Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the frequency of secondary evaluation to detect prostate cancer that was primarily manifested as abnormal hypermetabolism detected by 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET/CT). We also evaluated the association of maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) on PET/CT with clinicopathologic results.
Materials and methods
We evaluated PET/CT reports from a total of 12,037 patients to find cases with abnormal prostate hypermetabolism. Patients with known prostate cancer or a recent prostate procedure were excluded. We analyzed the frequency of secondary evaluations such as digital rectal exams (DRE), levels of serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and/or biopsy to confirm prostate cancer. Biopsied patients were categorized into benign and cancer groups. Clinicopathologic characteristics were compared between the groups.
Results
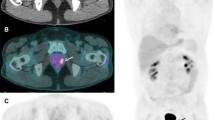
Among 12,037 PET/CT images, 184 (1.5 %) showed abnormal hypermetabolism in the prostate. Secondary evaluation was carried out in 120 patients. Biopsy was performed in 38 patients and prostate cancer was confirmed in 23 patients. The median serum PSA level was 3.2 and 49.7 ng/mL in the benign group and cancer group, respectively. The SUVmax was higher in the cancer group (5.7 ± 5.1) than in the benign group (4.8 ± 2.7), but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.37). In the cancer group, a high serum PSA level (≥20 ng/mL) was detected in 78.3 % of the patients. The Gleason score was 7 in 34.7 % and 8–10 in 56.5 % of prostate cancer patients.
Conclusions
Hypermetabolism in the prostate was incidentally detected in 1.5 % of patients, and only 65.2 % of these patients underwent further evaluation (DRE and/or serum PSA levels). Among cases of incidentally detected hypermetabolism in the prostate, patients with abnormal findings (DRE and/or PSA levels) showed high positivity by biopsy, and more than two-thirds of the positive biopsies showed significant prostate cancer. Therefore, patients with hypermetabolism in the prostate should not be ignored and should be secondarily evaluated by DRE and PSA level.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han EJ. H OJ, Choi WH, Yoo IR, Chung SK. Significance of incidental focal uptake in prostate on 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography CT images. Br J Radiol. 2010;83:915–20.
von Schulthess GK, Steinert HC, Hany TF. Integrated PET/CT: current applications and future directions. Radiology. 2006;238:405–22.
Lee JW, Kang KW, Paeng JC, Lee SM, Jang SJ, Chung JK, et al. Cancer screening using 18F-FDG PET/CT in Korean asymptomatic volunteers: a preliminary report. Ann Nucl Med. 2009;23:685–91.
Minamimoto R, Senda M, Uno K, Jinnouchi S, Iinuma T, Ito K, et al. Performance profile of FDG-PET and PET/CT for cancer screening on the basis of a Japanese Nationwide Survey. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21:481–98.
Bouchelouche K, Oehr P. Positron emission tomography and positron emission tomography/computerized tomography of urological malignancies: an update review. J Urol. 2008;179:34–45.
von Mallek D, Backhaus B, Muller SC, Matthies A, Palmedo H, Jaeger U, et al. Technical limits of PET/CT with 18FDG in prostate cancer. Aktuelle Urol. 2006;37:218–21.
Wang X, Koch S. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography potential pitfalls and artifacts. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2009;38:156–69.
Kojima S, Zhou B, Teramukai S, Hara A, Kosaka N, Matsuo Y, et al. Cancer screening of healthy volunteers using whole-body 18F-FDG-PET scans: the Nishidai clinic study. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43:1842–8.
Hoh CK, Seltzer MA, Franklin J, de Kernion JB, Phelps ME, Belldegrun A. Positron emission tomography in urological oncology. J Urol. 1998;159:347–56.
Lawrentschuk N, Davis ID, Bolton DM, Scott AM. Positron emission tomography and molecular imaging of the prostate: an update. BJU Int. 2006;97:923–31.
Kao PF, Chou YH, Lai CW. Diffuse FDG uptake in acute prostatitis. Clin Nucl Med. 2008;33:308–10.
Oyama N, Akino H, Kanamaru H, Okada K. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in diagnosis of untreated prostate cancer. Nihon Rinsho. 1998;56:2052–5.
Nathan M, Rohren E. FDG uptake in the prostate gland on PET/CT: a worrisome sign for prostate cancer regardless of PSA level. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(1 Suppl):180P.
Mohler J, Bahnson RR, Boston B, Busby JE, D’Amico A, Eastham JA, et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: prostate cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8:162–200.
Minamimoto R, Uemura H, Sano F, Terao H, Nagashima Y, Yamanaka S, et al. The potential of FDG-PET/CT for detecting prostate cancer in patients with an elevated serum PSA level. Ann Nucl Med. 2011;25:21–7.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, I., Chong, A., Jung, SI. et al. Is further evaluation needed for incidental focal uptake in the prostate in 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography–computed tomography images?. Ann Nucl Med 27, 140–145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0663-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0663-7