Abstract
Purpose
To report the outcomes and complications of reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA) in massive irreparable rotator cuff tears (MIRCT) and cuff tear arthropathy (CTA).
Methods
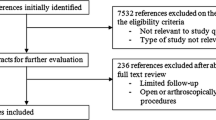
A systematic review of the literature contained in Medline, Cochrane, EMBASE, Google Scholar and Ovid databases was conducted on May 1, 2016, according to PRISMA guidelines. The key words “reverse total shoulder arthroplasty” or “reverse total shoulder prostheses” with “rotator cuff tears”; “failed rotator cuff surgery”; “massive rotator cuff tears”; “irreparable rotator cuff tears”; “cuff tear arthropathy”; “outcomes”; “complications” were matched. All articles reporting outcomes and complications of RSA for the management of MIRCT or CTA were included. The comparison between preoperative and postoperative clinical scores, as well as range of motion (ROM), was performed using the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test. P values lower than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
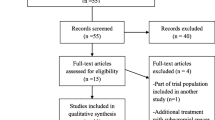
Seven articles were included in our qualitative synthesis. A statistically significant improvement in all clinical scores and ROM was found comparing the preoperative value with the postoperative value. The degrees of retroversion of the humeral stem of the RSA do not influence the functional outcomes in a statistically significant fashion. There were 17.4% of complications. The most frequent was heterotopic ossification, occurring in 6.6% of patients. Revision surgery was necessary in 7.3% of patients.
Conclusions
RSA restores pain-free ROM and improves function of the shoulder in patients with MIRCT or CTA. However, complications occur in a high percentage of patients. The lack of level I studies limits the real understanding of the potentials and limitations of RSA for the management of MIRCT and CTA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Longo UG et al (2011) Synthetic augmentation for massive rotator cuff tears. Sports Med Arthrosc 19(4):360–365
Cofield RH (1985) Rotator cuff disease of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67(6):974–979
Gerber C et al (1988) Latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of massive tears of the rotator cuff. A preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res 232:51–61
Neer CS, Craig EV, Fukuda H (1983) Cuff-tear arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65(9):1232–1244
Gerber C, Maquieira G, Espinosa N (2006) Latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(1):113–120
Longo UG et al (2012) Conservative treatment and rotator cuff tear progression. Med Sport Sci 57:90–99
Ackland DC et al (2010) Moment arms of the shoulder musculature after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(5):1221–1230
Boileau P et al (2006) Neer Award 2005: the Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 15(5):527–540
Kontaxis A, Johnson GR (2009) The biomechanics of reverse anatomy shoulder replacement—a modelling study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 24(3):254–260
Mohammed AA, Frostick SP (2016) Linked shoulder replacement: current design problems and a new design proposal. Musculoskelet Surg 100(1):25–29
Nalbone L et al (2014) Optimal positioning of the humeral component in the reverse shoulder prosthesis. Musculoskelet Surg 98(2):135–142
Randelli P et al (2014) Optimal glenoid component inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. How to improve implant stability. Musculoskelet Surg 98 Suppl 1:15–18
Boileau P et al (2006) Arthroplasty of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88(5):562–575
Gutiérrez S et al (2007) Center of rotation affects abduction range of motion of reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 458:78–82
Gutiérrez S et al (2008) Evaluation of abduction range of motion and avoidance of inferior scapular impingement in a reverse shoulder model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 17(4):608–615
Gutiérrez S et al (2008) Hierarchy of stability factors in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(3):670–676
Gutiérrez S et al (2011) Effects of tilt and glenosphere eccentricity on baseplate/bone interface forces in a computational model, validated by a mechanical model, of reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(5):732–739
Affonso J et al (2012) Complications of the reverse prosthesis: prevention and treatment. Instr Course Lect 61:157–168
Werner CM et al (2005) Treatment of painful pseudoparesis due to irreparable rotator cuff dysfunction with the Delta III reverse-ball-and-socket total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(7):1476–1486
Frankle M et al (2005) The reverse shoulder prosthesis for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency. A minimum two-year follow-up study of sixty patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(8):1697–1705
Guery J et al (2006) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Survivorship analysis of eighty replacements followed for five to ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(8):1742–1747
Simovitch RW et al (2007) Impact of fatty infiltration of the teres minor muscle on the outcome of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(5):934–939
Simovitch RW et al (2007) Predictors of scapular notching in patients managed with the Delta III reverse total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(3):588–600
Grassi FA et al (2009) Six-year experience with the Delta III reverse shoulder prosthesis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 17(2):151–156
Young SW et al (2009) The SMR reverse shoulder prosthesis in the treatment of cuff-deficient shoulder conditions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18(4):622–626
