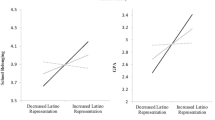
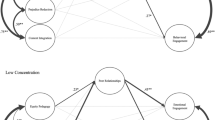
Abstract
In this paper we discuss the social identity processes by which discrimination can have an impact on ethnic-racial minority group students’ academic engagement. After considering the forms, targets and sources of discrimination, we argue that discrimination implies social identity threat. Threats to ethnic/racial identity compromise specific social identity needs (belongingness, esteem, control) which relate to important motives for academic engagement and performance. Minority students seek to cope with their threatened ethnic/racial identity, and increased engagement as well as protective disengagement with the academic domain, at both the individual level and the group level, are discussed as coping strategies. We also briefly consider the possible moderating roles of individual differences in the subjective importance of one’s ethnic or racial group membership, and of three classroom characteristics: classroom composition, student–teacher relation, and multicultural education. We conclude by providing directions for future research and consider some practical implications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, R. (2001). Building on the foundation of general strain theory: Specifying the types of strain most likely to lead to crime and delinquency. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 38, 319–361.
Ainsworth-Darnell, J. W., & Downey, D. B. (1998). Assessing the oppositional culture explanation for racial/ethnic differences in school performance. American Sociological Review, 63, 536–553.
Altschul, I., Oyserman, D., & Bybee, D. (2006). racial-ethnic identity in mid-adolescence: Content and change as predictors of academic achievement. Child Development, 77, 1155–1169.
Armenta, B. E., & Hunt, J. S. (2009). Responding to societal devaluation: Effects of perceived personal and group discrimination on the ethnic group identification and personal self-esteem of Latino/Latina adolescents. Group Processes and Intergroup Relations, 12, 23–39.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company.
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1995). The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 497–529.
Bayram Özdemir, S., & Stattin, H. (2014). Why and when is ethnic harassment a risk for immigrant adolescents’ school adjustment? Understanding the processes and conditions. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 43, 1252–1265.
Baysu, G., Celeste, L., Brown, R., Verschueren, K., & Phalet, K. (2016). Minority adolescents in ethnically diverse schools: Perceptions of equal treatment buffer threat effects. Child Development, 87, 1352–1366. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12609.
Begeny, C. T., & Huo, Y. J. (2017). When identity hurts: How positive intragroup experiences can yield negative mental health implications for ethnic and sexual minorities. European Journal of Social Psychology, 47, 803–817.
Benner, A. (2017). The toll of racial/ethnic discrimination on adolescents’ adjustment. Child Development Perspective, 11, 251–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12241.
Benner, A. D., & Graham, S. (2013). The antecedents and consequences of racial/ethnic discrimination during adolescence: Does the source of discrimination matter? Developmental Psychology, 49, 1602–1613.
Berkel, C., Knight, G. P., Zeiders, K. H., Tein, J. Y., Roosa, M. W., Gonzales, N. A., et al. (2010). Discrimination and adjustment for Mexican American adolescents: A prospective examination of the benefits of culturally related values. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 20, 893–915.
Breakwell, G. M. (1986). Coping with threatened identities. London: Routledge.
Brody, G. H., Miller, G. E., Yu, T., Bech, S. R. H., & Chen, E. (2016). Supportive family environments ameliorate the link between racial discrimination and epigenetic aging: A replication across two longitudinal cohorts. Psychological Science, 27, 530–541. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615626703.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Brown, C. S. (2017). Discrimination in childhood and adolescence: A developmental intergroup approach. New York: Routledge.
Brown, C. S., Alabi, B. O., Huynh, V. W., & Masten, C. L. (2011). Ethnicity and gender in late childhood and early adolescence: Group identity and awareness of bias. Developmental Psychology, 47, 463–471.
Brown, C. S., & Bigler, R. (2005). Children’s perceptions of discrimination: A developmental model. Child Development, 76, 533–553.
Brown, C. S., & Chu, H. (2012). Discrimination, ethnic identity, and academic outcomes of Mexican immigrant children: The importance of school context. Child Development, 83, 1477–1485.
Buhs, E. S., Ladd, G. W., & Herald, S. L. (2006). Peer exclusion and victimization: Processes that mediate the relation between peer group rejection and children’s classroom engagement and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.1.1.
