Abstract
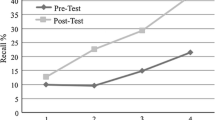
The current study investigated the inclusion of goal-based story events in the online story narrations of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), as compared with their peers, and explored the effect of stimulant medication on the narrations in children with ADHD. Children completed a narration task on two separate occasions. Children with ADHD (n = 17) completed one narration on medication and the other one on placebo. Results indicated that narrations of comparison children (n = 25) were significantly more likely than narrations of children with ADHD to include the story’s positive outcome, completion of the story’s overall goal, and specific attempts linked to the goal. Children with ADHD included a larger total number of clauses in their narrations when on stimulant medication than when on placebo, but medication showed no significant effects for any other variables. Results indicate that stimulant medication may not be effective at reducing goal-based story comprehension deficits in children with ADHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abikoff, H., Nissley-Tsiopinis, J., Gallagher, R., Zambenedetti, M., Seyffert, M., Boorady, R., et al. (2009). Effects of MPH-OROS on the organizational, time management, and planning behaviors of children with ADHD. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 48, 166–175.
Ackerman, B. P., Silver, D., & Glickman, I. (1990). Concept availability in the causal inferences by children and adults. Child Development, 61, 230–246.
Aman, C. J., Roberts, R. J., Jr., & Pennington, B. F. (1998). A neuropsychological examination of the underlying deficit in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Frontal lobe versus right parietal lobe theories. Developmental Psychology, 34, 956–969.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Barkley, R. A. (2006). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, 3rd ed.: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Berthiaume, K. S. (2006). Story comprehension and academic deficits in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: What is the connection? School Psychology Review, 35, 309–323.
Berthiaume, K. S., Lorch, E. P., & Milich, R. (2009). Getting clued in: Inferential processing and comprehension monitoring among boys with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders (in press).
Carlson, C. L., Pelham, W. E., Milich, R., & Dixon, J. (1992). Single and combined effects of methylphenidate and behavior therapy on the classroom performance of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 213–232.
Carte, E. T., Nigg, J. T., & Hinshaw, S. P. (1996). Neuropsychological functioning, motor speed, and language processing in boys with and without ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 24, 481–498.
Chandler, M., Greenspan, S., & Barenboim, C. (1974). Assessment and training of role-taking and referential communication skills in institutionalized emotionally disturbed children. Developmental Psychology, 10, 546–553.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 155–159.
Conners, C. K. (1997). Conners’ rating scales—revised: Technical manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi-Health Systems.
Denney, C. B., & Rapport, M. D. (2001). Cognitive pharmacology of stimulants in children with ADHD. In M. V. Solanto, A. F. T. Arnsten, & F. X. Castellanos (Eds.), Stimulant drugs and ADHD: Basic and clinical neuroscience (pp. 283–302). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
DuPaul, G. J., & Eckert, T. L. (1997). The effects of school-based interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analysis. School Psychology Review, 26, 5–27.
Elliot, R., Sahakian, B. J., Matthews, K., Bannerjea, A., Rimmer, J., & Robbins, T. W. (1997). Effects of methylphenidate on special working memory and planning in healthy young adults. Psychopharmacology, 131, 196–206.
Fabiano, G. A., & Pelham, W. E. (2002). Measuring impairment in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. ADHD Report, 10, 6–10.
Fischer, M., Barkley, R. A., Smallish, L., & Fletcher, K. (2002). Young adult follow-up of hyperactive children: Self-reported psychiatric disorders, comorbidity, and the role of childhood conduct problems and teen CD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 463–475.
Flory, K., Milich, R., Lorch, E. P., Hayden, A. N., Strange, C., & Welsh, R. (2006). Online story comprehension among children with ADHD: Which core deficits are involved? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 34, 853–865.
Francis, S., Fine, J., & Tannock, R. (2001). Methylphenidate selectively improves storyretelling in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 11, 217–228.
Freer, B., Little, S., Metze, A., Milich, R., & Lorch, E. P. (2008). The effectiveness formulating a story representation among children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and comparison children. Poster presented at the twentieth biennial conference on human development, Indianpolis, IN.
Graesser, A. C., & Clark, L. F. (1985). Structures and procedures of implicit knowledge. Norwood, NJ: Ablex.
Hechtman, L., & Greenfield, B. (2003). Long-term use of stimulants in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Safety, efficacy, and long-term outcome. Paediatric Drugs, 5, 787–794.
Jensen, P. S., Hinshaw, S. P., Swanson, J. M., Greenhill, L. L., Conners, C. K., Arnold, L. E., et al. (2001). Findings from the NIMH Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD (MTA): Implications and applications for primary care providers. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 22, 60–73.
Kalff, A. C., de-Sonnevile, L. M. J., Hurks, P. P. M., Hendriksen, J. G. M., Kroes, M., Feron, F. J. M., et al. (2003). Low- and high-level controlled processing in executive motor control tasks in 5–6-year-old children at risk of ADHD. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 44, 1049–1057.
Kendeou, P., Lynch, J. S., van den Broek, P., Espin, C., White, M., & Kremer, K. E. (2005). Developing successful readers: Building early comprehension skills through television viewing and listening. Early Childhood Education Journal, 33, 91–98.
King, S., Waschbusch, D. A., Pelham, W. E., Frankland, B. W., Andrade, B. F., Jacques, S., et al. (2009). Social information processing in elementary-school aged children with ADHD: Medication effects and comparisons with typical children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 579–589.
