Abstract
Purpose of Review
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a painful debilitating neurological condition that accounts for approximately 1.2% of adult chronic pain population. Ketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, is an anesthetic agent that has been used by some pain specialists for CRPS. There is a growing body of clinical evidence to support the use of ketamine in the treatment of neuropathic pain, especially CRPS. This meta-analysis study was aimed to examine the efficacy of ketamine in the treatment of CRPS.
Recent Findings
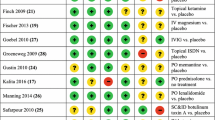
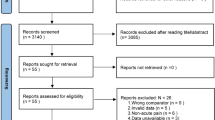
A search of Embase, Pubmed, Web of Knowledge, Cochrane, Clinical Trial.gov, and FDA.gov between Jan 1, 1950, and August 1, 2017, was conducted to evaluate ketamine infusion therapy in the treatment of CRPS. We selected randomized clinical trials or cohort studies for meta-analyses. I2 index estimates were calculated to test for variability and heterogeneity across the included studies. The primary outcome is pain relief. The effect of ketamine treatment for complex regional pain syndrome was assessed by 0–10 scale numerical rating pain score. The secondary outcome is the pain relief event rate, which is defined as the percentage of participants who achieved 30% or higher pain relief in each of the qualified studies. Our meta-analysis results showed that the Ketamine treatment led to a decreased mean of pain score in comparison to the self-controlled baseline (p < 0.000001). However, there is a statistical significance of between-study heterogeneity. The immediate pain relief event rate was 69% (95% confidence interval (CI) 53%, 84%). The pain relief event rate at the 1–3 months follow-ups was 58% (95% CI 41%, 75%).
Summary
The current available studies regarding ketamine infusion for CRPS were reviewed, and meta-analyses were conducted to evaluate the efficacy of ketamine infusion in the treatment of CRPS. Our findings suggested that ketamine infusion can provide clinically effective pain relief in short term for less than 3 months. However, because of the high heterogeneity of the included studies and publication bias, additional random controlled trials and standardized multicenter studies are needed to confirm this conclusion. Furthermore, studies are needed to prove long-term efficacy of ketamine infusion in the treatment of CRPS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Murphy KR, Han JL, Yang S, Hussaini SM, Elsamadicy AA, Parente B, et al. Prevalence of specific types of pain diagnoses in a sample of United States adults. Pain Physician. 2017;20(2):E257–68.
de Mos M, de Bruijn AG, Huygen FJ, Dieleman JP, Stricker BH, Sturkenboom MC. The incidence of complex regional pain syndrome: a population-based study. Pain. 2007;129(1):12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.008.
Veldman PH, Reynen HM, Arntz IE, Goris RJ. Signs and symptoms of reflex sympathetic dystrophy: prospective study of 829 patients. Lancet. 1993;342(8878):1012–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(93)92877-V.
Schwartzman RJ, Erwin KL, Alexander GM. The natural history of complex regional pain syndrome. Clin J Pain. 2009;25(4):273–80. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0b013e31818ecea5.
Bennett GJ. Update on the neurophysiology of pain transmission and modulation: focus on the NMDA-receptor. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2000;19:S2–6.
•• Correll GE, Maleki J, Gracely EJ, Muir JJ, Harbut RE. Subanesthetic ketamine infusion therapy: a retrospective analysis of a novel therapeutic approach to complex regional pain syndrome. Pain Med. 2004;5:263–75. This study reported several cases of ketamine-induced hepatotoxicity. This suggested liver functions should be monitored during ketamine infusion. If increased liver enzymes occur, ketamine infusion should be discontinued promptly.
Goebel A, Jayaseelan S, Sachane K, Gupta M, Frank B. Racemic ketamine 4.5-day infusion treatment of long-standing complex regional pain syndrome-a prospective service evaluation in five patients. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(1):146–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aev183.
Goldberg ME, Torjman MC, Schwartzman RJ, Mager DE, Wainer IW. Pharmacodynamic profiles of ketamine (r)- and (s)- with 5-day inpatient infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome. Pain physician. 2010;13(4):379–87.