Butler-Barnes, S. T., Chavous, T. M., Hurd, N., & Varner, F. (2013). African American adolescents’ academic persistence: A strengths-based approach. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 42, 1443–1458.
Byrd, C. M., & Carter Andrews, D. J. (2016). Variations in students’ perceived reasons for, sources of, and forms of in-school discrimination: A latent class analysis. Journal of School Psychology, 57, 1–14.
Chavous, T. M., Rivas-Drake, D., Smalls, C., Griffin, T., & Cogburn, C. (2008). Gender matters, too: The influences of school racial discrimination and racial identity on academic engagement outcomes among African American adolescents. Developmental Psychology, 44, 637–654.
Cogburn, C. D., Chavous, T. M., & Griffin, T. M. (2011). School-based racial and gender discrimination among African American adolescents: Exploring gender variation in frequency and implications for adjustment. Race and Social Problems, 3, 25–37.
Connell, J. P., & Wellborn, J. G. (1991). Competence, autonomy, and relatedness: A motivational analysis of self-system processes. In M. R. Gunnar & L. A. Sroufe (Eds.), Self processes and development (Vol. 23, pp. 43–77). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Cook, P. J., & Ludwig, J. (1998). The burden of “acting White”: Do Black adolescents disparage academic achievement? In C. Jencks & M. Phillips (Eds.), The black-white test score gap (pp. 375–400). Washington, DC: The Brookings Institution.
Coutinho, M. T., & Koinis-Mitchell, D. (2014). Black immigrants and school engagement: Perceptions of discrimination, ethnic identity, and American identity. Journal of Black Psychology, 40, 520–538.
Crocker, J., & Major, B. (1989). Social stigma and self-esteem: The self-protective properties of stigma. Psychological Review, 96, 608–630.
Crocker, J., Major, B., & Steele, C. (1998). Social stigma. In D. T. Gilbert, S. T. Fiske, & G. Lindzey (Eds.), The handbook of social psychology (4th ed., Vol. 2, pp. 504–553). Boston: McGraw-Hill.
D’hondt, F., Eccles, J. S., van Houtte, M., & Stevens, P. A. J. (2016). Perceived ethnic discrimination by teachers and ethnic minority students’ academic futility: Can parents prepare their youth for better or for worse? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45, 1–15.
Deaux, K., Bikmen, N., Gilkes, A., Ventuneac, A., Joseph, Y., Payne, Y. A., et al. (2007). Becoming American: Stereotype threat effects in Afro-Caribbean immigrant groups. Social Psychology Quarterly, 70, 384–404.
Downey, D. B. (2008). Black/white differences in school performance: The oppositional culture explanation. Annual Review of Sociology, 34, 107–126.
Downey, D. B., & Ainsworth-Darnell, J. W. (2002). The search for oppositional culture among black students. American Sociological Review, 67, 156–164.
Eccles, J. S., Adler, T. F., & Meece, J. L. (1984). Sex differences in achievement: A test of alternate theories. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46, 26–43.
Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Motivational beliefs, values, and goals. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 109–132.
Eccles, J. S., Wong, C. A., & Peck, S. C. (2006). Ethnicity as a social context for the development of African-American adolescents. Journal of School Psychology, 44, 407–426.
Ellemers, N., Spears, R., & Doosje, B. (2002). Self and social identity. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 161–186.
Elliot, A. J. (1999). Approach and avoidance motivation and achievement goals. Educational Psychologist, 34, 169–189.
Elliot, A. J., & Covington, M. V. (2001). Approach and avoidance motivation. Educational Psychology Review, 13, 73–92.
Faircloth, B. S., & Hamm, J. V. (2005). Sense of belonging among high school students representing four ethnic groups. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 34, 293–309.
Farkas, G., Lleras, C., & Maczuga, S. (2002). Comment: Does oppositional culture exist in minority poverty peer groups? American Sociological Review, 67, 148–155.
Finn, J. D., & Zimmer, K. S. (2012). Student engagement: What is it? Why does it matter? In S. L. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 97–131). New York: Springer.
Fordham, S. (1988). Racelessness as a factor in Black’s students school success: Pragmatic strategy or pyrrhic victory? Harvard Educational Review, 58, 54–84.
Fordham, S., & Ogbu, J. (1986). Black students’ school success: Coping with the “burden of acting white”. Urban Review, 18, 176–206.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74, 59–109.
