Abstract
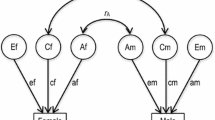
We examined the Simple View of reading from a behavioral genetic perspective. Two aspects of word decoding (phonological decoding and word recognition), two aspects of oral language skill (listening comprehension and vocabulary), and reading comprehension were assessed in a twin sample at age 9. Using latent factor models, we found that overlap among phonological decoding, word recognition, listening comprehension, vocabulary, and reading comprehension was primarily due to genetic influences. Shared environmental influences accounted for associations among word recognition, listening comprehension, vocabulary, and reading comprehension. Independent of phonological decoding and word recognition, there was a separate genetic link between listening comprehension, vocabulary, and reading comprehension and a specific shared environmental link between vocabulary and reading comprehension. There were no residual genetic or environmental influences on reading comprehension. The findings provide evidence for a genetic basis to the “Simple View” of reading.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron, P. G., Joshi, M., & Williams, K. A. (1999). Not all reading disabilities are alike. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 32, 120–137.
Akaike, H. (1987). Factor analysis and the AIC. Psychometrika, 52, 317–332.
Betjemann, R. S., Willcutt, E. G., Olson, R. K., Keenan, J. M., DeFries, J. C., & Wadsworth, S. J. (2008). Word reading and reading comprehension: Stability, overlap and independence. Reading and Writing, 21, 539–558.
Braze, D., Tabor, W., Shankweiler, D. P., & Mencl, M. E. (2007). Speaking up for vocabulary: Reading skill differences in young adults. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 40, 226–243.
Byrne, B., Coventry, W. L., Olson, R. K., Samuelsson, S., Corley, R., Willcutt, E. G., et al. (2009). Genetic and environmental influences on aspects of literacy and language in early childhood: Continuity and change from preschool to Grade 2. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 22, 219–236.
Byrne, B., Samuelsson, S., Wadsworth, S., Hulslander, J., Corley, R., DeFries, J. C., et al. (2007). Longitudinal twin study of early literacy development: Preschool through Grade 1. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 20, 77–102.
Catts, H. W., Adlof, S. M., & Weismer, S. E. (2006). Language deficits in poor comprehenders: A case for the simple view of reading. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 49, 278–293.
Catts, H. W., Hogan, T. P., & Adlof, S. M. (2005). Developmental changes in reading and reading disabilities. In H. Catts & A. Kamhi (Eds.), The connections between language and reading disabilities (pp. 25–40). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 155–159.
Connor, C. M., Morrison, F. J., & Katch, E. L. (2004). Beyond the reading wars: The effect of classroom instruction by child interactions on early reading. Scientific Studies of Reading, 8, 305–336.
Cutting, L. E., & Scarborough, H. S. (2006). Prediction of reading comprehension: Relative contributions of word recognition, language proficiency, and other cognitive skills can depend on how comprehension is measured. Scientific Studies of Reading, 10, 277–299.
Edmonds, M. S., Vaughn, S., Wexler, J., Reutebuch, C., Cable, A., Tackett, K. K., et al. (2009). A synthesis of reading interventions and effects on reading comprehension outcomes for older struggling readers. Review of Educational Research, 79, 262–300.
Gayán, J., & Olson, R. K. (2003). Genetic and environmental influences on individual differences in printed word recognition. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 84, 97–123.
Gillam, R., & Pearson, N. (2004). Test of narrative language. Austin: Pro-Ed.
Goodglass, H., & Kaplan, E. (2001). The Boston Naming Test (2nd ed.). New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, reading, and reading disability. Remedial and Special Education, 7, 6–10.
Griffin, E. A., & Morrison, F. J. (1997). The unique contribution of home literacy environment to differences in early literacy skills. Early Child Development & Care, 127–128, 233–243.
Harlaar, N., Spinath, F. M., Dale, P. S., & Plomin, R. (2005). Genetic influences on early word recognition abilities and disabilities: A study of 7-year-old twins. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46, 373–384.
Harm, M., & Seidenberg, M. (2004). Computing the meanings of words in meaning: Cooperative division of labor between visual and phonological processes. Psychological Review, 111, 662–720.