Kiefer RT, Rohr P, Ploppa A, Dieterich HJ, Grothusen J, Koffler S, et al. Efficacy of ketamine in anesthetic dosage for the treatment of refractory complex regional pain syndrome: an open-label phase II study. Pain Med. 2008;9(8):1173–201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2007.00402.x.
Kiefer RT, Rohr P, Ploppa A, Nohe B, Dieterich HJ, Grothusen J, et al. A pilot open-label study of the efficacy of subanesthetic isomeric s(+)-ketamine in refractory CRPS patients. Pain Med (Malden, Mass.). 2008;9:44–54.
Patil S, Anitescu M. Efficacy of outpatient ketamine infusions in refractory chronic pain syndromes: a 5-year retrospective analysis. Pain Medicine (Malden, Mass). 2012;13:263–9.
Kiefer R, Rohr P, Unertl K, Altemeyer KH, Grothusen J, Schwartzman RJ. Recovery from intractable complex regional pain syndrome type I (RSD) under high-dose intravenous ketamine-midazolam sedation International Research Foundation For RSD/CRPS. 2002;NEUROLOGY A474.
• Schwartzman RJ, Alexander GM, Grothusen JR, Paylor T, Reichenberger E, Perreault M. Outpatient intravenous ketamine for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: a double-blind placebo controlled study. Pain. 2009;147:107–15. This is the only double-blind placebo-controlled study on the topic of intravenous ketamine for CRPS. This study showed outpatient intravenous ketamine can provide pain relief.
Webster LR, Walker MJ. Safety and efficacy of prolonged outpatient ketamine infusions for neuropathic pain. Am J Ther. 2006;13(4):300–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/00045391-200607000-00004.
Dahan A, Olofsen E, Sigtermans M, Noppers I, Niesters M, Aarts L, Bauer M, Sarton E. Population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of ketamine-induced pain relief of chronic pain. Eur J Pain (London). 2011;15:258–267.
Koffler SP, Hampstead BM, Irani F, Tinker J, Kiefer RT, Rohr P, et al. The neurocognitive effects of 5 day anesthetic ketamine for the treatment of refractory complex regional pain syndrome. Arch Clin Neuropsychol: Off J Natl Acad Neuropsychol. 2007;22(6):719–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acn.2007.05.005.
Schilder JC, Sigtermans MJ, Schouten AC, Putter H, Dahan A, Noldus LP, et al. Pain relief is associated with improvement in motor function in complex regional pain syndrome type 1: secondary analysis of a placebo-controlled study on the effects of ketamine. J Pain: Off J Am Pain Soc. 2013;14(11):1514–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2013.07.013.
Sheehy KA, Muller EA, Lippold C, Nouraie M, Finkel JC, Quezado ZM. Subanesthetic ketamine infusions for the treatment of children and adolescents with chronic pain: a longitudinal study. BMC Pediatr. 2015;15(198) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-015-0515-4.
Sigtermans M, Noppers I, Sarton E, Bauer M, Mooren R, Olofsen E, et al. An observational study on the effect of s+−ketamine on chronic pain versus experimental acute pain in complex regional pain syndrome type 1 patients. Eur J Pain (London). 2010;14:302–7.
Sigtermans MJ, van Hilten JJ, Bauer MC, Arbous MS, Marinus J, Sarton EY, et al. Ketamine produces effective and long-term pain relief in patients with complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Pain. 2009;145(3):304–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2009.06.023.
Farrar JT, Young JP Jr, La Moreaux L, Werth JL, Poole RM. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain. 2001;94(2):149–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3959(01)00349-9.
Venancio C, Antunes L, Felix L, Rodrigues P, Summavielle T, Peixoto F. Chronic ketamine administration impairs mitochondrial complex I in the rat liver. Life Sci. 2013;93(12-14):464–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2013.08.001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Jianli Zhao, Yajing Wang, and Dajie Wang declare no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Hot Topics in Pain and Headache
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Wang, Y. & Wang, D. The Effect of Ketamine Infusion in the Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: a Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr Pain Headache Rep 22, 12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-018-0664-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-018-0664-x