., & O’Leary, K. (1992). Depressive symptomatology, self-esteem, and self blame in battered women. Journal of Family Violence, 7(4), 249–259.
Conger, K., Rueter, M., & Conger, R. (2000). The role of economic pressure in the lives of parents and their adolescents: the family stress model. In L. Crockett & R. Silbereisen (Eds.), Negotiating adolescence in times of social change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Davies, P., & Lindsay, L. (2001). Does gender moderate the effects of marital conflict on children? In J. Grych & F. Fincham (Eds.), Interparental conflict and child development: Theory, research and application. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Duggan, A., McFarlane, E., Windham, A., Rohde, C., Salkever, D., Fuddy, L., & Sia, C. (1999). Evaluation of Hawaii’s healthy start program. The Future of Children, 9(1), 66–90.
Duggan, A., Fuddy, L., Burrell, L., Higman, S., McFarlane, E., Windham, A., & Calvin, S. (2004a). Randomized trial of a statewide home visiting program to prevent child abuse: impact in reducing parental risk factors. Child Abuse & Neglect, 28(6), 623–643.
Duggan, A., McFarlane, E., Fuddy, L., Burrell, L., Higman, S., Windham, A., & Sia, C. (2004b). Randomized trial of a statewide home visiting program: impact in preventing child abuse and neglect. Child Abuse & Neglect, 28(6), 597–622.
Duggan, A., Caldera, D., Rodriguez, K., Burrell, L., Rohde, C., & Crowne, S. (2007). Impact of a statewide home visiting program to prevent child abuse. Child Abuse & Neglect, 31(8), 801–827.
Ermentrout, D., Rizo, C., & Macy, R. (2014). “This Is About Me”: feasibility findings from the children’s component of an IPV intervention for justice-involved families. Violence Against Women, 20(6), 653–676.
Evans, S. E., Davies, C., & DiLillo, D. (2008). Exposure to domestic violence: a meta-analysis of child and adolescent outcomes. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 13, 131–140.
Graham-Bermann, S. A., Howell, K. H., Lilly, M., & Devoe, E. (2011). Mediators and moderators of change in adjustment following intervention for children exposed to intimate partner violence. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 26(9), 1815–1833.
Gross, D., Fogg, L., Young, M., Ridge, A., Cowell, J. M., Richardson, R., & Sivan, A. (2006). The equivalence of the Child Behavior Checklist/1 1/2-5 across parent race/ethnicity, income level and language. Psychological Assessment, 18(3), 313–323.
Hayes, A. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis. New York: The Guilford Press.
Holmes, M. (2013). Aggressive behavior of children exposed to intimate partner violence: an examination of maternal mental health, maternal warmth and child maltreatment. Child Abuse & Neglect, 37(8), 520–530.
Holt, S., Buckley, H., & Whelan, S. (2006). The impact of exposure to domestic violence on children and young people: a review of the literature. Child Abuse & Neglect, 32, 797–810.
Home Visiting Research Network (HVRN). (2013). National Home Visiting Research Agenda. Home Visiting Research Network. Retrieved from http://www.hvrn.org/uploads/3/2/1/0/3210553/home_visiting_research_agenda_2013_10_29_final.pdf.
Hungerford, A., Wait, S. K., Fritz, A. M., & Clements, C. M. (2012). Exposure to intimate partner violence and children’s psychological adjustment, cognitive functioning, and social competence: a review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 17(4), 373–382.
Husaini, B. A., Neef, J. A., Harrington, J. B., Hughes, M. D., & Stone, R. H. (1980). Depression in rural communities: validating the CES-D scale. Journal of Community Psychology, 8(1), 20–27.
Iverson, K. M., McLaughlin, K. A., Adair, K. C., & Monson, C. M. (2014). Anger-related dysregulation as a factor linking childhood physical abuse and interparental violence to intimate partner violence experiences. Violence and Victims, 29(4), 564–578.
Kerig, P. K. (1998). Gender and appraisals as mediators of adjustment in children exposed to inter-parental violence. Journal of Family Violence, 13(4), 345–363.
