Abstract
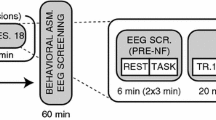
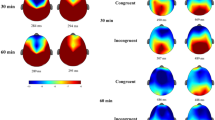
Building on recent favourable outcomes using working memory (WM) training, this study examined the behavioural and physiological effect of concurrent computer-based WM and inhibition training for children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (AD/HD). Using a double-blind active-control design, 29 children with AD/HD completed a 5-week at-home training programme and pre- and post-training sessions which included the assessment of overt behaviour, resting EEG, as well as task performance, skin conductance level and event-related potentials (ERPs) during a Go/Nogo task. Results indicated that after training, children from the high-intensity training condition showed reduced frequency of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms. Although there were trends for improved Go/Nogo performance, increased arousal and specific training effects for the inhibition-related N2 ERP component, they failed to reach standard levels of statistical significance. Both the low- and high-intensity conditions showed resting EEG changes (increased delta, reduced alpha and theta activity) and improved early attention alerting to Go and Nogo stimuli, as indicated by the N1 ERP component, post-training. Despite limitations, this preliminary work indicates the potential for cognitive training that concurrently targets the interrelated processes of WM and inhibition to be used as a treatment for AD/HD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Given the exploratory nature of this study and the small number of participants involved, we felt that it was also appropriate to report post-hoc tests on the other variables that relate to the primary hypotheses, even though the trends for an interaction did not reach the standard levels of significance. Accordingly, these results need to be interpreted with some caution.
References
Achenbach TM, Conners CK, Quay HC, Verhulst FC, Howell CT (1989) Replication of empirically derived syndromes as a basis for taxonomy of child/adolescent psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 17:299–323
APA (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Barkley RA (1997) Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull 121:65–94
Barkley RA (1999) Response inhibition in Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 5:177–184
Barry RJ, Sokolov EN (1993) Habituation of phasic and tonic components of the orienting reflex. Int J Psychophysiol 15:39–42
Barry RJ, Clarke AR, Johnstone SJ (2003a) A review of electrophysiology in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: I. Qualitative and quantitative electroencephalography. Clin Neurophysiol 114:171–183
Barry RJ, Johnstone SJ, Clarke AR (2003b) A review of electrophysiology in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: II. Event-related potentials. Clin Neurophysiol 114:184–198
Brandeis D, Van Leeuwen TH, Rubia K et al (1998) Neuroelectric mapping reveals precursor of stop failures in children with attention deficits. Behav Brain Res 94:111–125
Broyd SJ, Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ et al (2005) The effect of methylphenidate on response inhibition and the event-related potential of children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Int J Psychophysiol 58:47–58
Clark JM (1996) Contributions of inhibitory mechanisms to unified theory in neuroscience and psychology. Brain Cogn 30:127–152
Clarke AR, Barry RJ, Bond D, McCarthy R, Selikowitz M (2002) Effects of stimulant medications on the EEG of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychopharmacology 164:277–284
Clarke AR, Barry RJ, McCarthy R, Selikowitz M, Johnstone SJ (2007) Effects of stimulant medications on the EEG of girls with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin Neurophysiol 118:2700–2708
Conners CK (1997) Conners parent rating scale revised. Abbott Laboratories, Chicago
Dimoska A, Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ, Clarke AR (2003) Inhibitory motor control in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Event-related potentials in the stop-signal paradigm. Biol Psychiatry 54:1345–1354
Duffy E (1962) Activation and behavior. Wiley, New York
Geurts HM, Verte S, Oosterlaan J, Roeyers H, Sergeant JA (2005) ADHD subtypes: do they differ in their executive functioning profile? Arch Clin Neuropsychol 20:457–477
Hasher L, Zacks RT (1988) Working memory, comprehension, and aging: a review and a new view. In: Bower GH (ed) The psychology of learning and motivation. Academic Press, San Diego
Jodo E, Kayama Y (1992) Relation of a negative ERP component to response inhibition in a Go/No-go task. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 82:477–482
Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ (1996) Auditory event-related potentials to a two-tone discrimination paradigm in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Res 64:179–192
Johnstone SJ, Pleffer CB, Barry RJ, Clarke AR, Smith JL (2005) Development of inhibitory processing during the Go/NoGo task: a behavioral and event-related potential study of children and adults. J Psychophysiol 19:11–23
Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ, Clarke AR (2007) Behavioural and ERP indices of response inhibition during a Stop-signal task in children with two subtypes of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Int J Psychophysiol 66:37–47
Kida N, Oda S, Matsumura M (2005) Intensive baseball practice improves the Go/No go reaction time, but not the simple reaction time. Cogn Brain Res 22:257–264
Kimko HC, Cross JT, Abernethy DR (1999) Pharmacokinetics and clinical effectiveness of methylphenidate. Clin Pharmacokinet 37:457–470
Klingberg T, Forssberg H, Westerberg H (2002) Training of working memory in children with ADHD. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 24:781–791