Hayiou-Thomas, M. E. (2008). Genetic and environmental influences on early speech, language and literacy development. Journal of Communication Disorders, 41, 397–408.
Hayiou-Thomas, M. E., Harlaar, N., Dale, P. S., & Plomin, R. (2006). Genetic and environmental mediation of the prediction from preschool language and nonverbal ability to 7-year reading. Journal of Research in Reading, 29, 50–74.
Hoff, E. (2006). How social contexts support and shape language development. Developmental Review, 26, 55–88.
Hohnen, B., & Stevenson, J. (1999). The structure of genetic influences on general cognitive, language, phonological, and reading abilities. Developmental Psychology, 35, 590–603.
Hoover, W. A., & Gough, P. B. (1990). The simple view of reading. Reading & Writing, 2, 127–160.
Hu, F. B. (2009). Diet and lifestyle influences on risk of coronary heart disease. Current Atherosclerosis Reports, 11, 257–263.
Justice, L. M., McGinty, A. S., Cabell, S. Q., Kilday, C. R., Knighton, K., & Huffman, G. (2010). Language and literacy curriculum supplement for preschoolers who are academically at risk: A feasibility study. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 41, 161–178.
Keenan, J. M., Betjemann, R. S., & Olson, R. K. (2008). Reading comprehension tests vary in the skills they assess: Differential dependence on decoding and oral comprehension. Scientific Studies of Reading, 12, 281–300.
Keenan, J. M., Betjemann, R. S., Wadsworth, S. J., DeFries, J. C., & Olson, R. K. (2006). Genetic and environmental influences on reading and listening comprehension. Journal of Research in Reading, 29, 79–91.
Kendeou, P., van den Broek, P., White, M. J., & Lynch, J. S. (2009). Predicting reading comprehension in early elementary school: The independent contributions of oral language and decoding skills. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101, 765–778.
Kendler, K. S., & Gardner, C. O. (1998). Twin studies of adult psychiatric and substance dependence disorders: Are they biased by differences in the environmental experiences of monozygotic and dizygotic twins in childhood and adolescence? Psychological Medicine, 28, 625–633.
Kovas, Y., Hayiou-Thomas, M. E., Oliver, B., Dale, P. S., Bishop, D. V. M., & Plomin, R. (2005). Genetic influences in different aspects of language development: The etiology of language skills in 4.5-year-old twins. Child Development, 76, 632–651.
Kirby, J. R., & Savage, R. S. (2008). Can the simple view deal with the complexities of reading? Literacy, 42, 75–82.
Leach, J. M., Scarborough, H. S., & Rescorla, L. (2003). Late-emerging reading disabilities. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95, 211–224.
Lewis, B. A., Shriberg, L. D., Freebairn, L. A., Hansen, A. J., Stein, C. M., Taylor, H. G., et al. (2006). The genetic bases of speech sound disorders: Evidence from spoken and written language. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 49, 1294–1312.
Loehlin, J. C. (2004). Latent variable models: An introduction to factor, path, and structural equation analysis (4th ed.). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Loehlin, J., & Nichols, R. (1976). Heredity, environment and personality. Austin: University of Texas Press.
Lovett, M. W., Borden, S. L., DeLuca, T., Lacerenza, L., Benson, M. J., & Brackston, D. (1994). Treating the core deficits of developmental dyslexia: Evidence of transfer of learning after phonologically- and strategy-based reading training programs. Developmental Psychology, 30, 805–822.
Markwardt, F. C. (1989; 1997 Normative Update). Peabody Individual Achievement Test—revised. Bloomington: Pearson Assessments.
Mol, S. E., Bus, A. G., de Jong, M. T., & Smeets, D. J. H. (2008). Added value of dialogic parent–child book readings: A meta-analysis. Early Education and Development, 19, 7–26.
Nation, K., & Angell, P. (2006). Learning to read and learning to comprehend. London Review of Education, 4, 77–87.
Neale, M. C., Boker, S. M., Xi, G., & Maes, H. H. (2006). Mx: Statistical modeling (7th ed.). Richmond: Department of Psychiatry.
Neale, M. C., & Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for genetic studies of twins and families. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Ouellette, G. (2006). What’s meaning got to do with it: the role of vocabulary in word reading and reading comprehension. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 554–566.