Fuligni, A. (2001). A comparative longitudinal approach to acculturation among children from immigrant families. Harvard Educational Review, 71, 566–578.
Furrer, C., & Skinner, E. (2003). Sense of relatedness as a factor in children’s academic engagement and performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95, 148–162.
Gougis, R. A. (1986). The effects of prejudice and stress on the academic performance of Black-Americans. In U. Neisser (Ed.), The school achievement of minorit children: New perspectives (pp. 145–158). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Graham, S. (2006). Peer victimization in school: Exploring the ethnic context. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 15, 317–321.
Griffin, C. B., Cooper, S. M., Metzger, I. W., & Golden, A. R. (2017). School racial climate and the academic achievement of African American high school students: The mediating role of school engagement. Psychology in the Schools, 54, 673–688. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22026.
Harris, A. L. (2006). I (don’t) hate school: Revisiting oppositional culture theory of Black’s resistance to schooling. Social Forces, 85, 797–834.
Harris, A. L., & Robinson, K. (2007). Schooling behaviors or prior skills? A cautionary tale of omitted variable bias within oppositional culture theory. Sociology of Education, 80, 139–157.
Harter, S. (1999). The construction of the self. New York: The Guilford Press.
Hughes, D., Del Toro, J., Harding, J. F., Way, N., & Rarick, J. R. D. (2016). Trajectories of discrimination across adolescence: Associations with academic, psychological, and behavioral outcomes. Child Development, 87, 1337–1351. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12591.
Huynh, V. W., & Fuligni, A. (2010). Discrimination hurts: The academic, psychological, and physical well-being of adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 20, 916–941.
Kaiser, C. R., & Pratt-Hyatt, J. S. (2009). Distributing prejudice unequally: Do Whites direct their prejudice toward strongly identified minorities? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 96, 432–445.
Liebkind, K., & Jasinskaja-Lahti, I. (2000). The influence of experiences of discrimination on psychological stress: A comparison of seven immigrant groups. Journal of Community & Applied Social Psychology, 10, 1–16.
Liebkind, K., Jasinskaja-Lahti, I., & Solheim, E. (2004). Cultural identity, perceived discrimination, and parental support as determinants of immigrants’ school adjustments: Vietnamese youth in Finland. Journal of Adolescent Research, 19, 635–656.
Major, B., Quinton, W. J., & Schmader, T. (2003). Attributions to discrimination and self-esteem: Impact of group identification and situational ambiguity. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 39(3), 220–231.
Major, B., Spencer, S., Schmader, T., Wolfe, C., & Crocker, J. (1998). Coping with negative stereotypes about intellectual performance: The role of psychological disengagement. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 24, 34–50.
Masten, A. S. (2001). Ordinary magic: Resilience processes in development. American Psychologist, 56, 227–238.
McKown, C., & Weinstein, R. S. (2003). The development and consequences of stereotype consciousness in middle childhood. Child Development, 74, 498–515.
Mendoza-Denton, R., Downey, G., Purdie, V., Davis, A., & Pietrzak, J. (2002). Sensitivity to status-based rejection: Implications for African-American students’ college experience. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 83, 896–918. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.83.4.896.
Motti-Stefanidi, F., & Masten, A. S. (2013). School success and school engagement of immigrant children and adolescents. European Psychologist, 18, 126–135.
Mroczkowski, A. L., & Sánchez, B. (2015). The role of racial discrimination in the economic value of education among urban, low-income Latina/o youth: Ethnic identity and gender as moderators. American Journal of Community Psychology, 56, 1–11.
Niemiec, C. P., & Ryan, R. M. (2009). Autonomy, competence, and relatedness in the classroom: Applying self-determination theory to educational practice. Theory and Research in Education, 7, 133–144.
Ogbu, J. U. (2003). Black American students in an affluent suburb: A study of academic disengagement. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Okonofua, J. A., & Eberhardt, J. L. (2015). Two strikes: Race and the disciplining of young students. Psychological Science, 26(5), 617–624. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615570365.
Osborne, J. (1997). Race and academic disidentification. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89, 231–241.
Pascoe, E. A., & Smart Richman, L. (2009). Perceived discrimination and health: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 135, 531–554.
Perreira, K., Fuligni, A., & Potochnick, S. (2010). Fitting in: The roles of social acceptance and discrimination in shaping the academic motivations of Latino youth in the US southeast. Journal of Social Issues, 66, 131–153.
