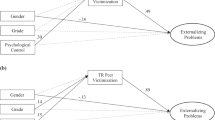
Abstract
Controversy exists with regard to the use of corporal punishment (CP) in childrearing. However, parental aggression toward children is not always physical in nature, and parental disciplinary strategies can also include psychological aggression (PA). Survey data collected from university students were used to examine the impact of aggressive parental discipline strategies experienced in childhood on externalizing problem behaviors in early adulthood. At the bivariate level, both CP and PA in childhood were associated with intimate partner violence perpetration, criminality, and alcohol abuse in early adulthood. In multivariate analyses, childhood CP predicted intimate partner violence perpetration in early adulthood, even after the effects of numerous contextual variables and concurrent protective factors were taken into account. Implications of these findings are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, B. (2008). An analysis of the impact of diverse forms of childhood psychological maltreatment on emotional adjustment in early adulthood. Child Maltreatment, 13(3), 307–312. doi:10.1177/1077559508318394.
American Professional Society on the Abuse of Children. (1995). Psychosocial evaluation of suspected psychological maltreatment in children and practice guidelines. Chicago: American Professional Society on the Abuse of Children.
Baker, A. J. L. (2009). Adult recall of childhood psychological maltreatment: definitional strategies and challenges. Children and Youth Services Review, 31, 703–714. doi:10.1016/j.childyouth.2009.03.001.
Barber, B. K. (1996). Parental psychological control: revisiting a neglected construct. Child Development, 67, 3296–3319. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.1996.tb01915.x.
Barber, B. K., & Harmon, E. L. (2002). Violating the self: Parental psychological control of children and adolescents. In B. K. Barber (Ed.), Intrusive parenting: How psychological control affects children and adolescents (pp. 15–52). Washington: American Psychological Association.
Barry, T. D., Dunlop, S. T., Lochman, J. E., & Wells, K. C. (2009). Inconsistent discipline as a mediator between maternal distress and aggression in boys. Child and Family Behavior Therapy, 31, 1–19. doi:10.1080/07317100802701186.
Baumrind, D. (1997). The discipline encounter: contemporary issues. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 2, 321–335. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(97)00018-9.
Baumrind, D., Larzelere, R. E., & Cowan, P. A. (2002). Ordinary physical punishment: is it harmful? Comment on Gershoff (2002). Psychological Bulletin, 128, 580–589. doi:10.1037//0033-2909.128.4.580.
Bender, H. L., Allen, J. P., McElhaney, K. B., Antonishak, J., Moore, C. M., Kelly, H. O., & Davies, S. M. (2007). Use of harsh physical discipline and developmental outcomes in adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 19, 227–242. doi:10.1017/ 50954579407070125.
Calvete, E., & Orue, I. (2013). Cognitive mechanisms of the transmission of violence: exploring gender differences among adolescents exposed to family violence. Journal of Family Violence, 28, 73–84. doi:10.1007/s10896-012-9472-y.
Canadian Foundation for Children, Youth and the Law v. Canada [Attorney General], 2004, SCC 4 (2004) 1 SC.R., 76.
Clément, M.-È., & Chamberland, C. (2007). Physical violence and psychological aggression towards children: five-year trends in practices and attitudes from two population surveys. Child Abuse & Neglect, 31, 1001–1011. doi:10.1016/jchiabu.2007.04.005.
Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health. (1998). Guidance for effective discipline. Pediatrics, 101, 723–728.
Criminal Code of Canada (1985). R.S., c. C-34, s. 42.
Cuadra, L. E., Jaffe, A. E., Thomas, R., & DiLillo, D. (2014). Child maltreatment and adult criminal behavior: does criminal thinking explain the association? Child Abuse & Neglect, 38, 1399–1408. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.02.005.
Darling, N., & Steinberg, L. (1993). Parenting style as context: an integrative model. Psychological Bulletin, 113, 487–496. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.113.3.487.
Douglas, E. M., & Straus, M. A. (2006). Assault and injury of dating partners by university students in 19 countries and its relation to corporal punishment experienced as a child. European Journal of Criminology, 3, 293–318. doi:10.1177/1477370806065584.
Durrant, J., & Ensom, R. (2012). Physical punishment of children: lessons from 20 years of research. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 184, 1373–1377. doi:10.1503/ cmaj.101314.
Fergusson, D. M., & Lynskey, M. T. (1997). Physical punishment/maltreatment during childhood and adjustment in young adulthood. Child Abuse & Neglect, 21, 617–630. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(97)00021-5.
Gershoff, E. T. (2002). Corporal punishment by parents and associated child behaviors and experiences: a meta-analytic and theoretical review. Psychological Bulletin, 128, 539–579. doi:10.1037//0033-2909.128.4.539.
Glaser, D. (2002). Emotional abuse and neglect (psychological maltreatment): a conceptual framework. Child Abuse & Neglect, 26, 697–714. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(02)00342-3.
Hart, S. N., & Brassard, M. R. (1987). Psychological maltreatment: a major threat to children’s mental health. American Psychologist, 42, 160–165. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.42.2.160.