Boileau P et al (2011) Bony increased-offset reversed shoulder arthroplasty: minimizing scapular impingement while maximizing glenoid fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(9):2558–2567
Favard L et al (2011) Reverse prostheses in arthropathies with cuff tear: are survivorship and function maintained over time? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(9):2469–2475
Bries AD et al (2012) Accuracy of obtaining optimal base plate declination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(12):1770–1775
Coe MP et al (2012) The cost-effectiveness of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty compared with hemiarthroplasty for rotator cuff tear arthropathy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(10):1278–1288
Day JS et al (2012) Polyethylene wear in retrieved reverse total shoulder components. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(5):667–674
Lawrence TM et al (2012) Patient reported activities after reverse shoulder arthroplasty: part II. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(11):1464–1469
Ek ET et al (2013) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for massive irreparable rotator cuff tears in patients younger than 65 years old: results after five to fifteen years. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 22(9):1199–1208
Ji JH et al (2013) Early clinical results of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in the Korean population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 22(8):1102–1107
Young SW et al (2013) Comparison of functional outcomes of reverse shoulder arthroplasty with those of hemiarthroplasty in the treatment of cuff-tear arthropathy: a matched-pair analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95(10):910–915
Wiater BP et al (2013) Early outcomes of staged bilateral reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a case-control study. Bone Joint J 95-B(9):1232–1238
Mulieri P et al (2010) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tear without glenohumeral arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(15):2544–2556
Sadoghi P et al (2011) Impact of previous rotator cuff repair on the outcome of reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(7):1138–1146
Valenti P et al (2011) Do less medialized reverse shoulder prostheses increase motion and reduce notching? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(9):2550–2557
Nolan BM, Ankerson E, Wiater JM (2011) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty improves function in cuff tear arthropathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(9):2476–2482
Jobin CM et al (2012) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for cuff tear arthropathy: the clinical effect of deltoid lengthening and center of rotation medialization. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(10):1269–1277
Leung B et al (2012) Functional outcome of hemiarthroplasty compared with reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in the treatment of rotator cuff tear arthropathy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(3):319–323
Frankle M et al (2006) The reverse shoulder prosthesis for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency. A minimum two-year follow-up study of sixty patients surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(Suppl 1 Pt 2):178–190
Longo UG et al (2011) Scoring systems for the functional assessment of patients with rotator cuff pathology. Sports Med Arthrosc 19(3):310–320
MacDermid JC, Solomon P, Prkachin K (2006) The Shoulder Pain and Disability Index demonstrates factor, construct and longitudinal validity. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 7:12
Boileau P et al (2005) Grammont reverse prosthesis: design, rationale, and biomechanics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14(1 Suppl S):147S–161S
Nyffeler RW et al (2004) Analysis of a retrieved delta III total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(8):1187–1191
Berton A et al (2015) The effect of humeral version on teres minor muscle moment arm, length, and impingement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty during activities of daily living. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24(4):578–586
Goutallier D et al (1995) Fatty infiltration of disrupted rotator cuff muscles. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 62(6):415–422
Longo UG et al (2011) Latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for massive irreparable rotator cuff tears: a systematic review. Sports Med Arthrosc 19(4):428–437
Grammont PM, Baulot E (1993) Delta shoulder prosthesis for rotator cuff rupture. Orthopedics 16(1):65–68
Grammont PM et al (1987) Etude et realization d’une novelle prothese d’epaule. Rheumatologie 39:17–22
Gulotta LV et al (2012) Humeral component retroversion in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(9):1121–1127
Stephenson DR et al (2011) Effect of humeral component version on impingement in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(4):652–658
Henninger HB et al (2012) Effect of deltoid tension and humeral version in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(4):483–490
Sirveaux F et al (2004) Grammont inverted total shoulder arthroplasty in the treatment of glenohumeral osteoarthritis with massive rupture of the cuff. Results of a multicentre study of 80 shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(3):388–395
Lawrence TM et al (2012) Patient reported activities after reverse shoulder arthroplasty: part II. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 21(11):1464–1469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrillo, S., Longo, U.G., Papalia, R. et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for massive irreparable rotator cuff tears and cuff tear arthropathy: a systematic review. Musculoskelet Surg 101, 105–112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-017-0474-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-017-0474-z