Abstract
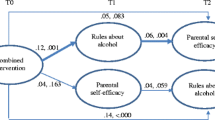
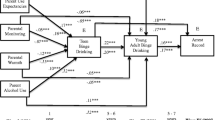
The aim of this study was to examine the effect of a theory-based in-home family intervention (In control: No alcohol!) on adolescent alcohol cognitions via its putative mediators using a randomized controlled design. In the South Holland region of the Netherlands, a total of 213 children (11–12 years) and their mothers were randomly assigned to the prevention program (108 dyads) and the control condition (105 dyads). Mediation effects were analyzed using pretest and two follow-up measurements (5 and 12 months after baseline). A path model was estimated (using Mplus) to examine the effect of the intervention on the putative mediators (frequency- and quality of mother–child communication, rules about alcohol, establishing a nondrinking agreement, and parental monitoring of the child's whereabouts). Outcomes were adolescents' perceived harmfulness of drinking and intention to drink. Multigroup analyses were performed to examine potential differences across gender. The program led to an increase in frequency of alcohol-specific communication, nondrinking agreements, and parental monitoring. Moreover, adolescents in the experimental condition perceived drinking to be more harmful and had less intention to drink compared to adolescents in the control condition. The effect of the program on adolescent alcohol cognitions was significantly mediated through having more frequent conversations about alcohol, yet only among boys. Although results on actual drinking need to be added, findings indicate that this relatively inexpensive, easy-to-administer home intervention is promising.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Bonomo, Y., Coffey, C., Wolfe, R., Lynskey, M., Bowes, G., & Patton, G. (2001). Adverse outcomes of alcohol use in adolescents. Addiction, 96, 1485–1496. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2001.9610148512.x.
Boone, T. L., & Lefkowitz, E. S. (2007). Mother–adolescent health communication: Are all conversations created equally? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36, 1038–1047. doi:10.1007/s10964-006-9138-2.
Bryan, A., Schmiege, S. J., & Broaddus, M. R. (2007). Mediational analysis in HIV/AIDS research: Estimating multivariate path analytic models in a structural equation modelling framework. AIDS and Behavior, 11, 365–383. doi:10.1007/s10461-006-9150-2.
Cole, D. A., & Maxwell, S. E. (2003). Testing mediational models with longitudinal data: Questions and tips in the use of structural equation modeling. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 112, 558–577. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.112.4.558.
Danielsson, A.-K., Romelsjö, A., & Tengström, A. (2011). Heavy episodic drinking in early adolescence: Gender-specific risk and protective factors. Substance Use & Misuse, 46, 633–645. doi:10.3109/10826084.2010.528120.
DeWit, D. J., Adlaf, E. M., Offord, D. R., & Ogborne, A. C. (2000). Age at first alcohol use: A risk factor for the development of alcohol disorders. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 157, 745–750. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.157.5.745.
Dorsselaer, S., van de Looze, M., Vermeulen-Smit, E., de Roos, S., Verdurmen, J., Ter Bogt, T., & Vollebergh, W. (2010). Gezondheid, welzijn en opvoeding van jongeren in Nederland: HBSC 2009. [Health, well-being and parenting among Dutch adolescents: HBSC 2009]. Utrecht, The Netherlands: Trimbos-instituut.
Ennett, S. T., Bauman, K. E., Foshee, V. A., Pemberton, M., & Hicks, K. A. (2001). Parent–child communication about adolescent tobacco and alcohol use: What do parents say and does it affect youth behavior? Journal of Marriage and the Family, 63, 48–62. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2001.00048.x.
Ennett, S. T., Bauman, K. E., Pemberton, M., Foshee, V. A., Chuang, Y. C., King, T. S., & Koch. (2001). Mediation in a family-directed program for prevention of adolescent tobacco and alcohol use. Preventive Medicine, 33, 333–346. doi:10.1006/pmed.2001.0892.