Phalet, K., & Claes, W. (1993). A comparative study of Turkish and Belgian youth. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 24, 319–343.
Phinney, J. S. (1989). Stages of ethnic identity development in minority group adolescents. Journal of Early Adolescence, 9, 34–49.
Powell, C. L., & Arriola, K. R. J. (2003). Relationship between psychosocial factors and academic achievement among African American students. The Journal of Educational Research, 96, 175–181.
Quinn, D. M., Kallen, R. W., & Spencer, S. J. (2010). Stereotype threat. In J. F. Dovidio, M. Hewstone, P. Glick, & V. M. Esses (Eds.), The Sage handbook of prejudice, stereotyping and discrimination (pp. 379–394). London: Sage.
Quintana, S. M. (2007). Racial and ethnic identity: Developmental perspectives and research. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 54, 259–270.
Reeve, J. (2012). A self-determination theory perspective on student engagement. In S. L. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 149–172). New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-2018-7.
Reschly, A. L., & Christenson, S. L. (2012). Jingle, jangle, and conceptual haziness: Evolution and future directions of the motivational construct. In S. L. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 3–19). New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-2018-7.
Richman, L. S., & Leary, M. R. (2009). Reactions to discrimination, stigmatization, ostracism, and other forms of interpersonal rejection: A multimotive model. Psychological Bulletin, 116, 365–383.
Rivas-Drake, D., Seaton, E. K., Markstrom, C., Quintana, S., Syed, M., Lee, R. M., et al. (2014). Ethnic and racial identity in adolescence: Implications for psychosocial, academic, and health outcomes. Child Development, 85, 40–57.
Roche, C., & Kuperminc, G. P. (2012). Acculturative stress and school belonging among Latino youth. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 34, 61–76.
Roorda, D. L., Koomen, H. M. Y., Spilt, J. L., & Oort, F. J. (2011). The influence of affective teacher-student relationships on students’ school engagement and achievement: A meta-analytic approach. Review of Educational Research, 81, 493–529.
Rothon, C. (2005). An assessment of the “oppositional culture” explanation for ethnic differences in educational attainment in Britain. Sociology Working papers 2005-02. University of Oxford: Department of Sociology.
Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs, 80, 1–28.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55, 68–78.
Sanchez, D., Whittaker, T. A., & Hamilton, E. (2016). Perceived discrimination, peer influence and sexual behaviors in Mexican American preadolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45, 928–944.
Schachner, M. K., Noack, P., Van de Vijver, F. J. R., & Eckstein, K. (2016a). Cultural diversity climate and psychological adjustment at school: Equality and inclusion versus cultural pluralism. Child Development, 87, 1175–1191.
Schachner, M. K., Noack, P., Van de Vijver, F. J. R., & Eckstein, K. (2016b). Cultural diversity climate and psychological adjustment at school: Equality and inclusion versus cultural pluralism. Child Development, 87, 1175–1191.
Scheepers, D. (2013). Studying social identity-based threats and challenges using cardiovascular measures. In B. Derks, D. Scheepers, & N. Ellemers (Eds.), Neuroscience of prejudice and intergroup relations (pp. 243–259). New York: Psychology Press.
Scheepers, D., & Derks, B. (2016). Revisiting social identity theory from a neuroscience perspective. Current Opinion in Psychology, 11, 74–78.
Schmader, T., Major, B., & Gramzow, R. H. (2001). Coping with ethnic stereotypes in academic domain: Perceived injustice and psychological disengagement. Journal of Social Issues, 57, 93–111.
Schmitt, M. T., Branscombe, N. R., Postmes, T., & Garcia, A. (2014). The consequences of perceived discrimination for psychological well-Being: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 140, 921–948.
Seaton, E. K. (2010). The influence of cognitive development and perceived racial discrimination on the psychological well-being of African American youth. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39, 694–703.
Seol, K. O., Lee, R. M., Yoo, H. C., Park, J. E., & Kyeong, Y. (2016). Racial and ethnic socialization as moderators of racial discrimination and school adjustment of adopted and nonadopted Korean American adolescents. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 63(3), 294–306.
Shapiro, J. R., & Neuberg, S. L. (2007). From stereotype threat to stereotype threats: Implications of a multi-threat framework for causes, moderators, mediators, consequences and interventions. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 11, 107–130.
