Abstract
Purpose
Emotional eating is a risk factor for eating pathology across the life- and weight-span. Research demonstrates that negative emotions are a precipitant of emotional eating, particularly among female college students. However, the underlying factors that explain this relationship are unclear. Experiential avoidance, a propensity toward being unwilling to remain in contact with aversive private experiences, may explain the association between negative emotions and emotional eating. The purpose of this study was to examine whether experiential avoidance would mediate the association between negative emotions and emotional eating.
Methods
A sample of 132 women (17.4 % African American, 59.8 % White) completed measures of mood, experiential avoidance and emotional eating. Bias-corrected bootstrapping mediational analyses were conducted.
Results
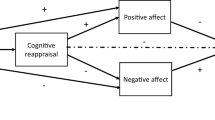
Experiential avoidance mediated the relationship between negative emotions and emotional eating b = −0.21, 95 % BC CI [−0.43, −0.07]. The indirect effect through experiential avoidance accounted for 9 % of the variance, which represents a medium effect (k 2 = 0.09, 95 % BC CI [0.03, 0.18]).
Conclusions
Results suggest that experiential avoidance is important for understanding the relationship between negative emotions and emotional eating and may inform potential strategies for prevention and treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnow B, Kenardy J, Agras W (1995) The Emotional Eating Scale: the development of a measure to assess coping with negative affect by eating. Int J Eat Disord 18:79–90. doi:10.1002/1098-108X
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn, text revision. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington
Lindeman M, Stark K (2001) Emotional eating and eating disorder psychopathology. Eat Disord 9:251–259. doi:10.1080/10640260127552
Evers C, Stok F, Ridder D (2010) Feeding your feelings: emotion regulation strategies and emotional eating. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 36:792–804. doi:10.1177/0146167210371383
van-Strien T, Frijters J, Roosen R, Knuiman-Hijl W, Defares P (1985) Eating behavior, personality traits and body mass in women. Addict Behav 10:333–343. doi:10.1016/0306-4603(85)90029-2
Vandewalle J, Moens E, Beyers W, Braet C (2016) Can we link emotional eating with the emotion regulation skills of adolescents? Psychol Health. doi:10.1080/08870446.2016.1149586
Ganley R (1989) Emotion and eating in obesity: a review of the literature. Int J Eat Disord 8:343–361
Greeno C, Wing R (1994) Stress-induced eating. Psychol Bull 115:444–464. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.115.3.444
Oliver G, Wardle J, Gibson E (2000) Stress and food choice: a laboratory study. J Biobehav Med 62:853–865
Annesi JJ, Mareno N, McEwen K (2016) Psychosocial predictors of emotional eating and their weight-loss treatment-induced changes in women with obesity. Eat Weight Disord 21:289–295. doi:10.1007/s40519-015-0209-9
Ricca V, Castellini G, Fioravanti G, Sauro C, Rotella F, Ravaldi C, Lazzeretti L, Faravelli C (2012) Emotional eating in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Compr Psychiatry 53:245–251. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2011.04.062
Fairburn C, Bohn K (2005) Eating disorder NOS (EDNOS): an example of the troublesome “not otherwise specified” (NOS) category of the DSM-IV. Behav Res Ther 43:691–701. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2004.06.011
Klainberg M, Ewing B, Ryan M (2010) Reducing stress on a college campus. J N Y State Nurses Assoc 1:1–7
Eisenberg D, Nicklett E, Roader K, Kirtz N (2011) Eating disorder symptoms among college students: prevalence, persistence, correlates, and treatment-seeking. J Am Coll Health 59:700–707
Mills J, Polivy J, McFarlane T, Crosby R (2012) The natural course of eating pathology in female university students. Eat Behav 13:297–304. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2012.07.005
American College Health Association (2009) American College Health Association—National College Health Assessment Spring 2008 reference group data report. J Am Coll Health 57:469–479
