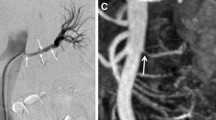
Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to investigate the efficacy and safety of percutaneous renal denervation with the Symplicity catheter for reducing blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension resistant to medical therapy (systolic blood pressure >160 mmHg despite the use of three or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic).
Materials and methods
In September 2010, five patients affected by essential hypertension resistant to medical therapy were treated. All patients were studied by computed tomography angiography (CTA) of the renal arteries before the procedure and underwent follow-up at 30 and 60 days with colour Doppler ultrasound (CDUS) with evaluation of resistive index, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), 24-h blood pressure and serum catecholamine concentration. Student’s t test was used to assess the effectiveness of the procedure in lowering blood pressure.
Results
In treated patients, mean blood pressure at baseline was 171/100 mmHg [standard deviation (SD)±8/10]; mean GFR was 91.6 ml/min/1.73 m2 (SD±15). Blood pressure after the procedure was reduced by −18/−5 and −13/−10 mmHg at 30 and 60 days, respectively, with a mean medication reduction of 3.6. No complications occurred during the intra- or periprocedural period or during short-term follow-up.
Conclusions
The Symplicity system proved to be efficacious and without serious adverse events in reducing blood pressure and antihypertensive medication use in patients affected by essential hypertension resistant to medical therapy. Although encouraging, our data are preliminary and need to be validated by larger prospective randomised studies.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Scopo del presente studio è stato valutare l’efficacia e la sicurezza della procedura di simpaticectomia renale percutanea a radiofrequenza mediante catetere Symplicity nel ridurre la pressione arteriosa sistemica in pazienti con ipertensione essenziale resistenti alla terapia farmacologica convenzionale (pressione sistolica>160 mmHg con 3 o più farmaci antiipertensivi, incluso diuretico).
Materiali e metodi
Nel mese di settembre 2010, sono stati trattati 5 pazienti affetti da ipertensione arteriosa essenziale non rispondenti a terapia. È stata eseguita angio-tomografia computerizzata (TC) delle arterie renali pre-procedurale e follow-up a 30 e 60 giorni con eco-color Doppler, valutazione degli indici di resistenza, del filtrato glomerulare, monitoraggio della pressione arteriosa nelle 24 ore e misurazione della catecolaminemia. L’analisi dei dati è stata effettuata mediante il test t di Student.
Risultati
I valori pressori medi basali della popolazione erano 171/100 mmHg [deviazione standard (DS)±8/10], con filtrato glomerulare medio di 91,6 ml/min/1,73 m2 (DS±15). Il decremento pressorio medio post-procedurale è stato di −18/−5 mmHg e −13/−10 mmHg a 30 e 60 giorni con riduzione media di 3,6 farmaci. Non vi sono state complicanze intra-/peri-procedurali e nel successivo follow-up a breve termine.
Conclusioni
Il sistema Symplicity si è dimostrato efficace nel ridurre i livelli pressori e la somministrazione dei farmaci anti-ipertensivi, in assenza di evidenti eventi avversi. Nonostante incoraggianti premesse, sarà necessario validare i preliminari dati ottenuti mediante più ampi studi prospettici randomizzati.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M et al (2009) Heart disease and stroke statistics — 2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 119:480–486
Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S et al (2008) Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional research. Hypertension 51:1403–1419
Pisoni R, Ahmed MI, Calhoun DA (2009) Characterization and treatment of resistant hypertension. Curr Cardiol Rep 11:407–413
Armario P, Oliveras A, Hernàndez Del Rey R et al (2009) Prevalence of target organ damage and factors associated with cardiovascular events in subjects with refractory hypertension. Med Clin (Barc) 133:127–131
Morissey DM, Brookes VS, Cooke WT (1953) Sympathectomy in the treatment of hypertension; review of 122 cases. Lancet 1:403–408
Schlaich MP, Socratous F, Hennebry S et al (2009) Sympathetic activation in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:933–939
Malpas SC (2009) Sympathetic nervous system overactivity and its role in the development of cardiovascular disease. Physiol Rev 90:513–557
Mancia G, Bousquet P, Elghozi JL et al (2007) The sympathetic nervous system and the metabolic syndrome. J Hypertens 25:909–920
Barajas L, Liu L, Powers K (1992) Anatomy of the renal innervations: intrarenal aspects and ganglia of origin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 70:735–749
Moss N (1982) Renal function and renal afferent and efferent nerve activity. Am J Physiol 243:F425–F433
Di Bona GF, Sawin LL, Jones SY (1996) Characteristics of renal sympathetic nerve activity in sodiumretaining disorders. Am J Physiol 271:R295–R302
Burck SL, Evans RG, Head GA (2010) Effects of chronic sympathoinhibition on reflex control of renal blood flow and plasma rennin activity in renovascular hypertension. Br J Pharmacol 159:438–448
Di Bona GF (2000) Nervous kidney interaction between renal sympathetic nerves and the renin-angiotensin system in the control of renal function. Hypertension 36:1083–1088
Kopp UC, Jones Sy, Di Bona GF (2008) Afferent renal denervation impairs baro reflex control of efferent renal sympathetic nerve activity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:1882–1890
Ciriello J, de Oliveira CV (2002) Renal afferents and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 4:136–142
Schlaich MP, Sobotka AP, Krum H et al (2009) Renal sympathetic-nerve ablation for uncontrolled hypertension. N Engl J Med 361:932–934
Schlaich MP, Sobotka AP, Krum H et al (2009) Renal denervation as a therapeutic approach for hypertension: novel implications for an old concept. Hypertension 54:1195–1201
Fajardo J, Lopez-Novoa JM et al (1986) Effect of chemical sympathectomy on renal hydroelectrolytic handling in dogs with chronic caval constriction. Clin Physiol Biochem 4:252–256
le Noble JL, Janssen BJ, Lappe RW et al (1985) Pharmacological evidence for rapid destruction of efferent renal nerves in rats by intrarenal infusion of 6-hydroxydopamine. J Hypertension 38(Suppl): S137–S140
Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R et al (2009) Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet 373:1275–1281
Schlaich MP, Sobotka AP, Krum H et al (2009) Renal sympathetic nerve ablation for the treatment of uncontrolled hypertension. N Engl J Med 361:932–934
Fagius J (2003) Sympathetic nerve activity in metabolic control-some basic concepts. Acta Physiol Scand 177:337–343
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonetti, G., Spinelli, A., Gandini, R. et al. Endovascular radiofrequency renal denervation in treating refractory arterial hypertension: a preliminary experience. Radiol med 117, 426–444 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-011-0766-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-011-0766-6