Kerr, D. C. R., Lopez, N. L., Olson, S. L., & Sameroff, A. J. (2004). Parental discipline and externalizing behavior problems in early childhood: the roles of moral regulation and child gender. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32, 369–383. doi:10.1023/B:JACP.0000030291.72775.96.
Krevans, J., & Gibbs, J. C. (1996). Parents’ use of inductive discipline: relations to children’s empathy and prosocial behavior. Child Development, 67, 3262–3277. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.1996.tb01913.x.
Larzelere, R. E. (2000). Child outcomes of nonabusive and customary physical punishment by parents: an updated literature review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 3, 199–221.
McKee, L., Roland, E., Coffelt, N., Olson, A. L., Forehand, R., Massari, C., & Zens, M. S. (2007). Harsh discipline and child problem behaviors: the roles of positive parenting and gender. Journal of Family Violence, 22, 187–196. doi:10.1007/s10896-007-9070-6.
McLoyd, V. C., & Smith, J. (2002). Physical discipline and behavior problems in African American, European American, and Hispanic children: emotional support as a moderator. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 64, 40–53. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737. 2002.00040.x.
Miller-Perrin, C. L., Perrin, R. D., & Kocur, J. L. (2009). Parental physical and psychological aggression: psychological symptoms in young adults. Child Abuse & Neglect, 33, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2008.12.001.
Newell, P. (2005). The human rights imperative for ending all corporal punishment of children. In S. N. Hart (Ed.), Eliminating corporal punishment: The way forward to constructive child discipline (pp. 25–48). Paris: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
Ponce, A. N., Williams, M. K., & Allen, G. J. (2004). Experience of maltreatment as a child and acceptance of violence in adult intimate relationships: mediating effects of distortions in cognitive schemas. Violence and Victims, 19, 97–108. doi:10.1891/vivi.19.1.97.33235.
Straus, M. A. (1979). Measuring intrafamily conflict and violence: the Conflict Tactics (CT) Scales. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 41, 75–88.
Straus, M. A., & Fauchier, A. (n.d.). International parenting study. Durham, NH: Family Research Laboratory. Retrieved from http://pubpages.unh.edu/~mas2/IPS.htm.
Straus, M. A., & Douglas, E. M. (2004). A short form of the Revised Conflict Tactics Scales, and typologies for severity and mutuality. Violence and Victims, 19(5), 507–520.
Straus, M. A., & Fauchier, A. (2007). Manual for the Dimensions of Discipline Inventory (DDI). Durham, NH: Family Research Laboratory, University of New Hampshire. Retrieved from http://pubpages.unh.edu/~mas2/DD01S12%20Manual.pdf.
Straus, M. A., & Field, C. J. (2003). Psychological aggression by American parents: national data on prevalence, chronicity, and severity. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 65, 795–808. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2003.00795.x.
Straus, M. A., & Kaufman Kantor, G. (1994). Corporal punishment of adolescents by parents: a risk factor in the epidemiology of depression, suicide, alcohol abuse, child abuse, and wife beating. Adolescence, 29, 543–561.
Straus, M. A., Hamby, S. L., Boney-McCoy, S., & Sugarman, D. B. (1996). The Revised Conflict Tactics Scales (CTS2): development and preliminary psychometric data. Journal of Family Issues, 17, 283–316. doi:10.1177/019251396017003001.
Straus, M. A., Hamby, S. L., Boney-McCoy, S., & Sugarman, D. B. (1999). Manual for the Personal and Relationships Profile (PRP). Durham: Family Research Laboratory, University of New Hampshire.
Swinford, S. P., DeMaris, A., Cernkovich, S. A., & Giordano, P. C. (2000). Harsh physical discipline in childhood and violence in later romantic involvements: the mediating role of problem behaviors. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 62, 508–519. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2000.00508.x.
Taillieu, T. L., & Brownridge, D. A. (2013). Aggressive parental discipline experienced in childhood and internalizing problems in early adulthood. Journal of Family Violence, 28, 445–458. doi:10.1007/s10896-013-9513-1.
United Nations (1989). The commission on the rights of a child. Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. Adopted by the General Assembly resolution 44/25, 20 November 1989. Retrieved from http://www.crin.org/docs/treaties/uncrc.asp.
Van Harmelen, A.-L., de Jong, P. J., Glashouwer, K. A., Spinhoven, P., Penninx, B. W. J. H., & Elzinga, B. M. (2010). Child abuse and negative explicit and automatic self-associations: the cognitive scars of emotional maltreatment. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 48, 486–494. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2010.02.003.
Wright, M. O., Crawford, E., & Del Castillo, D. (2009). Childhood emotional maltreatment and later psychological distress among college students: the mediating role of maladaptive schemas. Child Abuse & Neglect, 33, 59–68. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2008.12.007.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by a Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada Graduate Scholarship to Tamara L. Taillieu. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Angele Fauchier and Dr. Murray Straus at the University of New Hampshire for their invaluable assistance in making this research possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taillieu, T.L., Brownridge, D.A. The Impact of Aggressive Parental Discipline Experienced in Childhood on Externalizing Problem Behavior in Early Adulthood. Journ Child Adol Trauma 8, 253–264 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40653-015-0063-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40653-015-0063-y