Lowe M, Annunziato R, Markowtiz J, Didie E, Bellace D, Riddell L, Stice E (2006) Multiple types of dieting prospectively predict weight gain during the freshman year of college. Appetite 47:83–90. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2006.03.160
Stice E, Shaw H (2004) Eating disorder prevention programs: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Bull 130:206–227. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.130.2.206
Pinaquy S, Chabrol H, Simon C, Louvet J, Barbe P (2003) Emotional eating, alexithymia, and binge-eating disorder in obese women. Obes Res 11:195–201. doi:10.1038/oby.2003.31
Racine S, Keel P, Burt S, Sisk C, Neale M, Boker S, Klump K (2013) Exploring the relationship between negative urgency and dysregulated eating: etiologic associations and the role of negative affect. J Abnorm Psychol 122:433–444. doi:10.1037/a0031250
Gross J (2007) Handbook of emotion regulation. Guildford Press, New York
Spoor S, Bekker M, van Strein T, Heck G (2007) Relations between negative affect, coping, and emotional eating. Appetite 48:368–376. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2006.10.005
Haedt-Matt A, Keel P (2011) Revisiting the affect regulation model of binge eating: a meta-analysis of studies using ecological momentary assessment. Psychol Bull 137:660–681. doi:10.1037/a0023660
Haedt-Matt A, Keel P, Racine S, Burt S, Hu J, Boker S, Klump K (2014) Do emotional eating urges regulate affect? Concurrent and prospective associations and implications for risk models of binge eating. Int J Eat Disord. doi:10.1002/eat.22247
Polivy J, Herman CP (1993) Etiology of binge eating: psychological mechanisms. In: Fairburn CG, Wilson GT (eds) Binge eating: nature, assessment, and treatment. Guilford Press, New York, pp 173–205
Hawkins RC, Clement PF (1984) Binge eating: measurement problems and a conceptual model. In: Hawkins RC, Fremouw WJ, Clement PF (eds) The binge purge syndrome: diagnosis, treatment, and research. Springer, New York, pp 229–251
van Strien T, Konttinen H, Homberg J, Engels R, Winkens L (2016) Emotional eating as a mediator between depression and weight gain. Appetite 100:216–224. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2016.02.034
Hayes S, Wilson K, Gifford E, Follette V, Strosahl K (1996) Experiential avoidance and behavioral disorders: a functional dimensional approach to diagnosis and treatment. J Consult Clin Psychol 64:1152–1168. doi:10.1037/0022006X.64.6.1152
Hayes S, Strosahl K, Wilson KG (1999) Acceptance and commitment therapy: an experiential approach to behavior change. Guilford Press, New York
Folkman S, Lazarus RS, Gruen RJ, DeLongis A (1986) Appraisal, coping, health status, and psychological symptoms. J Personal Soc Psychol 50:571–579
Karekla M, Panayiotou G (2011) Coping and experiential avoidance: unique or overlapping constructs? J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 42:163–170. doi:10.1016/j.jbtep.2010.10.002
Kashdan T, Barrios V, Forsyth J, Steger M (2006) Experiential avoidance as a generalized psychological vulnerability: comparisons with coping and emotion regulation strategies. Behav Res Ther 44:1301–1320. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2005.10.003
Hayes S, Strosahl K, Wilson KG (2012) Acceptance and commitment therapy: an experiential approach to behavior change, 2nd edn. Guilford Press, New York
Fledderus M, Bohlmeijer E, Pieterse M (2010) Does experiential avoidance mediate the effects of maladaptive coping styles on psychopathology and mental health. Behav Modif 34:503–519. doi:10.1177/0145445510378379
Rawal A, Park RJ, Williams JMG (2010) Rumination, experiential avoidance, and dysfunctional thinking in eating disorders. Behav Res Ther 48:851–859. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2010.05.009
Hayes S, Luoma J, Bond F, Masuda A, Lillis J (2006) Acceptance and commitment therapy: model, processes and outcomes. Behav Res Ther 44:1–25. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2005.06.006
Cowdrey F, Park R (2012) The role of experiential avoidance, rumination, and mindfulness in eating disorders. Eat Behav 13:100–105. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2012.01.001