Shorey, H. S., Cowan, G., & Sullivan, M. P. (2002). Predicting perceptions of discrimination among Hispanics and Anglos. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 24, 3–22.
Simiem, E. M. (2005). Race, gender and linked fate. Journal of Black Studies, 35(5), 529–550. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021934704265899.
Skinner, E. A., & Belmont, M. J. (1993). Motivation in the classroom: Reciprocal effects of teacher behavior and student engagement across the school year. Journal of Educational Psychology, 85, 571–581.
Skinner, E. A., Zimmer-Gembeck, M. J., & Connell, J. P. (1998). Individual differences and the development of perceived control. Monographs of the Society for Child Development, Vol. 63, Serial No. 254.
Smalls, C., White, R., Chavous, T., & Sellers, R. (2007). Racial ideology beliefs and racial discrimination experiences as predictors of academic engagement among African American adolescents. Journal of Black Psychology, 33, 299–330.
Smeekes, A., & Verkuyten, M. (2013). Collective self-continuity, group identification and in-group defense. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 49, 984–994.
Stark, T. (2011). Integration in schools: A process perspective on students’ interethnic attitudes and interpersonal relationships. Groningen: ICS.
Stevens, G. W. J. M., & Thijs, J. (2018). Perceived group discrimination and psychological well-being in ethnic minority adolescents. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 48, 559–570.
St-Hilaire, A. (2002). The social adaptation of children of Mexican immigrants: Educational aspirations beyond junior high school. Social Science Quarterly, 83, 1026–1043.
Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. (1979). An integrative theory of intergroup conflict. In W. G. Austin & S. Worchel (Eds.), The social psychology of intergroup relations (pp. 7–24). Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Taylor, D. M., Wright, S. C., & Porter, L. E. (1994). Dimensions of perceived discrimination: The personal/group discrimination discrepancy. In M. P. Zanna & J. M. Olson (Eds.), The psychology of prejudice: The Ontario symposium (Vol. 7, pp. 233–255). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Tenenbaum, H. R., & Ruck, M. D. (2007). Are teachers’ expectations different for racial minority than for European American Students? Journal of Educational Psychology, 99, 253–273.
Teny, C., Devleeshouwer, P., & Hanquinet, L. (2013). Educational aspirations among ethnic minority youth in Brussels: Does the perception of ethnic discrimination in the labour market matter? A mixed-method approach. Ethnicities, 13, 584–606.
Thijs, J., Keim, A., & Geerlings, J. (2018). Classroom identification in ethnic minority and majority students: Effects of relationships and ethnic composition (re-submitted manuscript)
Thijs, J., & Verkuyten, M. (2014). School ethnic diversity and students’ interethnic relations. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 84, 1–21.
Tseng, V. (2004). Family interdependence and academic adjustment in college: Youth from immigrant and US-born families. Child Development, 75, 966–983.
Tyson, K. (2002). Weighing in: Elementary-age students and the debate on attitudes toward schooling among black students. Social Forces, 80, 1157–1189.
Umaña-Taylor, A. J. (2016). A post-racial society in which ethnic-racial discrimination still exists and has significant consequences for youths sdjustment. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 25, 111–118.
Umaña-Taylor, A. J., Quintana, S. M., Lee, R. M., Cross, W. E., Jr., Rivas-Drake, D., Schwartz, S. J., et al. (2014). Ethnic and racial identity during adolescence and into young adulthood: An integrated conceptualization. Child Development, 85, 21–39.
Urdan, T., & Munoz, C. (2012). Multiple contexts, multiple method: A study of academic and cultural identity among children of immigrant parents. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 27, 247–265.
Van den Bergh, L., Denessen, E., Hornstra, L., Voeten, M., & Holland, R. W. (2010). The implicit prejudiced attitudes of teachers: Relations to teacher expectations and the ethnic achievement gap. American Educational Research Journal, 47(2), 497–527. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831209353594.
Van Laar, C. (2001). Declining optimism in ethnic minority students: The role of attributions and self-esteem. In F. Salili, C. Chiu, & Y. Yi Hong (Eds.), Student motivation: The culture and context of learning. New York: Plenum.
Van Tubergen, F., & Van Gaans, M. (2016). Is there an oppositional culture among immigrant adolescents in the Netherlands? Youth and Society, 48, 202–219.