Klingberg T, Fernell E, Olesen PJ et al (2005) Computerized training of working memory in children with ADHD—a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 44:177–186
Kotwal DB, Burns WJ, Montgomery DD (1996) Computer-assisted cognitive training for ADHD: a case study. Behav Modif 20:85–96
Lawrence CA, Barry RJ, Clarke AR et al (2005) Methylphenidate effects in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: electrodermal and ERP measures during a continuous performance task. Psychopharmacology 183:81–91
Lazzaro I, Gordon E, Li W et al (1999) Simultaneous EEG and EDA measures in adolescent attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Int J Psychophysiol 34:123–134
Magee CA, Clarke AR, Barry RJ, McCarthy R, Selikowitz M (2005) Examining the diagnostic utility of EEG power measures in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin Neurophysiol 116:1033–1040
Mannuzza S, Klein RG, Moulton Iii JL (2008) Lifetime criminality among boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a prospective follow-up study into adulthood using official arrest records. Psychiatry Res 160:237–246
McNab F, Leroux G, Strand F et al (2008) Common and unique components of inhibition and working memory: an fMRI, within-subjects investigation. Neuropsychologia 46:2668–2682
Mitchell P (2007) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents in New South Wales—2007. Final report of the Special Review. Sydney, Clinical Excellence Commission
Naatanen R, Picton T (1987) The N1 wave of the human electric and magnetic response to sound: a review and an analysis of the component structure. Psychophysiology 24:375–425
Neale MD (1999) Neale analysis of reading ability. ACER, Melbourne
Nieuwenhuis S, Yeung N, Van Den Wildenberg W, Ridderinkhof KR (2003) Electrophysiological correlates of anterior cingulate function in a go/no-go task: effects of response conflict and trial type frequency. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3:17–26
Oosterlaan J, Sergeant JA (1996) Inhibition in ADHD, aggressive, and anxious children: a biologically based model of child psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 24:19–36
Pennington BF, Ozonoff S (1996) Executive functions and developmental psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 37:51–87
Pliszka SR, Liotti M, Woldorff MG (2000) Inhibitory control in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: event-related potentials identify the processing component and timing of an impaired right-frontal response-inhibition mechanism. Biol Psychiatry 48:238–246
Quay HC (1997) Inhibition and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Abnorm Child Psychol 25:7–13
Raven JC (1989) Standard progressive matrices Australian manual. Australian Council for Education Research, Victoria
Roberts RJ, Pennington BF (1996) An interactive framework for examining prefrontal cognitive processes. Dev Neuropsychol 12:105–126
Roodenrys S (2006) Working memory function in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. In: Packiam Alloway T, Gathercole SE (eds) Working memory and neurodevelopmental condition. Psychology Press, Hove
Rubia K, Overmeyer S, Taylor E et al (1999) Hypofrontality in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder during higher-order motor control: a study with functional MRI. Am J Psychiatry 156:891–896
Satterfield JH, Dawson ME (1971) Electrodermal correlates of hyperactivity in children. Psychophysiology 8:191–197
Satterfield JH, Schell AM, Backs RW, Hidaka KC (1984) A cross-sectional and longitudinal study of age effects of electrophysiological measures in hyperactive and normal children. Biol Psychiatry 19:973–990
Semlitsch HV, Anderer P, Schuster P, Presslich OA (1986) A solution for reliable and valid reduction of ocular artifacts, applied to the P300 ERP. Psychophysiology 23:695–703
Sergeant J (2000) The cognitive-energetic model: an empirical approach to Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:7–12
Smith JL, Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ (2003) Aiding diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and its subtypes: discriminant function analysis of event-related potential data. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 44:1067–1075
Smith JL, Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ (2004) Inhibitory processing during the Go/NoGo task: an ERP analysis of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1320–1331
Smith JL, Johnstone SJ, Barry RJ (2007) Response priming in the Go/NoGo task: the N2 reflects neither inhibition nor conflict. Clin Neurophysiol 118:343–355
Swanson JM, Elliott GR, Greenhill LL et al (2007) Effects of stimulant medication on growth rates across 3 years in the MTA follow-up. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:1015–1027
Verbruggen F, Logan GD (2008) Automatic and controlled response inhibition: associative learning in the Go/No-Go and stop-signal paradigms. J Exp Psychol Gen 137:649–672
Westwood PS (1979) South Australian spelling test. Education Department of South Australia Adelaide
Young SE, Friedman NP, Miyake A et al (2009) Behavioral disinhibition: liability for externalizing spectrum disorders and its genetic and environmental relation to response inhibition across adolescence. J Abnorm Psychol 118:117–130
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by a small internal grant from the University of Wollongong.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnstone, S.J., Roodenrys, S., Phillips, E. et al. A pilot study of combined working memory and inhibition training for children with AD/HD. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord 2, 31–42 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-009-0017-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-009-0017-z