Abstract
Purpose
Growing awareness of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) has increased the need for concise and reliable screening tools. The Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS) has been validated in numerous languages and ethnic groups, since it was originally designed for the English-speaking population. The STOP questionnaire was developed as a novel OSAS screening tool in surgical patients, but has not been validated in the general population. The present study was undertaken to provide reliable and validated ESS in the Croatian language and to evaluate the ESS and STOP as screening instruments for OSAS.
Methods
The Croatian version of ESS and STOP questionnaire was administered to 217 patients referred to the Split Sleep Medicine Center and 208 healthy control subjects. Test–retest reliability was investigated in 20 healthy subjects.
Results
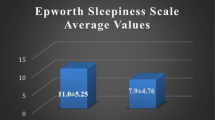
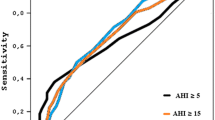
The ESS score was significantly higher for the patients referred to the Split Sleep Medicine Center compared to the control group (8.2 ± 5.0 vs. 5.9 ± 3.8, p < 0.001). Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the ESS Croatian version was 0.84 indicating an excellent internal consistency. Reproducibility revealed no significant difference in each item or in the total ESS scores. Receiver operating curve of the ESS for identification of cases with AHI >5/h was 0.64, and for the STOP questionnaire, it was 0.84.
Conclusions
Both ESS and STOP questionnaires successfully distinguished healthy subjects from subjects with OSAS. The STOP questionnaire had better probability to correctly predict high-risk patients for OSAS compared to ESS. We propose that the STOP questionnaire could be used as an easy-to-use and accurate screening tool in identification of patients with risk for OSAS in the general population, but it has not been tested in the Croatian population yet.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Johns MW (1993) Daytime sleepiness, snoring, and obstructive sleep apnea. The Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Chest 103:30–36
Basta M, Lin HM, Pejovic S, Sarrigiannidis A, Bixler E, Vgontzas AN (2008) Lack of regular exercise, depression, and degree of apnea are predictors of excessive daytime sleepiness in patients with sleep apnea: sex differences. J Clin Sleep Med 4:19–25
Fry JM (1998) Treatment modalities for narcolepsy. Neurology 50:S43–48
Roth T, Drake C (2004) Evolution of insomnia: current status and future direction. Sleep Med 5(Suppl 1):S23–30
Lavault S, Dauvilliers Y, Drouot X, Leu-Semenescu S, Golmard JL, Lecendreux M, Arnulf I (2011) Benefit and risk of modafinil in idiopathic hypersomnia vs. narcolepsy with cataplexy. Sleep Med 12:550–556
Kallweit U, Khatami R, Pizza F, Mathis J, Bassetti CL (2010) Dopaminergic treatment in idiopathic restless legs syndrome: effects on subjective sleepiness. Clin Neuropharmacol 33:276–278
Stroe AF, Roth T, Jefferson C, Hudgel DW, Roehrs T, Moss K, Drake CL (2010) Comparative levels of excessive daytime sleepiness in common medical disorders. Sleep Med 11:890–896
Bixler E (2009) Sleep and society: an epidemiological perspective. Sleep Med 10(Suppl 1):S3–6
Nguyen AT, Baltzan MA, Small D, Wolkove N, Guillon S, Palayew M (2006) Clinical reproducibility of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. J Clin Sleep Med 2:170–174
Bloch KE, Schoch OD, Zhang JN, Russi EW (1999) German version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Respiration 66:440–447
Chen NH, Johns MW, Li HY, Chu CC, Liang SC, Shu YH, Chuang ML, Wang PC (2002) Validation of a Chinese version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Qual Life Res 11:817–821
Vignatelli L, Plazzi G, Barbato A, Ferini-Strambi L, Manni R, Pompei F, D'Alessandro R (2003) Italian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale: external validity. Neurol Sci 23:295–300
Tsara V, Serasli E, Amfilochiou A, Constantinidis T, Christaki P (2004) Greek version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath 8:91–95
Izci B, Ardic S, Firat H, Sahin A, Altinors M, Karacan I (2008) Reliability and validity studies of the Turkish version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath 12:161–168
Beiske KK, Kjelsberg FN, Ruud EA, Stavem K (2009) Reliability and validity of a Norwegian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep Breath 13:65–72