Vansteenkiste, M., Lens, W., & Deci, E. L. (2006). Intrinsic versus extrinsic goal contents in self-determination theory: Another look at the quality of academic motivation. Educational Psychologist, 41, 19–31.
Verkuyten, M. (1998). Perceived discrimination and self-esteem among ethnic minority adolescents. The Journal of Social Psychology, 138, 479–493.
Verkuyten, M. (2002). Perceptions of ethnic discrimination by minority and majority early adolescents in the Netherlands. International Journal of Psychology, 37, 321–333.
Verkuyten, M. (2016). Further conceptualizing ethnic and racial identity research: The social identity approach and its dynamic model. Child Development, 87, 1796–1812. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev125555.
Verkuyten, M., & Brug, P. (2003). Educational performance and psychological disengagement among ethnic minority and Dutch adolescents. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 164, 189–200.
Verkuyten, M., & Reijerse, A. (2008). Intergroup structure and identity management among ethnic minority and majority groups: The interactive effects of perceived stability, legitimacy, and permeability. European Journal of Social Psychology, 38, 106–127.
Verkuyten, M., & Thijs, J. (2002). Racist victimization among children in The Netherlands: The effect of ethnic group and school. Ethnic and Racial Studies, 25, 310–331.
Verkuyten, M., & Thijs, J. (2004). Psychological disengagement from the academic domain among ethnic minority adolescents in the Netherlands. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 74, 109–125.
Verkuyten, M., Thijs, J. (2013). Multicultural education and inter-ethnic attitudes: An intergroup perspective. European Psychologist, 18, 179–190.
Verkuyten, M., Thijs, J., & Canatan, K. (2001). Achievement motivation and academic performance among Turkish early and young adolescents in the Netherlands. Genetic, Social, and General Psychology Monographs, 127, 378–408.
Vignoles, V. L. (2011). Identity motives. In S. J. Schwartz, K. Luyckx, & V. L. Vignoles (Eds.), Handbook of identity theory and research (pp. 403–432). New York: Springer.
Vignoles, V. L., Regalia, C., Manzi, C., Golledge, J., & Scabini, E. (2006). Beyond self-esteem: Influence of multiple motives on identity construction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 90, 308–333.
Walton, G. M., & Cohen, G. L. (2007). A question of belonging: Race, social fit, and achievement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92, 82–96. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.1.82.
Wang, M. T., & Huguley, J. P. (2012). Parental racial socialization as a moderator of the effects of racial discrimination on educational success among African American adolescents. Child Development, 83, 1716–1731. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2012.01808.x.
Weiner, B. (2000). Intrapersonal and interpersonal theories of motivation from an attributional perspective. Educational Psychology Review, 12, 1–14.
Wentzel, K. R., & Wigfield, A. (1998). Academic and social motivation influences on students’ academic performance. Educational Psychology Review, 10, 155–175.
White, R. M. B., Zeiders, K. H., Knight, G. P., Roosa, M. W., & Tein, J.-Y. (2014). Mexican origin youths’ trajectories of perceived peer discrimination from middle childhood to adolescence: Variation by neighborhood ethnic concentration. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 43, 1700–1714.
Wigfield, A., & Cambria, J. (2010). Students’ achievement values, goal orientations, and interest: Definitions, development, and relations to achievement outcomes. Developmental Review, 30, 1–35.
Williams, K. (2001). Ostracism: The power of silence. London: Guildford.
Wolfgramm, C., Morf, C. C., & Hannover, B. (2014). Ethnically based rejection sensitivity and academic achievement: The danger of retracting into one’s heritage culture. European Journal of Social Psychology, 44, 313–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.2018.
Wong, C. A., Eccles, J. S., & Sameroff, A. (2003). The influence of ethnic discrimination and ethnic identification on African American adolescents’ school and socioemotional adjustment. Journal of Personality, 71, 1197–1232.
Yeager, D. S., Purdie-Vaughns, V., Hooper, S. Y., & Cohen, G. L. (2017). Loss of institutional trust among racial and ethnic minority adolescents: A consequence of procedural injustice and a cause of life-span outcome. Child Development, 88, 658–676. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12697.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verkuyten, M., Thijs, J. & Gharaei, N. Discrimination and academic (dis)engagement of ethnic-racial minority students: a social identity threat perspective. Soc Psychol Educ 22, 267–290 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-018-09476-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-018-09476-0