Hawkins, J. D., Graham, J. W., Maguin, E., Abbott, R., Hill, K. G., & Catalano, R. F. (1997). Exploring the effects of age of alcohol use initiation and psychosocial risk factors on subsequent alcohol misuse. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 58, 280–290.
Hibell, B., Guttormsson, U., Ahlström, S., Balakireva, O., Bjarnason, T., Kokkevi, A., & Kraus, L. (2009). The 2007 ESPAD report—substance use among students in 35 European countries. Stockholm: The Swedish Council for Information on Alcohol and Other Drugs (CAN).
Hiemstra, M., Ringlever, L., Otten, R., Jackson, C., van Schayck, O. C., & Engels, R. C. (2009). Efficacy of smoking prevention program ‘Smoke-free Kids’: Study protocol of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health, 9, 477. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-9-477.
Jackson, C., & Dickinson, D. (2003). Can parents who smoke socialize their children against smoking? Results from the Smoke-free Kids intervention trial. Tobacco Control, 12, 52–59. doi:10.1136/tc.12.1.52.
Jackson, C., & Dickinson, D. (2006). Enabling parents who smoke to prevent their children from initiating smoking. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 160, 56–62. doi:10.1001/archpedi.160.1.56.
Jones, D. J., Olson, A., Forehand, R., Gaffney, C. A., Zens, M. S., & Bau, J. J. (2005). A family based randomized control trial to prevent adolescent alcohol and tobacco use: The moderating roles of positive parenting and adolescent gender. Behavior Therapy, 36, 347–355. doi:10.1016/S0005-7894(05)80116-9.
Kelly, A. B., O'Flaherty, M., Toumbourou, J. W., Connor, J. P., Hemphill, S., & Catalano, R. F. (2011). Gender differences in the impact of families on alcohol use: A lagged longitudinal study of pre-teens. Addiction, 106, 1427–1436. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03435.x.
Kerr, M., & Stattin, H. (2000). What parents know, how they know it, and several forms of adolescent adjustment: Further support for a reinterpretation of monitoring. Developmental Psychology, 36, 366–380. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.36.3.366.
Kish, L. (1965). Survey sampling. New York: Wiley.
Koning, I. M., Vollebergh, W. A. M., Smit, F., Verdurmen, J. E., Van Den Eijnden, R. J., Ter Bogt, T. F., Stattin, H., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2009). Preventing heavy alcohol use in adolescents (PAS): Cluster randomized trial of a parent and student intervention offered separately and simultaneously. Addiction, 104, 1669–1678. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02677.x.
Koning, I. M., Engels, R. C. M. E., Verdurmen, J. E. E., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2010). Alcohol-specific socialization practices and alcohol use in Dutch early adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 33, 93–100. doi:10.1016/j.adolescence.2009.05.003.
Koning, I. M., van den Eijnden, R. J. J. M., Engels, R. C. M. E., Verdurmen, J. E. E., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2011). Why target early adolescents and parents in alcohol prevention? The mediating effects of self-control, rules and attitudes about alcohol use. Addiction, 106, 538–546. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.03198.x.
Koning, I. M., van den Eijnden, R. J. J. M., Verdurmen, J. E. E., Engels, R. C. M. E., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2011). Long-term effects of a parent and student intervention on alcohol use in adolescents: A cluster randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 40, 541–547. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02677.x.
Koning, I. M., van den Eijnden, R. J. J. M., Verdurmen, J. E., Engels, R. C. M. E., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2012). Developmental alcohol-specific parenting profiles in adolescence and their relationships with adolescents' alcohol use. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41, 1502–1511.
Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Haggerty, K. P., Spoth, R., & Redmond, C. (2001). Preparing for the drug free years: Session-specific effects of a universal parent training intervention with rural families. Journal of Drug Education, 31, 47–68. doi:10.2190/3KP9-V42V-V38L-6G0Y.
Kumpfer, K. L., Alvarado, R., & Whiteside, H. O. (2003). Family-based interventions for substance use and misuse prevention. Substance Use & Misuse, 38, 1759–1787. doi:10.1081/JA-120024240.
