Abstract
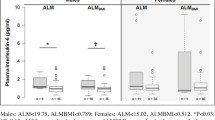
Ageing is associated with a chronic low-grade inflammatory profile (CLIP). Physical exercise could circumvent the deleterious effects of CLIP by influencing circulating inflammatory mediators and neurotrophic growth factors. This study aimed at assessing whether 12 weeks of progressive strength training (PST) influences circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-10 in elderly individuals. Forty community-dwelling persons aged 62–72 years participated. Twenty participants were assigned to 12-week PST (70–80 % of maximal strength, three times per week). Matched control individuals (n = 20) maintained daily activity levels. Serum was collected for BDNF, IL-6 and IL-10 assay from all participants before and after 12 weeks (for PST subjects 24–48 h after the last training). In PST, muscle strength was significantly improved (+49 % for leg extension, p = 0.039), and basal IL-6 levels significantly reduced (p = 0.001), which remained unchanged in control (p = 0.117). No significant change in BDNF was observed in PST subjects (p = 0.147) or control (p = 0.563). IL-10 was below the detection limit in most subjects. Gender and health status did not influence the results. Our results show that after 12-week PST, muscle performance improved significantly, and basal levels of IL-6 were significantly decreased in older subjects. However, serum BDNF was not altered. The lack of an observable change in BDNF might be due to a short-lived BDNF response, occurring acutely following exercise, which might have been washed out when sampling. Furthermore, blood levels of BDNF may not reflect parallel increases that occur locally in the brain and muscle. These hypotheses need confirmation by further studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson-Hanley C, Arciero PJ, Brickman AM, Nimon JP, Okuma N, Westen SC, Merz ME, Pence BD, Woods JA, Kramer AF, Zimmerman EA (2012) Exergaming and older adult cognition: a cluster randomized clinical trial. Am J Prev Med 42(2):109–119. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.10.016
Babaei P, Azali Alamdari K, Soltani Tehrani B, Damirchi A (2013) Effect of six weeks of endurance exercise and following detraining on serum brain derived neurotrophic factor and memory performance in middle aged males with metabolic syndrome. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 53(4):437–443
Baker LD, Frank LL, Foster-Schubert K, Green PS, Wilkinson CW, McTiernan A, Plymate SR, Fishel MA, Watson GS, Cholerton BA, Duncan GE, Mehta PD, Craft S (2010) Effects of aerobic exercise on mild cognitive impairment: a controlled trial. Arch Neurol 67(1):71–79. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2009.307
Bautmans I, Mets T (2005) A fatigue resistance test for elderly persons based on grip strength: reliability and comparison with healthy young subjects. Aging Clin Exp Res 17(3):217–222
Bautmans I, Lambert M, Mets T (2004) The six-minute walk test in community dwelling elderly: influence of health status. BMC Geriatr 4:6. doi:10.1186/1471-2318-4-6
Bautmans I, Njemini R, Vasseur S, Chabert H, Moens L, Demanet C, Mets T (2005) Biochemical changes in response to intensive resistance exercise training in the elderly. Gerontology 51(4):253–265
Beyer I, Mets T, Bautmans I (2012) Chronic low-grade inflammation and age-related sarcopenia. Curr Opin in Clin Nutr Metab Care 15(1):12–22. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834dd297
Bruunsgaard H, Bjerregaard E, Schroll M, Pedersen BK (2004) Muscle strength after resistance training is inversely correlated with baseline levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in the oldest old. J Am Geriatr Soc 52(2):237–241
Chimienti G, Mezzapesa A, Rotelli MT, Lupo L, Pepe G (2012) Plasma concentrations but not serum concentrations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor are related to pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery. Clin Biochem 45 (9):631–636. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.02.025
Cho HC, Kim J, Kim S, Son YH, Lee N, Jung SH (2012) The concentrations of serum, plasma and platelet BDNF are all increased by treadmill VO (2) max performance in healthy college men. Neurosci Lett 519(1):78–83. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.05.025
Coelho FM, Pereira DS, Lustosa LP, Silva JP, Dias JM, Dias RC, Queiroz BZ, Teixeira AL, Teixeira MM, Pereira LS (2012) Physical therapy intervention (PTI) increases plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in non-frail and pre-frail elderly women. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 54(3):415–420. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2011.05.014
Coelho FG, Gobbi S, Andreatto CA, Corazza DI, Pedroso RV, Santos-Galduroz RF (2013) Physical exercise modulates peripheral levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): a systematic review of experimental studies in the elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 56(1):10–15. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2012.06.003
Corsonello A, Garasto S, Abbatecola AM, Rose G, Passarino G, Mazzei B, Pranno L, Guffanti EE, Bustacchini S, Lattanzio F (2010) Targeting inflammation to slow or delay functional decline: where are we? Biogerontology 11(5):603–614. doi:10.1007/s10522-010-9289-0
