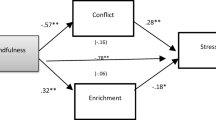
Abstract
The psychological pressure of high strength, often cause teachers teaching dissatisfaction, absenteeism and employee turnover. The current study examined the impact of work stress on job burnout, mainly focused on confirmation of the mediator role of self-efficacy. A total of 387 middle school teachers were as participants involving in this research. Data were collected by using the Perceived Stress Scale, General Self-Efficacy Scale and Maslach Burnout Inventory-General Survey. The results revealed that both work stress and self-efficacy were significantly correlated with job burnout. Structural equation modeling indicated that self efficacy partially mediated work stress to job burnout. The final model also revealed significant both paths from work stress to job burnout through self efficacy. The findings extended prior researches and provided valuable evidence on how to promote mental health of teachers at the workplaces.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Finally, thanks are due to for funding by the Education Department in Anhui China. (foundation NO.: 2012jyxm395 & NO.: 2013SQRW094ZD).
References
Abenavoli, R. M., Jennings, P. A., Greenberg, M. T., Harris, A. R., & Katz, D. A. (2013). The protective effects of mindfulness against burnout among educators. Psychology of Education Review, 37(2), 57–69.
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411–423.
Brissie, J. S., Hoover-Dempsey, K. V., & Bassler, O. C. (1988). Individual, situational contributors to teacher burnout. The Journal of Educational Research, 82(2), 106–112.
Carson, R. L., Baumgartner, J. J., Matthews, R. A., & Tsouloupas, C. N. (2010). Emotional exhaustion, absenteeism, and turnover intentions in childcare teachers examining the impact of physical activity behaviors. Journal of Health Psychology, 15(6), 905–914.
Chiron, B., Michinov, E., Olivier-Chiron, E., Laffon, M., & Rusch, E. (2010). Job satisfaction, life satisfaction and burnout in French anaesthetists. Journal of Health Psychology, 15(6), 948–958.
Chwalisz, K., Altmaier, E. M., & Russell, D. W. (1992). Causal attributions, self-efficacy cognitions, and coping with stress. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 11(4), 377–400.
Cohen, S. (1986). Contrasting the Hassles Scale and the Perceived Stress Scale: Who’s really measuring appraised stress? American Psychologist, 41, 716–718.
Conen, W. S., Henkens, K., & Schippers, J. (2012). Employers’ attitudes and actions towards the extension of working lives in Europe. International Journal of Manpower, 33(6), 648–665.
Consiglio, C., Borgogni, L., Alessandri, G., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2013). Does self-efficacy matter for burnout and sickness absenteeism? The mediating role of demands and resources at the individual and team levels. Work & Stress, 27(1), 22–42.
Cupertino, A.-P., Berg, C., Gajewski, B., Hui, S.-K. A., Richter, K., Catley, D., et al. (2012). Change in self-efficacy, autonomous and controlled motivation predicting smoking. Journal of Health Psychology, 17(5), 640–652.
Egyed, C. J., & Short, R. J. (2006). Teacher self-efficacy, burnout, experience and decision to refer a disruptive student. School Psychology International, 27(4), 462–474.
Evers, W. J., Brouwers, A., & Tomic, W. (2002). Burnout and self-efficacy: A study on teachers’ beliefs when implementing an innovative educational system in the Netherlands. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 72(2), 227–243.
Freudenberger, H. J. (1974). Staff burn-out. Journal of Social Issues, 30(1), 159–165.
Friedman, I. A., & Farber, B. A. (1992). Professional self-concept as a predictor of teacher burnout. The Journal of Educational Research, 86(1), 28–35.
Friedman-Krauss, A. H., Raver, C. C., Morris, P. A., & Jones, S. M. (2014). The role of classroom-level child behavior problems in predicting preschool teacher stress and classroom emotional climate. Early Education and Development, 25(4), 530–552.
Glickman, C. D., & Tamashiro, R. T. (1982). A comparison of first-year, fifth-year, and former teachers on efficacy, ego development, and problem solving. Psychology in the Schools, 19(4), 558–562.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55.
Jou, R.-C., Kuo, C.-W., & Tang, M.-L. (2013). A study of job stress and turnover tendency among air traffic controllers: The mediating effects of job satisfaction. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 57, 95–104.
