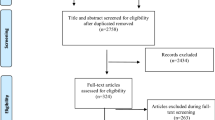
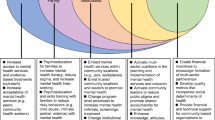
Abstract
The primary aim of family-based prevention programs is to promote children’s health. Unfortunately, it is difficult to reach families with such evidence-based prevention programs (EBP). Therefore, implementing EBP on a population level could be a promising approach to reach more families, including those faced with socioeconomic challenges who are usually less likely to participate in randomized controlled trials (RCT). Is a population rollout appropriate to reach more and different families than those participating in RCT, especially those representative of the target population? We implemented three EBP in a city in an uncontrolled trial. The effects of this population rollout were tracked on the level of the participating families and on the level of all families living in the city. More than 3480 families (30 % of the population) with children up to 12 years of age participated based on practitioner report. Analyses indicate that a greater percentage of low socioeconomic-status families attended a program compared with a randomly surveyed sample from the city’s general population. The sizes of the within-subject effect for parental strategies, child behavior problems, and children’s quality of life for a subsample of n = 411 families were similar to those of other uncontrolled EBP studies. The study contributes to highly needed type 2 translation research. The population-based dissemination of EBP could be a promising approach to reach families at risk. However, there are considerable barriers to the implementation process, which currently limit the effectiveness of this rollout in a community.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, D. S., O'Leary, S. G., Wolff, L. S., & Acker, M. M. (1993). The Parenting Scale: A measure of dysfunctional parenting in discipline situations. Psychological Assessment, 5, 137–144. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.5.2.137.
Belfer, M. L. (2008). Child and adolescent mental disorders: The magnitude of the problem across the globe. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49, 226–236.
Bertram, R., Blase, K., Shern, D., Shea, P., & Fixsen, D. (2011). Policy research brief: Implementation opportunities and challenges for prevention and promotion initiatives. Alexandria, VA: National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors (NASMHPD).
Bullinger, M., Levke Brütt, A., Erhart, M., Ravens-Sieberer, U., & the BELLA Study Group. (2008). Psychometric properties of the KINDL-R questionnaire: Results of the BELLA study. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 17, 125–132. doi:10.1007/s00787-008-1014-z.
Eisner, M., Nagin, D., Ribeaud, D., & Malti, T. (2012). Effects of a universal parenting program for highly adherent parents: A propensity score matching approach. Prevention Science, 13, 252–266. doi:10.1007/s11121-011-0266-x.
Fagan, A. A., Hanson, K., Briney, J. S., & Hawkins, J. D. (2012). Sustaining the utilization and high quality implementation of tested and effective prevention programs using the Communities That Care prevention system. American Journal of Community Psychology, 49, 365–377. doi:10.1007/s10464-011-9463-9.
Fixsen, D. L., Blase, K. A., Naoom, S. F., & Wallace, F. (2009). Core implementation components. Research on Social Work Practice, 19, 531–540. doi:10.1177/1049731509335549.
Forgatch, M. S., Patterson, G. R., & Gewirtz, A. H. (2013). Looking forward the promise of widespread implementation of parent training programs. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 8, 682–694. doi:10.1177/1745691613503478.
Frantz, I., & Heinrichs, N. (2014). Umgebungsgebundene Förderung: Eltern als Zielgruppe [Environmental-based promotion of child development: Parents as target group]. In A. Lohaus & M. Glüer (Eds.), Entwicklungsförderung im Kindesalter. Göttingen, Germany: Hogrefe.
Frantz, I., & Heinrichs, N. (2015a). Effekte einer Werbekampagne für ausgewählte evidenzbasierte Präventionsprogramme [Effects of a communication strategy for evidence-based prevention programs]. Kindheit und Entwicklung, 24, 20–27.
Frantz, I. & Heinrichs, N. (2015b). Populationseffekte einer flächendeckenden Implementierung familienbasierter Präventionsprogramme [Population-level effects of family-based prevention programs]. Manuscript in preparation.
Glasgow, R. E., & Emmons, K. M. (2007). How can we increase translation of research into practice? Types of evidence needed. Annual Review of Public Health, 28, 413–433. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.28.021406.144145.
Glazemakers, I. (2012). A population health approach to parenting support: Disseminating the Triple P- Positive Parenting Program in the Province of Antwerp. Dissertation, University of Antwerp, Antwerp.
Goodman, R. (1997). The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: A research note. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38, 581–586. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01545.x.
Lösel, F., & Stemmler, M. (2012). Preventing child behavior problems in the Erlangen-Nuremberg Development and Prevention Study: Results from preschool to secondary school age. International Journal of Conflict and Violence, 6, 214–224.
McMahon, R. J., & Forehand, R. L. (2003). Helping the noncompliant child: Family-based treatment for oppositional behavior. New York: Guilford Press.
Mihalic, S., Irwin, K., Fagan, A., Ballard, D., & Elliott, D. (2004). Successful program implementation: Lessons from blueprints. Juvenile Justice Bulletin. Retrieved May, 13, 2014, from https://www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/ojjdp/204273.pdf.