Kernic, M., Wolf, M., Holt, V., McNight, B., Huebner, C., & Rivara, F. (2003). Behavioral problems among children whose mothers are abused by an intimate partner. Child Abuse & Neglect, 27(11), 1231–1246.
Levendosky, A. A., & Graham-Bermann, S. A. (1998). The moderating effects of parenting stress on children’s adjustment in woman-abusing families. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 13(3), 383–397.
Maddoux, J., Symes, L., McFarlane J., Koci, A., Gilroy, H., & Fredland, N. (2014). Problem-solving and mental health outcomes of women and children in the wake of intimate partner violence. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 708198.
Margolin, G. (2005). Children’s exposure to violence: exploring developmental pathways to diverse outcomes. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 20(1), 72–81.
Mayfield, D., McLeod, G., & Hall, P. (1974). The CAGE questionnaire: validation of a new alcoholism screening instrument. American Journal of Psychiatry, 131(10), 1121–1123.
McFarlane, J. M., Groff, J. Y., O’Brien, J. A., & Watson, K. (2003). Behaviors of children who are exposed and not exposed to intimate partner violence: an analysis of 330 Black, White and Hispanic children. Pediatrics, 112(3), e202–e207.
Miller, L. E., Howell, K. H., & Graham-Bermann, S. A. (2014). Developmental changes in threat and self-blame for preschoolers exposed to intimate partner violence (IPV). Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 29(9), 1535–1553.
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). (2008). National Institute of Mental Health Strategic Plan for Research. Retrieved from http://www.nimh.nih.gov/about/strategic-planning-reports/index.shtml#strategic-objective1.
Olds, D. L., Robinson, J., Pettitt, L., Luckey, D. W., Holmberg, J., Ng, R. K., & Henderson, C. R., Jr. (2004). Effects of home visits by paraprofessionals and by nurses: age 4 follow-up results of a randomized trial. Pediatrics, 114(6), 1560–1568.
Owen, A., Thompson, M., & Kaslow, N. (2006). The mediating role of parenting stress in the relation between intimate partner violence and child adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 20(3), 505–513.
Postmus, J. L., Huang, C. C., & Mathisen-Stylianou, A. (2012). The impact of physical and economic abuse on maternal mental health and parenting. Children and Youth Services Review, 34(9), 1922–1928.
Renner, L. M. (2009). Intimate partner violence victimization and parenting stress: assessing the mediating role of depressive symptoms. Violence Against Women, 15(11), 1380–1401.
Shoultz, J., Magnussen, L., Kreidman, N., Oneha, M. F., Iannce-Spencer, C., & Hayashi-Simpliciano, R. (2015). Engaging native Hawaiians and Pilipinos in creating supportive and safe violence-free communities for women through a piloted “talkstory” intervention: implications for program development. Evaluation and Program Planning, 51, 78–84.
Straus, M. A., Hamby, S. L., Boney-McCoy, S., & Sugarman, D. B. (1996). The Revised Conflict Tactics Scales (CTS2): development and preliminary psychometric data. Journal of Family Issues, 17(3), 283–316.
The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). (2006). Behind Closed Doors: The Impact of Domestic Violence on Children. Retrieved from http://www.unicef.org/protection/files/BehindClosedDoors.pdf.
Acknowledgments
Dr Bair-Merritt is funded by a Career Development Award (K23HD057180) sponsored by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The parent study, evaluation of the Hawaii Healthy Start Program, was supported in part by the Federal Maternal and Child Health Bureau (R40MC00029 (formerly MCJ 240637) and R40 MC 00123 (formerly MCJ 240838); The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (18303); The Annie E. Casey Foundation (94–4041); The David and Lucile Packard Foundation (93–6051, 94–7957, 97–8058, and 98–3448); the Hawaii State Department of Health (99-29-J); and the National Institute of Mental Health, Epidemiological Center for Early Risk Behaviors, P30MH38725.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bair-Merritt, M.H., Ghazarian, S.R., Burrell, L. et al. Understanding How Intimate Partner Violence Impacts School Age Children’s Internalizing and Externalizing Problem Behaviors: a Secondary Analysis of Hawaii Healthy Start Program Evaluation Data. Journ Child Adol Trauma 8, 245–251 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40653-015-0066-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40653-015-0066-8