Kamen, C., Flores, S., Etter, D., Lazar, R., Patrick, R., Lee, S., et al. (2013). General self-efficacy in relation to unprotected sexual encounters among persons living with HIV. Journal of Health Psychology, 18(5), 658–666.
Kyriacou, C. (1987). Teacher stress and burnout: An international review. Educational Research, 29(2), 146–152.
Kyriacou, C. (2001). Teacher stress: Directions for future research. Educational Review, 53(1), 27–35.
Kyriacou, C., & Sutcliffe, J. (1979). Teacher stress and satisfaction. Educational Research, 21(2), 89–96.
Leiter, M. P. (1993). Burnout as a developmental process: Consideration of models. In Schaufeli, W. B., Maslach, C. E., & Marek, T. E. (Eds.), Professional burnout: Recent developments in theory and research (pp. 237–249). Philadelphia, US: Taylor & Francis.
Lian, P., Sun, Y., Ji, Z., Li, H., & Peng, J. (2014). Moving away from exhaustion: How core self-evaluations influence academic burnout. PLoS One, 9(1), e87152.
Maslach, C., & Jackson, S. E. (1981). The measurement of experienced burnout. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 2(2), 99–113.
Maslach, C., Schaufeli, W. B., & Leiter, M. P. (2001). Job burnout. Annual Review of Psychology, 52(1), 397–422.
Peng, J., Li, D., Zhang, Z., Tian, Y., Miao, D., Xiao, W., & Zhang, J. (2014). How can core self-evaluations influence job burnout? The key roles of organizational commitment and job satisfaction. Journal of Health Psychology. doi:10.1177/1359105314521478.
Peng, J., Miao, D., & Xiao, W. (2013). Why are gainers more risk seeking. Judgment & Decision Making, 8(2), 150–160.
Pines, A., & Maslach, C. (1978). Characteristics of staff burnout in mental health settings. Psychiatric Services, 29(4), 233–237.
Roeser, R. W., Schonert-Reichl, K. A., Jha, A., Cullen, M., Wallace, L., Wilensky, R., et al. (2013). Mindfulness training and reductions in teacher stress and burnout: Results from two randomized, waitlist-control field trials. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(3), 787.
Schaufeli, W. B., & Leiter, M. P. (1996). Maslach burnout inventory-general survey. The Maslach Burnout Inventory-Test Manual, 1, 19–26.
Schwarzer, R., & Jerusalem, M. (1995). Generalized self-efficacy scale. Measures in Health Psychology: A User’s Portfolio. Causal and Control Beliefs, 1, 35–37.
Shih, S.-P., Jiang, J. J., Klein, G., & Wang, E. (2013). Job burnout of the information technology worker: Work exhaustion, depersonalization, and personal accomplishment. Information & Management, 50(7), 582–589.
Slick, S. K. (1997). Assessing versus assisting: The supervisor’s roles in the complex dynamics of the student teaching triad. Teaching and Teacher Education, 13(7), 713–726.
Torsheim, T., & Wold, B. (2001). School-related stress, school support, and somatic complaints: A general population study. Journal of Adolescent Research, 16(3), 293–303.
Troman, G., & Woods, P. (2000). Careers under stress: Teacher adaptations at a time of intensive reform. Journal of Educational Change, 1(3), 253–275.
Veldman, I., van Tartwijk, J., Brekelmans, M., & Wubbels, T. (2013). Job satisfaction and teacher–student relationships across the teaching career: Four case studies. Teaching and Teacher Education, 32, 55–65.
Weber, M., Ruch, W., Littman-Ovadia, H., Lavy, S., & Gai, O. (2013). Relationships among higher-order strengths factors, subjective well-being, and general self-efficacy—The case of Israeli adolescents. Personality and Individual Differences, 55(3), 322–327.
Yankelevich, M., Broadfoot, A., Gillespie, J. Z., Gillespie, M. A., & Guidroz, A. (2012). General job stress: A unidimensional measure and its non-linear relations with outcome variables. Stress and Health, 28(2), 137–148.
Zhao, X., Huang, C., Li, X., Zhao, X., & Peng, J. (2014). Dispositional optimism, self‐framing and medical decision‐making. International Journal of Psychology. doi:10.1002/ijop.12079.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Wang, P., Zhai, X. et al. The Effect of Work Stress on Job Burnout Among Teachers: The Mediating Role of Self-efficacy. Soc Indic Res 122, 701–708 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0716-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0716-5