De Vita F, Lauretani F, Bauer JM, Bautmans I, Shardell M, Cherubini A, Bondi G, Zuliani G, Bandinelli S, Perdazzoni M, Dall’ Aglio E, Ceda GP, Maggio M (2014) Relationship between vitamin D and inflammatory markers in older individuals. AGE 36: in press. doi:10.1007/s11357-014-6964-4
Dipietro L, Caspersen CJ, Ostfeld AM, Nadel ER (1993) A survey for assessing physical-activity among older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25(5):628–642
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39(2):175–191
Fayad L, Keating MJ, Reuben JM, O’Brien S, Lee BN, Lerner S, Kurzrock R (2001) Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with phenotypic characteristics and outcome. Blood 97(1):256–263
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–198
Franceschi C, Capri M, Monti D, Giunta S, Olivieri F, Sevini F, Panourgia MP, Invidia L, Celani L, Scurti M, Cevenini E, Castellani GC, Salvioli S (2007) Inflammaging and anti-inflammaging: a systemic perspective on aging and longevity emerged from studies in humans. Mech Ageing Dev 128(1):92–105
Frazzitta G, Maestri R, Ghilardi MF, Riboldazzi G, Perini M, Bertotti G, Boveri N, Buttini S, Lombino FL, Uccellini D, Turla M, Pezzoli G, Comi C (2014) Intensive rehabilitation increases BDNF serum levels in parkinsonian patients: a randomized study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 28(2):163–168. doi:10.1177/1545968313508474
Gilder M, Ramsbottom R, Currie J, Sheridan B, Nevill AM (2014) Effect of fat free mass on serum and plasma BDNF concentrations during exercise and recovery in healthy young men. Neurosci Lett 560:137–141. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2013.12.034
Giovannini S, Onder G, Liperoti R, Russo A, Carter C, Capoluongo E, Pahor M, Bernabei R, Landi F (2011) Interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha as predictors of mortality in frail, community-living elderly individuals. J Am Geriatr Soc 59 (9):1679–1685. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03570.x
Gleeson M, Bishop NC, Stensel DJ, Lindley MR, Mastana SS, Nimmo MA (2011) The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(9):607–615. doi:10.1038/nri3041
Gomes WF, Lacerda AC, Mendonca VA, Arrieiro AN, Fonseca SF, Amorim MR, Teixeira AL, Teixeira MM, Miranda AS, Coimbra CC, Brito-Melo GE (2013) Effect of exercise on the plasma BDNF levels in elderly women with knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int. doi:10.1007/s00296-013-2786-0
Greiwe JS, Cheng B, Rubin DC, Yarasheski KE, Semenkovich CF (2001) Resistance exercise decreases skeletal muscle tumor necrosis factor alpha in frail elderly humans. Faseb J 15(2):475–482
Jankord R, Jemiolo B (2004) Influence of physical activity on serum IL-6 and IL-10 levels in healthy older men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(6):960–964
Knaepen K, Goekint M, Heyman EM, Meeusen R (2010) Neuroplasticity— exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a systematic review of experimental studies in human subjects. Sports Med 40(9):765–801. doi:10.2165/11534530-000000000-00000
Laske C, Banschbach S, Stransky E, Bosch S, Straten G, Machann J, Fritsche A, Hipp A, Niess A, Eschweiler GW (2010) Exercise-induced normalization of decreased BDNF serum concentration in elderly women with remitted major depression. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology/Official Scientific Journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum 13(5):595–602. doi:10.1017/S1461145709991234
Levinger I, Goodman C, Matthews V, Hare DL, Jerums G, Garnham A, Selig S (2008) BDNF, metabolic risk factors, and resistance training in middle-aged individuals. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(3):535–541. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e31815dd057
Marx J (2005) Neuroscience preventing Alzheimer’s: a lifelong commitment? Science 309(5736):864–866. doi:10.1126/science.309.5736.864
Mathur N, Pedersen BK (2008) Exercise as a mean to control low-grade systemic inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. doi: Artn 109502; doi:10.1155/2008/109502
Matthews VB, Astrom MB, Chan MH, Bruce CR, Krabbe KS, Prelovsek O, Akerstrom T, Yfanti C, Broholm C, Mortensen OH, Penkowa M, Hojman P, Zankari A, Watt MJ, Bruunsgaard H, Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is produced by skeletal muscle cells in response to contraction and enhances fat oxidation via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetologia 52(7):1409–1418. doi:10.1007/s00125-009-1364-1
Mendham AE, Donges CE, Liberts EA, Duffield R (2011) Effects of mode and intensity on the acute exercise-induced IL-6 and CRP responses in a sedentary, overweight population. Eur J Appl Physiol 111(6):1035–1045. doi:10.1007/s00421-010-1724-z
Nakahashi T, Fujimura H, Altar CA, Li J, Kambayashi J, Tandon NN, Sun B (2000) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett 470(2):113–117
Nemunaitis J, Fong T, Shabe P, Martineau D, Ando D (2001) Comparison of serum interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels between normal volunteers and patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer Investig 19(3):239–247
Ogawa K, Sanada K, Machida S, Okutsu M, Suzuki K (2010) Resistance exercise training-induced muscle hypertrophy was associated with reduction of inflammatory markers in elderly women. Mediat Inflamm 2010:171023. doi:10.1155/2010/171023
