Abstract
Objective
To develop and validate INCLEN Diagnostic Tool for Autism Spectrum Disorder (INDT-ASD).
Design
Diagnostic test evaluation by cross sectional design
Setting
Four tertiary pediatric neurology centers in Delhi and Thiruvanthapuram, India.
Methods
Children aged 2–9 years were enrolled in the study. INDT-ASD and Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) were administered in a randomly decided sequence by trained psychologist, followed by an expert evaluation by DSM-IV TR diagnostic criteria (gold standard).
Main outcome measures
Psychometric parameters of diagnostic accuracy, validity (construct, criterion and convergent) and internal consistency.
Results
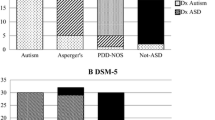
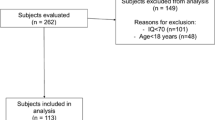
154 children (110 boys, mean age 64.2 mo) were enrolled. The overall diagnostic accuracy (AUC=0.97, 95% CI 0.93, 0.99; P<0.001) and validity (sensitivity 98%, specificity 95%, positive predictive value 91%, negative predictive value 99%) of INDT-ASD for Autism spectrum disorder were high, taking expert diagnosis using DSM-IV-TR as gold standard. The concordance rate between the INDT-ASD and expert diagnosis for’ ASD group’ was 82.52% [Cohen’s κ=0.89; 95% CI (0.82, 0.97); P=0.001]. The internal consistency of INDT-ASD was 0.96. The convergent validity with CARS (r = 0.73, P= 0.001) and divergent validity with Binet-Kamat Test of intelligence (r = −0.37; P=0.004) were significantly high. INDT-ASD has a 4-factor structure explaining 85.3% of the variance.
Conclusion
INDT-ASD has high diagnostic accuracy, adequate content validity, good internal consistency high criterion validity and high to moderate convergent validity and 4-factor construct validity for diagnosis of Autistm spectrum disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volkmar F, State M, Klin A. Autism and autism spectrum disorders: diagnostic issues for the coming decade. J Psychol Psychiatry. 2009; 50:108–115.
The International Classification of Disease (ICD-10): Classification of Mental and Behavioral Disorders. Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines: World Health Organization, Geneva; 2002.
American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th ed, text rev.) (DSM-IV-TR): Washington, DC; 2000.
Mandy WP, Charman T, Skuse DH. Testing the construct validity of proposed criteria for DSM-5 autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012; 51:41–50.
Frazier TW, Youngstrom EA, Speer L, Embacher R, Law P, Constantino J, et al. Validation of proposed DSM-5 criteria for autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012; 51:28–40.
Bakare MO, Munir KM. Excess of non-verbal cases of autism spectrum disorders presenting to orthodox clinical practice in Africa — a trend possibly resulting from late diagnosis and intervention. S Afr J Psychiatr. 2011; 17:118–120.
Sell NK, Giarelli E, Blum N, Hanlon AL, Levy SE. A comparison of autism spectrum disorder DSM-IV criteria and associated features among African American and white children in Philadelphia County. Disabil Health J. 2012; 5:9–17.
Lord C, Petkova E, Hus V, Gan W, Lu F, Martin DM, et al. A multisite study of the clinical diagnosis of different autism spectrum disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012; 69:306–313.
de Bosset V, Froehlich F, Rey JP, Thorens J, Schneider C, Wietlisbach V, et al. Do explicit appropriateness criteria enhance the diagnostic yield of colonoscopy? Endoscopy. 2002; 34:360–368.
Lord C, Risi S, Lambrecht L, Cook EH Jr, Leventhal BL, DiLavore PC, et al. The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: a standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. J Autism Dev Disord. 2000; 30:205–223.
Lord C, Rutter M, Le Couteur A. Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: a revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 1994;24:659–685.
Fischer RG. The Delphi method: a description, review and criticism. J Acad Librarianship. 1978:64–70.
Fitzpatrick R, Davey C, Buxton MJ, Jones DR. Evaluating patient-based outcome measures for use in clinical trials. Health Technol Assess. 1998; 2:1–74.
Schopler E, Reichler RJ, DeVellis RF, Daly K. Toward objective classification of childhood autism: Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). J Autism Dev Disord. 1980; 10:91–103.
