Abstract
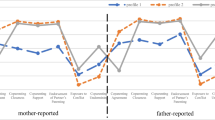
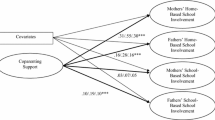
Behavioral and emotional problems are common in early childhood and put children at risk for developing more serious problems. This study tested the mediating mechanisms through which a universal coparenting intervention implemented during the transition to parenthood led to reduced child adjustment problems at age 3 and explored child gender as a potential moderator. One hundred sixty-nine heterosexual couples expecting their first child were randomly assigned to a control condition or Family Foundations, a series of eight classes that targeted the coparenting relationship. Data were collected through videotaped triadic mother–father–child interaction tasks when the child was 1 and 3 years of age. Separate longitudinal path analyses for mothers and fathers tested coparenting competition and positivity as mediators of program effects on child adjustment problems. Significant mediated effects for coparenting competition were found for fathers with both sons and daughters and for mothers with sons but not for mothers with daughters. These effects accounted for between 39 and 55 % of the intervention’s impact on child adjustment problems. Coparenting positivity did not mediate program effects. These results support the use of a prevention approach to reduce coparenting competition and enhance child adjustment and provide information that can be used to refine theory.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair, C., & Diamond, A. (2008). Biological processes in prevention and intervention: The promotion of self-regulation as a means of preventing school failure. Development and Psychopathology, 20, 899–911. doi:10.1017/S0954579408000436.
Blair, C., Granger, D. A., Kivlighan, K. T., Mills-Koonce, R., Willoughby, M. T., Greenberg, M., et al. (2008). Maternal and child contributions to cortisol response emotional arousal in young children from low-income, rural communities. Developmental Psychology, 44, 1095–1109. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.44.4.1095.
Breslau, J., Miller, E., Breslau, N., Bohner, K., Lucia, V., & Schweitzer, J. (2009). The impact of early behavior disturbances on academic achievement in high school. Pediatrics, 123, 1472–1476. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-1406.
Briggs-Gowan, M. J., Carter, A. S., Skuban, E. M., & Horwitz, S. M. (2001). Prevalence of social-emotional and behavioral problems in a community sample of 1- and 2-year old children. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 811–819. doi:10.1097/00004583-200107000-00016.
Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., Newman, D. L., & Silva, P. A. (1996). Behavioral observations at age 3 years predict adult psychiatric disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53, 1033–1039. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1996.01830110071009.
Coffman, D. L., & Kugler, K. C. (2012). Causal mediation of a human immunodeficiency virus preventive intervention. Nursing Research, 61, 224–230. doi:10.1097/NNR.0b013e318254165c.
Collins, L. M., Murphy, S. A., Nair, V. N., & Strecher, V. J. (2005). A strategy for optimizing and evaluating behavioral interventions. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 30, 65–73. doi:10.1207/s15324796abm3001_8.
Cowan, P. A., & Cowan, C. P. (2002). Interventions as tests of family systems theories: Marital and family relationships in children’s development and psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 14, 731–759. doi:10.1017/S0954579402004054.
Crowne, D. P., & Marlowe, D. (1964). The approval motive. New York: Wiley.
Davies, P. T., & Lindsay, L. L. (2001). Does gender moderate the effects of marital conflict on children? In J. H. Grych & F. D. Fincham (Eds.), Interparental conflict and child development (pp. 64–97). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Duvall, E. C. (1977). Marriage and family development. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott.
Feinberg, M. E. (2002). Coparenting and the transition to parenthood: A framework for prevention. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 5, 173–195. doi:10.1023/A:1019695015110.
Feinberg, M. E. (2003). The internal structure and ecological context of coparenting: A framework for research and intervention. Parenting: Science and Practice, 3, 95–132. doi:10.1207/S15327922PAR0302_01.
Feinberg, M. E., & Kan, M. L. (2008). Establishing Family Foundations: Intervention effects on coparenting, parent/infant well-being, and parent-child relations. Journal of Family Psychology, 22, 253–263. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.22.2.253
Feinberg, M. E., Kan, M. L., & Hetherington, E. M. (2007). The longitudinal influence of coparenting conflict on parental negativity and adolescent maladjustment. Journal of Marriage and Family, 69, 687–702. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2007.00400.x.
Feinberg, M. E., Kan, M. L., & Goslin, M. C. (2009). Enhancing coparenting, parenting, and child self-regulation: Effects of Family Foundations 1 year after birth. Prevention Science, 10, 276–285. doi:10.1007/s11121-009-0130-4.
Feinberg, M. E., Jones, D. E., Kan, M. L., & Goslin, M. C. (2010). Effects of Family Foundations on parents and children: 3.5 years after baseline. Journal of Family Psychology, 24, 532–542. doi:10.1037/a0020837.
Hafeman, D. M., & Schwartz, S. (2009). Opening the black box: A motivation for the assessment of mediation. International Journal of Epidemiology, 38, 838–845. doi:10.1093/ije/dyn372.
Kraemer, H. C., Wilson, G. T., Fairburn, C. G., & Agras, W. S. (2002). Mediators and moderators of treatment effects in randomized clinical trials. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59, 877–883. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.59.10.877.
Lawrence, E., Rothman, A. D., Cobb, R. J., Rothman, M. T., & Bradbury, T. N. (2008). Marital satisfaction across the transition to parenthood. Journal of Family Psychology, 22, 41–50. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.22.1.41.
Lindsey, E. W., & Caldera, Y. M. (2006). Mother-father-child triadic interaction and mother child dyadic interaction: Gender differences within and between contexts. Sex Roles, 55, 511–521. doi:10.1007/s11199-006-9106-z.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., & Williams, J. (2004). Confidence limits for the indirect effect: Distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39, 99–128. doi:10.1207/s15327906mbr3901_4.
