Abstract
Previous studies have shown that the mirror neuron system (MNS) plays an important role in action understanding. However, whether and how the MNS activity is different in individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) and typically developed (TD) individuals are still unclear. The current study used activation likelihood estimation to conduct a meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies that investigated action observation and imitation in ASD and TD individuals. Thirteen studies were selected, and the contrasts focused on the brain effects in ASD and TD participants and the differences between the two groups. The results showed that compared with TD individuals, ASD individuals exhibited stronger effects in the anterior inferior parietal lobule, a part of the putative human MNS. In addition, the ASD group demonstrated altered effects in the occipital cortex, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, cingulate cortex, and insula. These results suggest that ASD individuals demonstrate dysfunction of the MNS during action observation and imitation. Furthermore, brain regions involved in visual processing, executive function, and social cognitive function might also show dysfunction during action task performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington: American Psychiatric Association.
Annaz, D., Remington, A., Milne, E., Coleman, M., Campbell, R., Thomas, M. S., et al. (2010). Development of motion processing in children with autism. Developmental Science, 13(6), 826–838.
Barbey, A. K., Koenigs, M., & Grafman, J. (2013). Dorsolateral prefrontal contributions to human working memory. Cortex, 49(5), 1195–1205.
Chan, R. C. K., Shum, D., Toulopoulou, T., Chen, E. Y. H., Shum, D., Toulopoulou, T., et al. (2008). Assessment of executive functions: review of instruments and identification of critical issues. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 23(2), 201–216.
Clery, H., Andersson, F., Bonnet-Brilhault, F., Philippe, A., Wicker, B., & Gomot, M. (2013). fMRI investigation of visual change detection in adults with autism. Neuroimage Clinical, 2, 303–12.
Cook, J., & Bird, G. (2012). Atypical social modulation of imitation in autism spectrum conditions. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(6), 1045–1051.
Craig, A. D. (2002). How do you feel? Interoception: the sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nature Review Neuroscience, 3, 655–666.
Critchley, H. D. (2005). Neural mechanisms of autonomic, affective, and cognitive integration. Journal of Computational Neurology, 493, 154–166.
Crone, E. A., & Dahl, R. E. (2012). Understanding adolescence as a period of social-affective engagement and goal flexibility. Nature Review Neuroscience, 13, 636–650.
Di Martino, A., Yan, C. G., Li, Q., Denio, E., Castellanos, F. X., Alaerts, K., et al. (2013). The autism brain imaging data exchange: towards large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Molecular Psychiatry, 19, 659–667.
Dickstein, D. P., Pescosolido, M. F., Reidy, B. L., Galvan, T., Kim, K. L., & Seymour, K. E. (2013). Developmental meta-analysis of the functional neural correlates of autism spectrum disorders. Journal of American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 52(3), 279–289.
Ebisch, S. J., Gallese, V., Willems, R. M., Mantini, D., Groen, W. B., Romani, G. L., et al. (2011). Altered intrinsic functional connectivity of anterior and posterior insula regions in high-functioning participants with autism spectrum disorder. Human Brain Mapping, 32(7), 1013–1028.
Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Grefkes, C., Wang, L. E., Zilles, K., & Fox, P. T. (2009). Coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of neuroimaging data: a random-effects approach based on empirical estimates of spatial uncertainty. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 2907–2926.
Fecteau, S., Lepage, J. F., & Theoret, H. (2006). Autism spectrum disorder: seeing is not understanding. Current Biology, 16, R131–R133.
Fishman, I., Keown, C. L., Lincoln, A. J., Pineda, J. A., Müller, R. A. (2014). Atypical cross talk between mentalizing and mirror neuron networks in autism spectrum disorder. JAMA Psychiatry, 71, 751–760.
Fletcher, P. C., Happe, F., Frith, U., Baker, S. C., Dolan, R. J., Frackowiak, R. S., & Frith, C. D. (1995). Other minds in the brain: a functional imaging study of “theory of mind” in story comprehension. Cognition, 57, 109–128.
Fogassi, L., Ferrari, P. F., Gesierich, B., Rozzi, S., Chersi, F., & Rizzolatti, G. (2005). Parietal lobe: from action organization to intention understanding. Science, 308, 662–667.
Freitag, C. M., Konrad, C., Häberlen, M., Kleser, C., von Gontard, A., Reith, W., et al. (2008). Perception of biological motion in autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychologia, 46, 1480–1494.
Gallese, V., & Goldman, A. (1998). Mirror neurons and the simulation theory of mind-reading. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2, 493–501.
Gallese, V., Fadiga, L., Fogassi, L., & Rizzolatti, G. (1996). Action recognition in the premotor cortex. Brain, 119, 593–609.
Gallese, V., Keysers, C., & Rizzolatti, G. (2004). A unifying view of the basis of social cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 396–403.
Gallese, V., Rochat, M., Cossu, G., & Sinigaglia, C. (2009). Motor cognition and its role in the phylogeny and ontogeny of action understanding. Developmental Psychology, 45(1), 103–113.
