Abstract
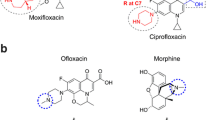
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics cause immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions, and may also affect internal organs and circulating blood cells. The underlying pathomechanisms are only partly understood. The extent of cross-reactivity among different quinolones depends on the type of clinical manifestation and its underlying mechanism. Despite recent advances, reliable diagnostic tests are still lacking. Recent studies have shown quinolone-specific IgE in vitro in more than 50% of patients with immediate-type reactions and a considerable cross-reactivity with related compounds. In maculopapular drug exanthems from ciprofloxacin, specific T-cell clones were identified, and cross-reactivity to related compounds was detected in approximately 50% of the clones. From re-exposure studies in patients with exanthems, cross-reactivity appears to be lower. Cellular tests such as lymphocyte transformation tests are currently not very useful. For prick and intradermal skin tests, widely divergent nonirritant test concentrations have been recommended. Desensitization may be possible in selected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Campi P, Pichler WJ: Quinolone hypersensitivity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2003, 3:275–281.
Bircher AJ: The lymphocyte transformation test in the diagnosis of immediate type hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins. In Exogenous Dermatology. Edited by Surber C,Elsner P, Bircher A. Basel: Karger; 1995:31–37.
Bircher AJ, Haldimann D, Weber J: CAST-ELISA testing for the diagnosis of immediate-type allergic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. ACI International 1996, 8:109–110.
Häusermann P, Scherer K, Weber M, Bircher AJ: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis to ciprofloxacin mimicking bullous drug eruption: second reported case confirmed by pustular patch test. Dermatology 2005, In press.
Carbon C: Comparison of side effects of levofloxacin versus other fluoroquinolones. Chemotherapy 2001, 47(Suppl3):9–14; discussion 44–48.
Manfredi M, Severino M, Testi S, et al.: Detection of specific IgE to quinolones. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004, 113:155–160.Prevalence of specific IgE to fluoroquinolones in a large patient group with immediate hypersensitivity reactions
Kurata M, Kasuga Y, Nanba E, et al.: Flush induced by fluoroquinolones in canine skin. Inflamm Res 1995, 44:461–465.
Deamer RL, Prichard JG, Loman GJ: Hypersensitivity and anaphylactoid reactions to ciprofloxacin. Ann Pharmacother 1992, 26:1081–1084.
Schmid DA, Depta JPH, Pichler WJ: T cell-mediated immunity to quinolones (abstract). Allergologie 2004, 27:180.
Ball P, Mandell L, Patou G, et al.: A new respiratory fluoroquinolone, oral gemifloxacin: a safety profile in context. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2004, 23:421–429.
Tsuda S, Kato K, Karashima T, et al.: Toxic pustuloderma induced by ofloxacin. Acta Derm Venereol 1993, 73:382–384.
Rodriguez-Morales A, Llamazares AA, Benito RP, Cocera CM: Fixed drug eruption from quinolones with a positive lesional patch test to ciprofloxacin. Contact Dermatitis 2001, 44:255.
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Schneeberger PM, van der Hoeven JG: Ciprofloxacin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Infection 2003, 31:428–429.
Tokura Y: Quinolone photoallergy: photosensitivity dermatitis induced by systemic administration of photohaptenic drugs. J Dermatol Sci 1998, 18:1–10.
Dawe RS, Ibbotson SH, Sanderson JB, et al.: A randomized controlled trial (volunteer study) of sitafloxacin, enoxacin, levofloxacin and sparfloxacin phototoxicity. Br J Dermatol 2003, 149:1232–1241.Experimental placebo-controlled study on phototoxicity of four fluoroquinolones in healthy, white volunteers.
Tokura Y, Seo N, Yagi H, et al.: Cross-reactivity in murine fluoroquinolone photoallergy: exclusive usage of TCR Vbeta13 by immune T cells that recognize fluoroquinolone-photomodified cells. J Immunol 1998, 160:3719–3728.
Blum MD, Graham DJ, McCloskey CA: Temafloxacin syndrome: review of 95 cases. Clin Infect Dis 1994, 18:946–950.