Hayaki J (2009) Negative reinforcement eating expectancies, emotion dysregulation, and symptoms of bulimia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord 42:552–556. doi:10.1002/eat.20646
Forman E, Butryn M, Hoffman K, Herbert J (2009) An open trial of acceptance-based behavioral intervention for weight loss. Cogn Behav Pract 16:223–235. doi:10.1016/j.cbpra.2008.09.005
Kingston J, Clarke S, Reminginton B (2010) Experiential avoidance and problematic behavior: a mediation analysis. Behav Modif 34:145–163. doi:10.1177/0145445510362575
Mendes AL, Ferreira C, Marta-Simoes J (2016) Experiential avoidance versus decentering abilities: the role of different emotional processes on disordered eating. Eat Weight Disord. doi:10.1007/s40519-016-0291-7
Evers C, Adriaanse M, Ridder D, Huberts J (2013) Good mood food. Positive emotion as a neglected trigger for food intake. Appetite 68:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2013.04.007
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A (1988) Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 54:1063–1070. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
Gamez W, Chmielewski M, Ruggero C, Kotov R, Watson D (2011) Development of a measure of experiential avoidance: the multidimensional experiential avoidance questionnaire. Psychol Assess 23:692–713. doi:10.1037/a0023242
Bond FW, Hayes SC, Baer RA, Carpenter KC, Guenole N, Orcutt HK, Waltz T, Zettle RD (2011) Preliminary psychometric properties of the acceptance and action questionnaire–II: a revised measure of psychological flexibility and acceptance. Behav Ther 42:676–688. doi:10.1016/j.beth.2011.03.007
Ozier A, Kendrick O, Knol L, Leeper J, Perko M, Burnham J (2007) The EADES (Eating and Appraisal Due to Emotions and Stress) Questionnaire: development and validation. J Am Diet Assoc 107:619–628. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2007.01.004
Keith TZ (2006) Multiple regression and beyond. Allyn & Bacon, Boston
Hayes K (2013) Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis. Guilford Press, New York
Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986) The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173
MacKinnon D, Lockwood C, Williams J (2004) Confidence limits for the indirect effect: distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivar Behav Res 39:99–128. doi:10.1207/s15327906mbr3901_4
Preacher K, Hayes A (2008) Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 40:879–891. doi:10.3758/BRM.40.3.879
Preacher K, Hayes A (2004) SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 36:717–731
Ozier A, Kendrick O, Leeper J, Knol L, Perko M, Burnham J (2008) Overweight and obesity are associated with emotion- and stress-related eating as measured by the eating and appraisal due to emotions and stress questionnaire. J Am Diet Assoc 103:49–56
Crawford J, Henry J (2004) The positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS): construct validity, measurement properties and normative data in a large non-clinical sample. Br J Clin Psychol 43:245–265
Preacher KJ, Kelley K (2011) Effect sizes measures for mediation models: quantitative strategies for communicating indirect effects. Psychol Methods 16(2):93–115
Safer DL, Telch CF, Chen EY (2009) Dialectical behavior therapy for binge eating and bulimia. Guilford Press, New York
Juarascio A, Shaw J, Forman E, Timko A, Herbert J, Butryn M, Lowe M (2013) Acceptance and commitment therapy as a novel treatment for eating disorders: an initial test of efficacy and mediation. Behav Modif 37:459–489. doi:10.1177/0145445513478633
Danitz S, Orsillo S (2014) The mindful way through the semester: an investigation of the effectiveness of an acceptance-based behavioral therapy program on psychological wellness in first-year students. Behav Modif 38:549–566. doi:10.1177/0145445513520218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Litwin, R., Goldbacher, E.M., Cardaciotto, L. et al. Negative emotions and emotional eating: the mediating role of experiential avoidance. Eat Weight Disord 22, 97–104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0301-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0301-9