National Research Council & Institute of Medicine. (2009). Preventing mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders among young people: Progress and possibilities. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Naumann, S., Bertram, H., Kuschel, A., Heinrichs, N., Hahlweg, K., & Döpfner, M. (2010). Der Erziehungsfragebogen (EFB)-Ein Fragebogen zur Erfassung elterlicher Verhaltenstendenzen in schwierigen Erziehungssituationen [The Parenting Questionnaire. An instrument to assess parental behavioral tendencies in discipline situations with their children]. Diagnostica, 56, 144–157. doi:10.1026/0012-1924/a000018.
Nowak, C., & Heinrichs, N. (2008). A comprehensive meta-analysis of Triple P-Positive Parenting Program using hierarchical linear modeling: Effectiveness and moderating variables. Clinical Child and Family Psychological Review, 11, 114–144. doi:10.1007/s10567-008-0033-0.
Olds, D. L. (2000). The nurse–family partnership: An evidence-based preventive intervention. Infant Mental Health Journal, 27, 5–25. doi:10.1002/imhj.20077.
Plueck, J., Eichelberger, I., Hautmann, C., Hanisch, C., Jaenen, N., & Doepfner, M. (2014). Effectiveness of a teacher-based indicated prevention program for pre-school children with externalizing problem behaviour. Prevention Science, 16, 233–241. doi:10.1007/s11121-014-0487-x.
Prinz, R. J., Sanders, M. R., Shapiro, C. J., Whitaker, D. J., & Lutzker, J. R. (2009). Population-based prevention of child maltreatment: The U.S. Triple P system population trail. Prevention Science, 10, 1–12. doi:10.1007/s11121-009-0123-3.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Wille, N., Erhart, M., Bettge, S., Wittchen, H.-U., Rothenberger, A., … as the BELLA study group (2008). Prevalence of mental health problems among children and adolescents in Germany: Results of the BELLA study within the National Health Interview and Examination Survey. European Child Adolescent Psychiatry, 17, 22–33. doi:10.1007/s00787-008-1003-2.
Rustenbach, S. J. (2003). Metaanalyse. Eine anwendungsorientierte Einführung [Meta-analysis: A user-oriented introduction]. Bern, Switzerland: Huber.
Salmivalli, C., & Poskiparta, E. (2012). KiVa antibullying program: Overview of evaluation studies based on a randomized controlled trial and national rollout in Finland. International Journal of Conflict and Violence, 6, 294–302.
Sanders, R. M., Kirby, J. N., Tellegan, C. L., & Day, J. J. (2014). The Triple P-Positive Parenting Program: A systematic review and meta-analysis of a multi-level system of parenting support. Clinical Psychological Review, 34, 337–357.
Schafer, J. L., & Graham, J. W. (2002). Missing data: Our view of the state of the art. Psychological Methods, 7, 147–177.
Shure, M. B. (1992). I Can Problem Solve: An interpersonal cognitive problem-solving program. Champaign: Research Press.
Spoth, R., Rohrbach, L. A., Greenberg, M., Leaf, P., Brown, C. H., Fagan, A., … Hawkins, J. D. (2013). Addressing core challenges for the next generation of type 2 translation research and systems: The translation science to population impact (TSci Impact) framework. Prevention Science, 14, 319–351. doi:10.1007/s11121-012-0362-6.
Statistical Federal Office (2012). Statistical Yearbook for the Federal Republic of Germany. Statistical Federal Office. Retrieved May, 15, 2014, from https://www.destatis.de/DE/Publikationen/StatistischesJahrbuch/StatistischesJahrbuch2012.pdf.
Strayhorn, J. M., & Weidman, C. S. (1988). A Parent Practices Scale and its relation to parent and child mental health. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 27, 613–618.
Tremblay, R. E., Vitaro, F., Gagnon, C., Piché, C., & Royer, N. (1992). A prosocial scale for the Preschool Behavior Questionnaire: Concurrent and predictive correlates. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 15, 227–245. doi:10.1177/016502549201500204.
Welsh, B. C., & Farrington, D. P. (2012). The Oxford handbook of crime prevention. Oxford: University Press.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the German Government of Justice [Gefördert von der Stiftung Deutsches Forum für Kriminalprävention und vom Bundesministerium der Justiz aufgrund eines Beschlusses des Deutschen Bundestages]. We are very grateful for Matthew Sanders’ feedback on the first revision of this manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
Nina Heinrichs and Kurt Hahlweg are members of the international scientific advisory committee for Triple P. Inga Frantz and Nina Heinrichs are members of the Triple P Research Network since 2014 (academic disclosure). Julia Plück is co-author of PEP and conducts courses for PEP trainers (financial disclosure).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frantz, I., Stemmler, M., Hahlweg, K. et al. Experiences in Disseminating Evidence-Based Prevention Programs in a Real-World Setting. Prev Sci 16, 789–800 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-015-0554-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-015-0554-y