LeFever, G. B., Villers, M. S., Morrow, A. L., & Vaughn, E. S. (2002). Parental perceptions of adverse educational outcomes among children diagnosed and treated for ADHD: A call for improved school/provider collaboration. Psychology in the Schools, 39, 63–71.
Leonard, M. A., Lorch, E. P., Milich, R., & Hagans, N. (2009). Parent–child joint picture-book reading among children with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 12, 361–371.
Loe, I. M., & Feldman, H. M. (2007). Academic and educational outcomes of children with ADHD. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 36, 643–654.
Lorch, E. P., Berthiaume, K., Milich, R., & van den Broek, P. (2007). Story comprehension impairments in children with ADHD. In K. Cain & J. Oakhill (Eds.), Cognitive bases of children’s language comprehension difficulties (pp. 128–155). New York: Guilford.
Lorch, E. P., Milich, R., Astrin, C. C., & Berthiaume, K. (2006). Cognitive engagement in typically developing children and children with ADHD from preschool through elementary school. Developmental Psychology, 42, 1206–1219.
Lorch, E. P., Sanchez, R. P., van den Broek, P., Milich, R., Murphy, E. L., Lorch, R. F., et al. (1999). The relation of story structure properties to recall of television stories in young children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and nonreferred peers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 27, 293–309.
Mandler, J. M., & Johnson, N. S. (1977). Remembrance of things parsed: Story structure and recall. Cognitive Psychology, 9, 111–151.
Mayer, M. (1967). A boy, a dog, and a frog. New York: Dial.
Mayer, M. (1969). Frog, where are you?. New York: Dial.
Nezworski, T., Stein, N. L., & Trabasso, T. (1982). Story structure versus content in children’s recall. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 21, 196–206.
Nigg, J. T. (2001). Is ADHD a disinhibitory disorder? Psychological Bulletin, 127, 571–598.
O’Brien, E. J., & Myers, J. L. (1987). The role of causal connections in the retrieval of text. Memory and Cognition, 15, 419–427.
Paulauskas, S. L., & Goodman Campbell, S. B. (1979). Social perspective-taking and teacher ratings of peer interaction in hyperactive boys. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 7, 483–493.
Pelham, W. E. (2000). Stimulants. In A. E. Kazdin (Ed.), Encyclopedia of psychology (Vol. 7, pp. 474–476). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Pelham, W. E., Hoza, B., Kipp, H. L., Gnagy, E. M., & Trane, S. T. (1997). Effects of methylphenidate and expectancy on ADHD children’s performance, self-evaluations, persistence, and attributions on a cognitive task. Experimental & Clinical Psychopharmacology, 5, 3–13.
Pelham, W. E., McBurnett, K., Harper, G. W., Milich, R., Murphy, D. A., Clinton, J., et al. (1990). Methylphenidate and baseball playing in ADHD children: Who’s on first? Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 58, 130–133.
Rapport, M. D., Scanlan, S. W., & Denney, C. B. (1999). Attention–deficit/hyperactivity disorder and scholastic achievement: A model of dual developmental pathways. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40, 1169–1183.
Reardon, S. M., & Naglieri, J. A. (1992). PASS cognitive processing characteristics of normal and ADHD males. Journal of School Psychology, 30, 151–163.
Renz, K., Lorch, E. P., Milich, R., Lemberger, C., Bodner, A., & Welsh, R. (2003). Online story representation in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31, 93–104.
Stein, N. L., & Glenn, C. G. (1979). An analysis of story comprehension in elementary school children. In R. Freedble (Ed.), Multidisciplinary approaches to discourse comprehension. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaun Associates.
Trabasso, T., & Nickels, M. (1992). The development of goal plans of action in the narration of a picture story. Discourse Processes, 15, 249–275.
Trabasso, T., Secco, T., & van den Broek, P. W. (1984). Causal cohesion and story coherence. In H. Mandler, N. L. Stein, & T. Trabasso (Eds.), Learning and comprehension of text (pp. 83–111). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Trabasso, T., & Sperry, L. L. (1985). Causal relatedness and importance of story events. Journal of Memory and Learning, 24, 595–611.
Trabasso, T., & Stein, N. L. (1997). Narrating, representing and remembering event sequences. In P. W. van den Broek, P. J. Bauer, & T. Bourg (Eds.), Developmental spans in event comprehension and representation: Bridging fictional and actual events (pp. 237–270). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Trabasso, T., Stein, N. L., Rodkin, P. C., Munger, M. P., & Baughn, C. R. (1992). Knowledge of goals and plans in the online narration of events. Cognitive Development, 7, 133–170.
Trabasso, T., & van den Broek, P. (1985). Causal thinking and the representation of narrative events. Journal of Memory and Language, 24, 612–630.
Weller, E. B., Weller, R. A., Fristad, M. A., Rooney, M. T., & Schecter, J. (2000). Children’s interview for psychiatric syndromes—parent version (PChIPS). Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 39, 76–84.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health Grant MH47386 and the National Institute on Drug Abuse grant DA 05312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derefinko, K.J., Bailey, U.L., Milich, R. et al. The Effects of Stimulant Medication on the Online Story Narrations of Children with ADHD. School Mental Health 1, 171–182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-009-9017-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-009-9017-6