Ouellette, G., & Beers, A. (2009). A not-so-simple view of reading: How oral vocabulary and visual-word recognition complicate the story. Reading and Writing, 23, 189–208.
Paracchini, S., Scerri, T., & Monaco, A. P. (2007). The genetic lexicon of dyslexia. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, 8, 57–79.
Perfetti, C., & Hart, L. (2002). The lexical quality hypothesis. In L. Verhoeven, C. Elbrow, & P. Reitsma (Eds.), Precursors of functional literacy (Vol. 11, pp. 67–86). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Petrill, S. A., Deater-Deckard, K., Thompson, L. A., DeThorne, L. S., & Schatschneider, C. (2006). Reading skills in early readers: Genetic and shared environmental influences. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 39, 48–55.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., McClearn, G. E., & McGuffin, P. (2008). Behavioral genetics (5th ed.). New York: Freeman.
Plomin, R., & Kovas, Y. (2005). Generalist genes and learning disabilities. Psychological Bulletin, 131, 592–617.
Price, T. S., Freeman, B., Craig, I., Petrill, S. A., Ebersole, L., & Plomin, R. (2000). Infant zygosity can be assigned by parental report questionnaire data. Twin Research, 3, 129–481.
Raftery, A. E. (1995). Bayesian model selection in social research. In P. V. Marsden (Ed.), Sociological methodology (pp. 111–163). Cambridge: Blackwell.
Rietveld, M. J. H., Posthuma, D., Dolan, C. V., & Boomsma, D. I. (2003). ADHD: Sibling interaction or dominance: An evaluation of statistical power. Behavior Genetics, 33, 247–255.
Scarr, S., & Carter-Saltzman, L. (1979). Twin method: Defense of a critical assumption. Behavior Genetics, 9, 527–542.
Semel, E. M., Wiig, E. H., & Secord, W. A. (2003). Clinical evaluation of language fundamentals—4. San Antonio: PsychCorp.
Share, D. L., & Leikin, M. (2004). Language impairment at school entry and later reading disability: Connections at lexical versus supralexical levels of reading. Scientific Studies of Reading, 8, 87–110.
Snowling, M. J., & Hayiou-Thomas, M. E. (2006). The dyslexia spectrum: Continuities between reading, speech, and language impairments. Topics in Language Disorders, 26, 108–124.
Spiegelhalter, D. J., Best, N. G., Carlin, B. P., & van der Linde, A. (2002). Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit (with discussion). Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B Statistical Methodology, 64, 583–639.
Torgesen, J. K., Wagner, R. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (1999). Test of Word Reading Efficiency. Austin: Pro-ed.
Torppa, M., Tolvanen, A., Poikkeus, A. M., Eklund, K., Lerkkanen, M. K., Leskinen, E., et al. (2007). Reading development subtypes and their early characteristics. Annals of Dyslexia, 57, 3–32.
US Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Assessment of Educational Progress (2005). The NAEP reading achievement levels by grade. Retrieved from http://nces.ed.gov/nationsreportcard/reading/achieveall.asp.
Verhoeven, L., & van Leeuwe, J. (2008). Prediction of the development of Reading comprehension: A longitudinal study. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 22, 407–423.
Wade, T. D., Wilkinson, J., & Ben Tovim, D. (2003). The genetic epidemiology of body attitudes, the attitudinal component of body image in women. Psychological Medicine, 33, 1395–1405.
Wilson, P. T., & Anderson, R. C. (1986). What they don’t know will hurt them: The role of prior knowledge in comprehension. In J. Orasanu (Ed.), Reading comprehension: From research to practice (pp. 31–48). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Woodcock, R. W. (1987). Woodcock Reading Mastery Tests, Form G—revised. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the ongoing contribution of the parents and children in the Western Research Reading Project (WRRP). WRRP is supported by NICHD grant HD38075 and NICHD/OSERS grant HD46167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harlaar, N., Cutting, L., Deater-Deckard, K. et al. Predicting individual differences in reading comprehension: a twin study. Ann. of Dyslexia 60, 265–288 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-010-0044-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-010-0044-7