Kumpfer, K. L., Smith, P., & Summerhays, J. F. (2008). A wakeup call to the prevention field: Are prevention programs for substance use effective for girls? Substance Use & Misuse, 43, 978–1001. doi:10.1080/10826080801914261.
Kumpfer, K. L., Whiteside, H. O., Greene, J. A., & Allen, K. C. (2010). Effectiveness outcomes of four age versions of the strengthening families program in statewide field sites. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research and Practice, 14, 211–229. doi:10.1037/a0020602.
Loveland-Cherry, C. J., Ross, L. T., & Kaufman, S. R. (1999). Effects of a home-based family intervention on adolescent alcohol use and misuse. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. Supplement, 13, 94–102.
MacKinnon, D., & MacKinnon, D. P. (2008). Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., & Williams, J. (2004). Confidence limits for the indirect effect: Distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39, 99–128. doi:10.1207/s15327906mbr3901_4.
Marcoux, B. C., & Shope, J. T. (1997). Application of the theory of planned behavior to adolescent use and misuse of alcohol. Health Education Research, 12, 323–331.
Mares, S. H. W., Van der Vorst, H., Vermeulen-Smit, E., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A., Verdurmen, J. E. E., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2012). Results of the “In control: No alcohol!” pilot study. Health Education Research, 27, 214–225. doi:10.1093/her/cyr081.
Martyn, K. K., Loveland-Cherry, C. J., Villarruel, A. M., Cabriales, E. G., Zhou, Y., Ronis, D. L., & Eakin, B. (2009). Mexican adolescents' alcohol use, family intimacy, and parent–adolescent communication. Journal of Family Nursing, 15, 152–170. doi:10.1177/1074840709332865.
Miller-Day, M., & Kam, J. A. (2010). More than just openness: Developing and validating a measure of targeted parent–child communication about alcohol. Health Communication, 25, 293–302. doi:10.1080/10410231003698952.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2007). Mplus user's guide (5th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Muthén, B., & Satorra, A. (1995). Complex sample data in structural equation modeling. In P. V. Marsden (Ed.), Sociological methodology (pp. 267–316). Oxford: Blackwell.
Noller, P., & Callan, V. J. (1990). Adolescents' perceptions of the nature of their communication with parents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 19, 349–362. doi:10.1007/BF01537077.
Oesterle, S., Hawkins, J. D., Fagan, A. A., Abbott, R. D., & Catalano, R. F. (2010). Testing the universality of the effects of the Communities That Care prevention system for preventing adolescent drug use and delinquency. Prevention Science, 11, 411–424. doi:10.1007/s11121-010-0178-1.
Pasch, K. E., Stigler, M. H., Perry, C. L., & Komro, K. A. (2010). Parents' and children's self-report of parenting factors: How much do they agree and which is more strongly associated with early adolescent alcohol use? Health Education Journal, 69, 31–42. doi:10.1177/ 0017896910363325.
Petrie, J., Bunn, F., & Byrne, G. (2007). Parenting programmes for preventing tobacco, alcohol or drugs misuse in children <18: A systematic review. Health Education Research, 22, 177–191. doi:10.1093/her/cyl061.
Petty, R. E., & Cacioppo, J. T. (1986). From communication and persuasion: Central and peripheral routes to attitude change. New York: Springer.
Pilgrim, C., Abbey, A., Hendrickson, P., & Lorenz, S. (1998). Implementation and impact of a family-based substance abuse prevention program in rural communities. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 18, 341–361. doi:10.1023/A:1024659012360.
Reimuller, A., Hussong, A., & Ennett, S. T. (2011). The influence of alcohol-specific communication on adolescent alcohol use and alcohol-related consequences. Prevention Science, 12, 389–400. doi:10.1007/s11121-011-0227-4.