MacKinnon, D. P., Fairchild, A. J., & Fritz, M. S. (2007). Mediation analysis. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 593–614. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085542.
Margolin, G., Gordis, E. B., & John, R. S. (2001). Coparenting: A link between marital conflict and parenting in two-parent families. Journal of Family Psychology, 15, 3–21. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.15.1.3.
Margolin, G., Gordis, E. B., & Oliver, P. H. (2004). Links between marital and parent–child interactions: Moderating role of husband-to-wife aggression. Development and Psychopathology, 16, 753–771. doi:10.1017/S0954579404004766.
Mathiesen, K. S., & Sanson, A. (2000). Dimensions of early childhood behavior problems: Stability and predictors of change from 18 to 30 months. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 15–31. doi:10.1023/A:1005165916906.
Maydeu-Olivares, A., Coffman, D. L., & Hartmann, W. M. (2007). Asymptotically distribution free (ADF) interval estimation of coefficient alpha. Psychological Methods, 12, 157–176. doi:10.1037/1082-989X.12.2.157.
McHale, J. P. (1995). Coparenting and triadic interactions during infancy: The roles of marital distress and child gender. Developmental Psychology, 31, 985–996. doi:10.1037/00121649.31.6.985.
McHale, J. P., & Rasmussen, J. L. (1998). Coparental and family group-level dynamics during infancy: Early family precursors of child and family functioning during preschool. Development and Psychopathology, 10, 39–59. doi:10.1017/S0954579498001527.
McHale, J. P., Kuersten-Hogan, R., & Lauretti, A. (2001). Evaluating coparenting and family level dynamics during infancy and early childhood: The coparenting and family rating system. In P. K. Kerig & K. M. Lindahl (Eds.), Family observational coding systems: Resources for systemic research (pp. 151–170). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
O’Leary, S. G., & Vidair, H. B. (2005). Marital adjustment, child-rearing disagreements, and overreactive parenting: Predicting child behavior problems. Journal of Family Psychology, 19, 208–216. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.19.2.208.
Olds, D., Henderson, C. R., Jr., Cole, R., Eckenrode, J., Kitzman, H., Luckey, D., et al. (1998). Long-term effects of nurse home visitation on children’s criminal and antisocial behavior: 15-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association, 280, 1238–1244. doi:10.1001/jama.280.14.1238.
Perren, S., von Wyl, A., Bürgin, D., Simoni, H., & von Klitzing, K. (2005). Depressive symptoms and psychosocial stress across the transition to parenthood: Associations with parental psychopathology and child difficulty. Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics and Gynecology, 26, 173–183. doi:10.1080/01674820400028407.
Raley, S., & Bianchi, S. (2006). Sons, daughters, and family processes: Does gender of children matter? Annual Review of Sociology, 32, 401–421. doi:10.1146/annurev.soc.32.061604.123106.
Reid, W. J., & Crisafulli, A. (1990). Marital discord and child behavior problems: A meta-analysis. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 18, 105–117. doi:10.1007/BF00919459.
Schoppe, S. J., Mangelsdorf, S. C., & Frosch, C. A. (2001). Coparenting, family process, and family structure: Implications for preschooler’s externalizing behavior problems. Journal of Family Psychology, 15, 526–545. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.15.3.526.
Shrout, P. E., & Bolger, N. (2002). Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychological Methods, 7, 422–445. doi:10.1037/1082-989X.7.4.422.
Tein, J., Sandler, I. N., Ayers, T. S., & Wolchik, S. A. (2006). Mediation of the effects of the Family Bereavement Program on mental health problems of bereaved children and adolescents. Prevention Science, 7, 179–195. doi:10.1007/s11121-006-0037-2.
Teubert, D., & Pinquart, M. (2010). The association between coparenting and child adjustment: A meta-analysis. Parenting: Science and Practice, 10, 286–307. doi:10.1080/15295192.2010.492040.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Reid, M. J. (2003). The incredible years parents, teachers and children training series: A multifaceted treatment approach for young children with conduct problems. In A. E. Kazdin & J. R. Weisz (Eds.), Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (pp. 224–240). New York: Guilford Press.
Zahn-Waxler, C., Cole, P. M., Richardson, D. T., Friedman, R. J., Michel, M. K., & Belouad, F. (1994). Social problem solving in disruptive preschool children: Reactions to hypothetical situations of conflict and distress. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 40, 98–119.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (K23-HD042575) and the National Institute of Mental Health (R21-MH064125), Mark E. Feinberg, principal investigator. We are grateful to the families who participated in this study. We appreciate the assistance of Karen Newell, Sherry Turchetta, Carole Brtalik, Sharolyn Ivory, David White, Ned Hoffner, Dan Marrow, Ellen McGowan, and Kathryn Siembieda in implementing the program. We thank Jesse Boring, Megan Goslin, Carmen Hamilton, Marni Kan, Richard Puddy, Carolyn Ransford, Samuel Sturgeon, and Jill Zeruth for their assistance in conducting the study.
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Feinberg created the Family Foundations program and is the owner of a private company, Community Strategies, which sells the Family Foundations program in DVD format and disseminates the class series curriculum (www.FamFound.net). Dr. Feinberg’s financial interest is periodically reviewed and any potential conflicts managed by the Institutional Review Board and the Conflict of Interest Committee at Pennsylvania State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solmeyer, A.R., Feinberg, M.E., Coffman, D.L. et al. The Effects of the Family Foundations Prevention Program on Coparenting and Child Adjustment: A Mediation Analysis. Prev Sci 15, 213–223 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-013-0366-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-013-0366-x