Norrby SR, Lietman PS: Safety and tolerability of fluoroquinolones. Drugs 1993, 45(Suppl 3):59–64.
Zimpfer A, Propst A, Mikuz G, et al.: Ciprofloxacin-induced acute liver injury: case report and review of literature. Virchows Arch 2004, 444:87–89.
Ball P, Tillotson G: Tolerability of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: past, present and future. Drug Saf 1995, 13:343–358.Risk factors and prevalence of macular exanthems and cross-reactivity among gemifloxacin and ciprofloxacin
Clark DW, Layton D, Wilton LV, et al.: Profiles of hepatic and dysrhythmic cardiovascular events following use of fluoroquinolone antibacterials: experience from large cohorts from the Drug Safety Research Unit Prescription-Event Monitoring database. Drug Saf 2001, 24:1143–1154.
Lucena MI, Andrade RJ, Rodrigo L, et al.: Trovafloxacininduced acute hepatitis. Clin Infect Dis 2000, 30:400–401.
Gauffre A, Mircheva J, Glotz D, et al.: Autoantibodies against a kidney-liver protein associated with quinolone-induced acute interstitial nephritis or hepatitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997, 12:1961–1962.
Erdem G, Staat MA, Connelly BL, Assa’ad A: Anaphylactic reaction to ciprofloxacin in a toddler: successful desensitization. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1999, 18:563–564.
Bacharier LB, Schneider LC, Twarog FJ: Antibiotic allergy and desensitization in a tertiary care pediatric hospital (abstract). J Allergy Clin Immunol 1997, 99:S430.
Colas S, Pola J, Zapata C, et al.: Quinolones hypersensitivitiy: clinical and immunological aspects (abstract). J Allergy Clin Immunol 1993, 91:365.
Arboit F, Bessot J, de Blay F, et al.: L’Allergie aux quinolones: à propos de huit observations. Rev Fr Allergol 1997, 37:15–19.
Empedrad RB, Earl HS, Gruchalla RS: Determination of nonirritating skin test concentrations of commonly used antimicrobial drugs (abstract). J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000, 105:S272.
Empedrad R, Darter AL, Earl HS, Gruchalla RS: Nonirritating intradermal skin test concentrations for commonly prescribed antibiotics. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003, 112:629–630.
Barbaud A, Trechot P, Reichert-Penetrat S, et al.: Relevance of skin tests with drugs in investigating cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Contact Dermatitis 2001, 45:265–268.
Davila I, Diez ML, Quirce S, et al.: Cross-reactivity between quinolones: report of three cases. Allergy 1993, 48:388–390.
Bircher AJ, Figueiredo V, Scherer K, Surber C: Accuracy of serial dilution concentrations for intradermal skin testing: a neglectable problem? (abstract). Contact Dermatitis 2004, 50:186–187.
Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Fléchet ML, et al.: Patch testing in severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Contact Dermatitis 1996, 35:234–236.
Kurumaji Y, Shono M: Scarified photopatch testing in lomefloxacin photosensitivity. Contact Dermatitis 1992, 26:5–10.
Baldo BA, Pham NH, Zhao Z: Chemistry of drug allergenicity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2001, 1:327–335.
Nyfeler B, Pichler WJ: The lymphocyte transformation test for the diagnosis of drug allergy: sensitivity and specificity. Clin Exp Allergy 1997, 27:175–181.
Nakamura M, Ohishi A, Aosaki N, Hamaguchi K: Norfloxacininduced acute interstitial nephritis. Nephron 2000, 86:204–205.
Hadimeri H, Almroth G, Cederbrant K, et al.: Allergic nephropathy associated with norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin therapy: report of two cases and review of the literature. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1997, 31:481–485.
Gea-Banacloche JC, Metcalfe DD: Ciprofloxacin desensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1996, 97:1426–1427.
Lantner RR: Ciprofloxacin desensitization in a patient with cystic fibrosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1995, 96:1001–1002.
Bircher AJ, Rutishauser M: Oral "desensitization" of maculopapular exanthema from ciprofloxacin. Allergy 1997, 52:1246–1248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scherer, K., Bircher, A.J. Hypersensitivity reactions to fluoroquinolones. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 5, 15–21 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-005-0049-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-005-0049-1