Pan W, Banks WA, Fasold MB, Bluth J, Kastin AJ (1998) Transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood–brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 37(12):1553–1561
Pedersen BK, Bruunsgaard H (2003) Possible beneficial role of exercise in modulating low-grade inflammation in the elderly. Scand J Med Sci Sports 13(1):56–62
Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA (2012) Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(8):457–465. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2012.49
Pereira DS, de Queiroz BZ, Miranda AS, Rocha NP, Felicio DC, Mateo EC, Favero M, Coelho FM, Jesus-Moraleida F, Gomes Pereira DA, Teixeira AL, Maximo Pereira LS (2013) Effects of physical exercise on plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and depressive symptoms in elderly women–a randomized clinical trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 94(8):1443–1450. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2013.03.029
Petersen AM, Pedersen BK (2005) The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol 98(4):1154–1162
Phillips MD, Flynn MG, McFarlin BK, Stewart LK, Timmerman KL (2010) Resistance training at eight-repetition maximum reduces the inflammatory milieu in elderly women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42(2):314–325. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181b11ab7
Raschke S, Eckel J (2013) Adipo-myokines: two sides of the same coin–mediators of inflammation and mediators of exercise. Mediat Inflamm 2013:320724. doi:10.1155/2013/320724
Rasmussen P, Brassard P, Adser H, Pedersen MV, Leick L, Hart E, Secher NH, Pedersen BK, Pilegaard H (2009) Evidence for a release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from the brain during exercise. Exp Physiol 94(10):1062–1069. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2009.048512
Schiffer T, Schulte S, Hollmann W, Bloch W, Struder HK (2009) Effects of strength and endurance training on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and insulin-like growth factor 1 in humans. Horm Metab Res 41(3):250–254. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1093322
Schulte-Herbruggen O, Nassenstein C, Lommatzsch M, Quarcoo D, Renz H, Braun A (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 regulate secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human monocytes. J Neuroimmunol 160(1–2):204–209. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2004.10.026
Seifert T, Brassard P, Wissenberg M, Rasmussen P, Nordby P, Stallknecht B, Adser H, Jakobsen AH, Pilegaard H, Nielsen HB, Secher NH (2010) Endurance training enhances BDNF release from the human brain. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298(2):R372–R377. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00525.2009
Simpson RJ, Lowder TW, Spielmann G, Bigley AB, LaVoy EC, Kunz H (2012) Exercise and the aging immune system. Ageing Res Rev 11(3):404–420. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2012.03.003
Sofi F, Valecchi D, Bacci D, Abbate R, Gensini GF, Casini A, Macchi C (2011) Physical activity and risk of cognitive decline: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Intern Med 269(1):107–117. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02281.x
Steensberg A, Keller C, Starkie RL, Osada T, Febbraio MA, Pedersen BK (2002) IL-6 and TNF-alpha expression in, and release from, contracting human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283(6):E1272–E1278. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00255.2002
Swift DL, Johannsen NM, Myers VH, Earnest CP, Smits JA, Blair SN, Church TS (2012) The effect of exercise training modality on serum brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 7(8):e42785. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042785
Voss MW, Erickson KI, Prakash RS, Chaddock L, Kim JS, Alves H, Szabo A, Phillips SM, Wojcicki TR, Mailey EL, Olson EA, Gothe N, Vieira-Potter VJ, Martin SA, Pence BD, Cook MD, Woods JA, McAuley E, Kramer AF (2013) Neurobiological markers of exercise-related brain plasticity in older adults. Brain Behav Immun 28:90–99. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2012.10.021
Yamamoto H, Gurney ME (1990) Human platelets contain brain-derived neurotrophic factor. The official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 10(11):3469–3478
Ziegenhorn AA, Schulte-Herbruggen O, Danker-Hopfe H, Malbranc M, Hartung HD, Anders D, Lang UE, Steinhagen-Thiessen E, Schaub RT, Hellweg R (2007) Serum neurotrophins—a study on the time course and influencing factors in a large old age sample. Neurobiol Aging 28(9):1436–1445. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.011
Zoladz JA, Pilc A (2010) The effect of physical activity on the brain derived neurotrophic factor: from animal to human studies. An official journal of the Polish Physiological Society 61(5):533–541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Forti, L.N., Njemini, R., Beyer, I. et al. Strength training reduces circulating interleukin-6 but not brain-derived neurotrophic factor in community-dwelling elderly individuals. AGE 36, 9704 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9704-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9704-6