Grecucci, A., Brambilla, P., Siugzdaite, R., Londero, D., Fabbro, F., & Rumiati, R. I. (2012). Emotional resonance deficits in autistic children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 43(3), 616–628.
Greene, J. D., Sommerville, R. B., Nystrom, L. E., Darley, J. M., & Cohen, J. D. (2001). An fMRI investigation of emotional engagement in moral judgment. Science, 293(5537), 2105–2108.
Grèzes, J., Wicker, B., Berthoz, S., de Gelder, B., & Grezes, J. (2009). A failure to grasp the affective meaning of actions in autism spec- trum disorder subjects. Neuropsychologia, 47, 1816–1825.
Hamilton, A. F. (2013). Reflecting on the mirror neuron system in autism: a systematic review of current theories. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 3, 91–105.
Hubbard, A. L., McNealy, K., Scott-Van Zeeland, A. A., Callan, D. E., Bookheimer, S. Y., Dapretto, M. (2012). Altered integration of speech and gesture in children with autism spectrum disorders. Brain and Behavior, 2, 606–619.
Iacoboni, M. (2005). Neural mechanisms of imitation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15, 632–637.
Iacoboni, M. (2009). Imitation, empathy, and mirror neurons. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 653–670.
Iacoboni, M., & Dapretto, M. (2006). The mirror neuron system and the consequences of its dysfunction. Nature Review of Neuroscience, 7, 942–951.
Ingersoll, B. (2007). The effect of context on imitation skills in children with autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2(2), 332–340.
Ingersoll, B., Schreibman, L., & Tran, Q. H. (2003). Effect of sensory feedback on immediate object imitation in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33(6), 673–683.
Jack, A., & Morris, J. P. (2014). Neocerebellar contributions to social perception in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 10, 77–92.
Keysers, C., Kaas, J. H., & Gazzola, V. (2010). Somatosensation in social perception. Nature Review Neuroscience, 11, 417–428.
Koldewyn, K., Whitney, D., & Rivera, S. M. (2010). The psychophysics of visual motion and global form processing in autism. Brain, 133(Pt 2), 599–610.
Laird, A. R., Fox, M., Price, C. J., Glahn, D. C., Uecker, A. M., Lancaster, J. L., et al. (2005). ALE meta-analysis: controlling the false discov- ery rate and performing statistical contrasts. Human Brain Mapping, 25, 155–164.
Lancaster, J. L., Tordesillas-Gutiérrez, D., Martinez, M., Salinas, F., Evans, A., Zilles, K., et al. (2007). Bias between MNI and Talairach coordinates analyzed using the ICBM-152 brain template. Human Brain Mapping, 28, 1194–1205.
Libero, L. E., Maximo, J. O., Deshpande, H. D., Klinger, L. G., Klinger, M. R., & Kana, R. K. (2014a). The role of mirroring and mentalizing networks in mediating action intentions in autism. Molecular Autism, 5, 50.
Libero, L. E., Stevens, C. E., Jr., & Kana, R. K. (2014b). Attribution of emotions to body postures: an independent component analysis study of functional connectivity in autism. Human Brain Mapping, 35, 5204–5218.
Mansouri, F. A., Buckley, M. J., & Tanaka, K. (2007). Mnemonic function of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in conflict-induced behavioral adjustment. Science, 318(5852), 987–990.
Marsh, L., & Hamilton, A. F. C. (2011). Dissociation of mirroring and mentalising systems in autism. NeuroImage, 56(3), 1511–1519.
Martineau, J., Andersson, F., Barthélémy, C., Cottier, J.-P. P., & Destrieux, C. (2010). Atypical activation of the mirror neuron system dur- ing perception of hand motion in autism. Brain Research, 1320, 168–175.
McKay, L. S., Simmons, D. R., McAleer, P., Marjoram, D., Piggot, J., & Pollick, F. E. (2012). Do distinct atypical cortical networks process biological motion information in adults with autism spectrum disorders? NeuroImage, 59, 1524–1533.
Milne, E., Swettenham, J., Hansen, P., Campbell, R., Jeffries, H., & Plaisted, K. (2002). High motion coherence thresholds in children with autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43(2), 255–263.
Monsell, S. (2003). Task switching. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(3), 134–140.
Oberman, L. M., & Ramachandran, V. S. (2007). The simulating social mind: the role of the mirror neuron system and simulation in the social and communicative deficits of autism spectrum disorders. Psychological Bulletin, 133, 310–327.
Okamoto, Y., Kitada, R., Tanabe, H. C., Hayashi, M. J., Kochiyama, T., Munesue, T., et al. (2014). Attenuation of the contingency detection effect in the extrastriate body area in autism spectrum disorder. Neuroscience Research, 87, 66–76.
Penny, W. D., & Holmes, A. P. (2004). Random effects analysis. In R. S. J. Frackowiak, K. J. Friston, R. Frith, K. J. Dolan, C. J. Price, S. Zeki, J. Ashburner, & W. D. Penny (Eds.), Human brain function (pp. 843–850). San Diego: Academic.