Takegami M, Suzukamo Y, Wakita T, Noguchi H, Chin K, Kadotani H, Inoue Y, Oka Y, Nakamura T, Green J, Johns MW, Fukuhara S (2009) Development of a Japanese version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (JESS) based on item response theory. Sleep Med 10:556–565
Kopitovic I, Trajanovic N, Prodic S, Drvenica MJ, Ilic M, Kuruc V, Kojicic M (2010) The Serbian version of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep Breath. doi:10.1007/s11325-010-0435-3
Abrishami A, Khajehdehi A, Chung F (2010) A systematic review of screening questionnaires for obstructive sleep apnea. Can J Anaesth 57:423–438
Choi JB, Nelesen R, Loredo JS, Mills PJ, Ancoli-Israel S, Ziegler MG, Dimsdale JE (2006) Sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnea: a harbinger of impaired cardiac function? Sleep 29:1531–1536
Santaolalla Montoya F, Iriondo Bedialauneta JR, Aguirre Larracoechea U, Martinez Ibarguen A, Sanchez Del Rey A, Sanchez Fernandez JM (2007) The predictive value of clinical and epidemiological parameters in the identification of patients with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA): a clinical prediction algorithm in the evaluation of OSA. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264:637–643
Mulgrew AT, Fox N, Ayas NT, Ryan CF (2007) Diagnosis and initial management of obstructive sleep apnea without polysomnography: a randomized validation study. Ann Intern Med 146:157–166
Chung F, Yegneswaran B, Liao P, Chung SA, Vairavanathan S, Islam S, Khajehdehi A, Shapiro CM (2008) STOP questionnaire: a tool to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology 108:812–821
Gander PH, Marshall NS, Harris R, Reid P (2005) The Epworth Sleepiness Scale: influence of age, ethnicity, and socioeconomic deprivation. Epworth Sleepiness scores of adults in New Zealand. Sleep 28:249–253
Sanford SD, Lichstein KL, Durrence HH, Riedel BW, Taylor DJ, Bush AJ (2006) The influence of age, gender, ethnicity, and insomnia on Epworth sleepiness scores: a normative US population. Sleep Med 7:319–326
Banhiran W, Assanasen P, Nopmaneejumruslers C, Metheetrairut C (2010) Epworth sleepiness scale in obstructive sleep disordered breathing: the reliability and validity of the Thai version. Sleep Breath. doi:10.1007/s11325-010-0405-9
Walter TJ, Foldvary N, Mascha E, Dinner D, Golish J (2002) Comparison of Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores by patients with obstructive sleep apnea and their bed partners. Sleep Med 3:29–32
Ross SD, Sheinhait IA, Harrison KJ, Kvasz M, Connelly JE, Shea SA, Allen IE (2000) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature regarding the diagnosis of sleep apnea. Sleep 23:519–532
Gottlieb DJ, Whitney CW, Bonekat WH, Iber C, James GD, Lebowitz M, Nieto FJ, Rosenberg CE (1999) Relation of sleepiness to respiratory disturbance index: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:502–507
Fong SY, Ho CK, Wing YK (2005) Comparing MSLT and ESS in the measurement of excessive daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. J Psychosom Res 58:55–60
Subramanian S, Hesselbacher SE, Aguilar R, Surani SR (2010) The NAMES assessment: a novel combined-modality screening tool for obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. doi:10.1007/s11325-010-0443-3
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jelena Baricevic for her technical assistance; professor Goran Racic from the Department of ENT, Head and Neck Surgery, Split University Hospital, Split, Croatia, for patient recruitment and all participating patients for their cooperation; and Jasmina Rogulj, Prof., MSc., from the University of Split School of Medicine, for the language correction of the manuscript. This work has been supported by the Croatian Ministry of Science, Education and Sport grants 216-2163166-0513 and 216-2163166-3342.
Declaration of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1

Appendix 2

Appendix 3

Appendix 4

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pecotic, R., Dodig, I.P., Valic, M. et al. The evaluation of the Croatian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale and STOP questionnaire as screening tools for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 16, 793–802 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0578-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0578-x