Smit, E., Verdurmen, J., Monshouwer, K., & Smit, F. (2008). Family interventions and their effect on adolescent alcohol use in general populations; a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 97, 195–206. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.03.032.
Southwell, B. G., & Yzer, M. C. (2007). The roles of interpersonal communication in mass media campaigns. In C. S. Beck (Ed.), Communication yearbook, 31 (pp. 420–462). New York: Erlbaum.
Spijkerman, R., Van den Eijnden, R. J. J. M., & Huiberts, A. (2008). Socioeconomic differences in alcohol-specific parenting practices and adolescents' drinking patterns. European Addiction Research, 14, 26–37. doi:10.1159/000110408.
Spoth, R., Redmond, C., & Shin, C. (1998). Direct and indirect latent-variable parenting outcomes of two universal family focused preventive interventions: Extending a public health oriented research base. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66, 385–399. doi:10.1037/0022006X.66.2.385.
Spoth, R. L., Redmond, C., Clair, S., Shin, C., Greenberg, M., & Feinberg, M. (2011). Preventing substance misuse through community–university partnerships: Randomized controlled trial outcomes 4½ years past baseline. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 40, 440–447. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2010.12.012.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration [SAMHSA]. (2002). The national cross-site evaluation of high-risk youth programs. Rockville: Center for Substance Abuse Prevention, DHHS Publication No. (SMA) 00-3375.
Tapert, S. F., Granholm, E., Leedy, N. G., & Brown, S. A. (2002). Substance use and withdrawal: Neuropsychological functioning over 8 years in youth. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 8, 873–883. doi:10.1017/S1355617702870011.
Trudeau, L., Spoth, R., Randall, G. K., & Azevedo, K. (2007). Longitudinal effects of a universal family-focused intervention on growth patterns of adolescent internalizing symptoms and polysubstance use: Gender comparisons. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36, 725–740. doi:10.1007/s10964-007-9179-1.
Van den Eijnden, R. J. J. M., Van de Mheen, D., Vet, R., & Vermulst, A. (2011). Alcohol-specific parenting and adolescents' alcohol-related problems: The interacting role of alcohol availability at home and parental rules. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 72, 408–417.
Van den Putte, B., Yzer, M., Southwell, B. G., de Bruijn, G. J., & Willemsen, M. C. (2011). Interpersonal communication as an indirect pathway for the effect of antismoking media content on smoking cessation. Journal of Health Communication, 16, 470–485. doi:10.1080/10810730.2010.546487.
Van der Vorst, H., Engels, R. C. M. E., Meeus, W., Dekovic, M., & Van Leeuwe, J. (2005). The role of alcohol-specific socialization in adolescents' drinking behaviour. Addiction, 100, 1464–1476. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2005.01193.x.
Van der Vorst, H., Engels, R. C. M. E., Meeus, W., & Dekovic, M. (2006). The impact of alcohol-specific rules, parental norms about early drinking and parental alcohol use on adolescents' drinking behavior. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47, 1299–1306. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01680.x.
Van der Vorst, H., Burk, W. J., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2010). The role of parental alcohol-specific communication in early adolescents' alcohol use. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 111, 183–190.
Velleman, R. (2009). Alcohol prevention programmes. A review of the literature for the Joseph Rowntree Foundation (part two). York: Joseph Rowntree Foundation.
White, H. R., Johnson, V., & Buyske, S. (2000). Parental modeling and parenting behavior effects on offspring alcohol and cigarette use. A growth curve analysis. Journal of Substance Abuse, 12, 287–310. doi:10.1016/S0899-3289(00)00056-0.
Yu, J. (2003). The association between parental alcohol-related behaviours and children's drinking. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 69, 253–262. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(02)00324-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Flow of participants through the trial (JPEG 889 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermeulen-Smit, E., Mares, S.H.W., Verdurmen, J.E.E. et al. Mediation and Moderation Effects of an In-Home Family Intervention: the “In control: No alcohol!” Pilot Study. Prev Sci 15, 633–642 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-013-0424-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-013-0424-4