Perkins, T. J., Bittar, R. G., McGillivray, J. A., Cox, I. I., & Stokes, M. A. (2015). Increased premotor cortex activation in high functioning autism during action observation. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 22(4), 664–669.
Poulin-Lord, M. P., Barbeau, E. B., Soulières, I., Monchi, O., Doyon, J., Benali, H., et al. (2014). Increased topographical variability of task-related activation in perceptive and motor associative regions in adult autistics. Neuroimage Clinical, 4, 444–453.
Priori, A., Mameli, F., Cogiamanian, F., Marceglia, S., Tiriticco, M., Mrakic-Sposta, S., et al. (2008). Lie-specific involvement of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in deception. Cerebral Cortex, 18, 451–455.
Ramsey, R., & Hamilton, A. F. (2012). How does your own knowledge influence the perception of another person’s action in the human brain? Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 7, 242–251.
Rizzolatti, G. (2005). The mirror neuron system and its function in humans. Anatomy and Embryology, 210, 419–421.
Rizzolatti, G., & Craighero, L. (2004). The mirror-neuron system. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 27, 169–192.
Rizzolatti, G., & Sinigaglia, C. (2010). The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations. Nature Review Neuroscience, 11, 264–274.
Rizzolatti, G., Fadiga, L., Gallese, V., & Fogassi, F. (1996). Premotor cortex and the recognition of motor actions. Cognitive Brain Research, 3(2), 131–141.
Rizzolatti, G., Fogassi, L., & Gallese, V. (2001). Neurophysiological mechanisms under- lying the understanding and imitation of action. Nature Review Neuroscience, 2, 661–670.
Rizzolatti, G., Fabbri-Destro, M., & Cattaneo, L. (2009). Mirror neurons and their clinical relevance. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology, 5, 24–34.
Rozzi, S., Ferrari, P. F., Bonini, L., Rizzolatti, G., & Fogassi, L. (2008). Functional organization of inferior parietal lobule convexity in the macaque monkey: electrophysiological characterization of motor, sensory and mirror responses and their correlation with cytoarchitectonic areas. European Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 1569–1588.
Saxe, R., & Kanwisher, N. (2003). People thinking about thinking people: the role of the temporo-parietal junction in “theory of mind. NeuroImage, 19, 1835–1842.
Seminowicz, D. A., & Davis, K. D. (2007). Interactions of pain intensity and cognitive load: the brain stays on task. Cerebral Cortex, 17, 1412–1422.
Shmuelof, L., & Zohary, E. (2007). Watching others’ actions: mirror representations in the parietal cortex. The Neuroscientist, 13, 667–672.
Spunt, R. P., Satpute, A. B., & Lieberman, M. D. (2011). Identifying the what, why, and how of an observed action: an fMRI study of mentalizing and mechanizing during action observation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23, 63–74.
Takarae, Y., Minshew, N. J., Luna, B., Krisky, C. M., & Sweeney, J. A. (2004). Pursuit eye movement deficits in autism. Brain, 127(Pt 12), 2584–2594.
Talairach, J., & Tournoux, P. (1988). Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain: 3-dimensional proportional system: An approach to cerebral imaging. Stuttgart: G. Thieme.
Taylor, K. S., Seminowicz, D. A., & Davis, K. D. (2008). Two systems of resting state connectivity between the insula and cingulate cortex. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 2731–2745.
Turkeltaub, P. E., Eden, G. F., Jones, K. M., & Zeffiro, T. A. (2002). Meta-analysis of the functional neuroanatomy of single-word reading: method and validation. NeuroImage, 16, 765–780.
Ubaldi, S., Barchiesi, G., & Cattaneo, L. (2015). Bottom-up and top-down visuomotor responses to action observation. Cerebral Cortex, 25(4), 1032–41.
Uddin, L. Q., Supekar, K., & Menon, V. (2013). Reconceptualizing functional brain connectivity in autism from a developmental perspective. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 458.
Williams, J. H., Whiten, A., Suddendorf, T., & Perrett, D. I. (2001). Imitation, mirror neurons and autism. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 25, 287–295.
Williams, J. H. G., Whiten, A., & Singh, T. (2004). A systematic review of action imitation in autistic spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(3), 285–299.
Williams, J. H. G., Waiter, G. D., Gilchrist, A., Perrett, D. I., Murray, A. D., & Whiten, A. (2006). Neural mechanisms of imitation and mirror neuron functioning in autistic spectrum disorder. Neuropsychologia, 44(4), 610–621.
Funding
This study was funded by Macquarie University (grant number 9201401500).
Compliance with ethical standards
ᅟ
Conflict of interest
Author Jie Yang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Jessica Hofmann declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
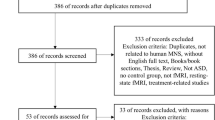
Supplementary Figure 1
The paper selection procedure of the current meta-analysis. (GIF 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Hofmann, J. Action observation and imitation in autism spectrum disorders: an ALE meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 960–969 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9456-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9456-7