McColl E, Jacoby A, Thomas L, Soutter J, Bamford C, Steen N, et al. Design and use of questionnaires: a review of best practice applicable to surveys of health service staff and patients. Health Technol Assess. 2001; 5:1–256.
Russell AJ, Mataix-Cols D, Anson MAW, Murphy DGM. Psychological treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder in people with autism spectrum disorders — A pilot study. Psychother Psychosom. 2009; 78:59–61.
Kulsrestha SK. Stanford Binet Intelligence Scale and Manual. Hindi Adaptation (Under third revision) Allahabad: Manas Seva Sansthan Prakashan; 1971.
Doll EA. A generic scale of social maturity. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1935; 5:180–188.
Volkmar FR, Cicchetti DV, Dykens E, Sparrow SS, Leckman JF, Cohen DF. An evaluation of the Autism Behavior Checklist. J Autism Dev Disord. 1988; 18:81–97.
Spitzer RL, Siegel B. The DSM-III-R field trial of pervasive developmental disorders. J Am Acad Child Adoles Psychiatry. 1990; 29:855–862.
Volkmar FR, Klin A, Siegal B, Szatmari P, Lord C, Campbell M, et al. Field trial for autistic disorder in DSMIV. Am J Psychiatry. 1994; 151:1361–1367.
McPartland JC, Reichow B, Volkmar FR. Sensitivity and specificity of proposed DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012; 51:368–383.
Ronald A, Happe F, Bolton P, Butcher LM, Price TS, Wheelwright S, et al. Genetic heterogeneity between the three components of the autism spectrum: A twin study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006; 45:691–699.
Ronald A, Happe F, Price TS, Baron-Cohen S, Plomin R. Phenotypic and genetic overlap between autistic traits at the extremes of the general population. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2006; 45:1206–1214.
Tanguay PE, Robertson J, Derrick A. A dimensional classiûcation of autism spectrum disorder by social communication domains. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998; 37:271–277.
Tadevosyan-Leyfer O, Dowd M, Mankoski R, Winklosky B, Putnam S, McGrath L, et al. A principal component analysis of the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2003; 42:864–872.
Charman T, Taylor E, Drew A, Cockerill H, Brown JA, Baird G. Outcome at 7 years of children diagnosed with autism at age 2: predictive validity of assessments conducted at 2 and 3 years of age and pattern of symptom change over time. Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2005; 46:500–513.
Sigman M, McGovern CW. Improvement in cognitive and language skills from preschool to adolescence in autism. J Autism Dev Disord. 2005; 35:15–23.
Van Lang NDJ, Boomsma A, Sytema S, de Bildt AA, Kraijer DW, Ketelaars C, et al. Structural equation analysis of a hypothesized symptom model in the autism spectrum. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2006; 47:37–44.
Boomsma A, Van Lang NDJ, De Jonge MV, De Bildt AA, Van Engeland H, Minderaa RB. A new symptom model for autism cross-validated in an independent sample. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2008; 49:809–816.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
INCLEN STUDY GROUP: Core Group: Alok Thakkar, Arun Singh, Gautam Bir Singh, Manju Mehta, Manoja K Das, Nandita Babu, Preveen Suman, Ramesh Konanaki, Rohit Saxena, Satinder Aneja, Savita Sapre, Sharmila Mukherjee, Sunanda K. Reddy, Tanuj Dada. Extended Group: A.K Niswade, Archisman Mohapatra, Arti Maria, Atul Prasad, B.C Das, Bhadresh Vyas, G.V.S Murthy, Gaurie M. Devi, Harikumaran Nair, J.C Gupta, K.K Handa, Leena Sumaraj, Madhuri Kulkarni, Muneer Masoodi, Poonam Natrajan, Rashmi Kumar, Rashna Dass, Rema Devi, Sandeep Bavdekar, Santosh Mohanty, Saradha Suresh, Shobha Sharma, Sujatha S. Thyagu, Sunil Karande, T.D Sharma, Vinod Aggarwal, Zia Chaudhary.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juneja, M., Mishra, D., Russell, P.S.S. et al. INCLEN diagnostic tool for autism spectrum disorder (INDT-ASD): Development and validation. Indian Pediatr 51, 359–365 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-014-0417-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-014-0417-9