Abstract
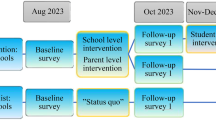
This paper presents the results of a post hoc component analysis designed to tease apart the effects of different intervention strategies used in Project Northland, a group-randomized, community-wide, multi-level intervention trial originally conducted in the 1990's to prevent and reduce alcohol use among a cohort of mainly White students in rural Minnesota. This study focuses on Phase I, when students were in 6th–8th grade. The intervention during this phase included five components: classroom curricula, peer leadership, youth-driven/led extra-curricular activities, parent involvement programs, and community activism. Student exposure to/participation in these components was followed over time using reliable process measures. These measures were used as time-varying covariates in growth curve analyses to estimate the effects of the intervention components over time. Multi-item scales from annually-administered student surveys were used to measure relevant outcome variables, like alcohol use. The impact of the components appears to have been differential. The strongest effects were documented for the planners of extra-curricular activities and parent program components. The classroom curricula proved moderately effective, but no effects were associated with differential levels of community activism. The interactions tested here did not provide support for synergistic effects between selected intervention components. Care must be taken when selecting and combining intervention strategies meant to reduce adolescent alcohol use.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Biglan, A., Ary, D. V., Smolkowski, T. D., and Black, C. (2000). A randomized controlled trial of a community intervention to prevent adolescent tobacco use. Tobacco Control, 9, 24–32.
Birnbaum, A. S., Lytle, L. A., Story, M., Perry, C. L., Murray, D. M. (2002). Are differences in exposure to a multicomponent school-based intervention associated with varying dietary outcomes in adolescents? Health Education and Behavior, 29(4), 427–443.
Carmona, M., and Stewart, K. (1996). A review of alternative activities and alternative programs in youth-oriented prevention. Rockville, MD: Center for Substance Abuse Prevention, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Cook, T. D., and Campbell, D. T. (1979). Quasi-experimentation: Design and analysis issues for field settings. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Cuijpers, P. (2002). Effective ingredients of school-based drug prevention programs: A systematic review. Addictive Behaviors, 27, 1009–1023.
Dusenbury, L., and Falco, M. (1995). Eleven components of effective drug abuse prevention curricula. Journal of School Health, 65(10), 420–425.
Du Toit, S., Du Toit, M., and Cudeck, R. (1999). Introduction to the analysis of multilevel models with LISREL ® 8.30. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International.
Flay, B. R. (2000). Approaches to substance use prevention utilizing school curriculum plus social environment change. Addictive Behaviors, 25(6), 861–885.
Flay, B. R., and Petraitis, J. (1994). The theory of triadic influence: A new theory of health behavior with implications for preventive interventions. In G. S. Albrecht (Ed.), Advances in medical sociology, vol IV: A reconsideration of models of health behavior change (pp. 19–44). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Gorman, D. M., and Speer, J. D. (1996). Preventing alcohol abuse and alcohol-related problems through community interventions: A review of evaluation studies. Psychology and Health, 11, 95–131.
Hansen, W. B. (1993). School-based alcohol prevention programs. Alcohol Health and Research World, 17(1), 54–60.
Joreskog, K., Sorbom, D., Du Toit, S., Du Toit, M. (1999). LISREL ® 8: New Statistical Features. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International.
Komro, K. A., Perry, C. L., Murray, D. M., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Williams, C. L., and Anstine, P. S. (1996). Peer-planned social activities for preventing alcohol use among young adolescents. Journal of School Health, 66(9), 328–334.
Komro, K. A., Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Stigler, M. H., Farbakhsh, K., and Veblen-Mortenson, S. (2001). How did Project Northland reduce alcohol use among youth?: Analysis of mediating variables. Health Education Research, 16(1), 59–70.
Komro, K. A., Perry, C. L., Veblen-Mortenson, S., and Williams, C. L. (1994). Peer participation in Project Northland: A community-wide alcohol use prevention project. Journal of School Health, 64(8), 318–322.
Komro, K. A., and Toomey, T. L. (2002). A research review of strategies to prevent underage drinking. Alcohol Health and Research World, 26(1), 5–14.
Kumpfer, K. L. (2000). Strengthening family involvement in school substance abuse programs. In W. B. Hansen, S. M. Giles, and M. D. Fearnow-Kenny (Eds.), Improving prevention effectiveness (pp. 127–137). Greensboro, NC: Tanglewood Research.
Murray, D. M. (1998). Design and analysis of group-randomized trials. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
National Institute on Drug Abuse (1997). Preventing drug use among children and adolescents. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health.
Norman, G. R., and Streiner, D. L. (2000). Biostatistics: The Bare Essentials (2nd ed.). Hamilton, Ontario: B. C. Decker, Inc.
Pentz, M. A., Dwyer, J. H., MacKinnon, D. P., Flay, B. R., Hansen, W. B., Wang, E. Y. I., and Johnson, C. A. (1989). A multicommunity trial for primary prevention of adolescent drug abuse. Journal of the American Medical Association, 261, 3259–3266.
Perry, C. L. (1999). Creating health behavior change: How to develop community-wide programs for youth. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Perry, C. L. (2000). Preadolescent and adolescent influences on health. In B. D. Smedley and S. L. Syme (Eds.)Promoting health: Intervention strategies from social and behavioral research (pp. 217–253). Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Perry, C. L., Kelder, S. H., Murray, D. M., and Klepp, K. I. (1992). Communitywide smoking prevention: Long-term outcomes of the Minnesota Heart Health Program and the Class of 1999 study. American Journal of Public Health, 82, 1210–1216.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Forster, J. L., Wolfson, M., Wagenaar, A. C., Finnegan, J. R., McGovern, P. G., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Komro, K. A., and Anstine, P. S. (1993). Background, conceptualization, and design of a community-wide research program on adolescent alcohol use: Project Northland. Health Education Research: Theory and Practice, 8(1), 125–136.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Komro, K. A., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Forster, J. L., Bernstein-Lachter, R., Pratt, L. K., Munson, K. A., and Farbakhsh, K. (1998, February). Project Northland – Phase II: Community action to reduce adolescent alcohol use. Paper presented at the Fourth Symposium on Community Action Research and the Prevention of Alcohol and other Drug Problems: A Kettil Bruun Society Thematic Meeting, Russell, New Zealand.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Komro, K. A., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Forster, J. L., Lachter, R. B., Pratt, L. K., Dudovitz, B., Munson, K. A., Farbakhsh, K., Finnegan, J., and McGovern, P. (2000). Project Northland high school interventions: Community action to reduce adolescent alcohol use. Health Education and Behavior, 27(1), 29–49.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Komro, K. A., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Stigler, M. H., Munson, K., Farbakhsh, K., Jones, R. M., and Forster, J. L. (2002). Project Northland: Long-term outcomes of community action to reduce adolescent alcohol use. Health Education and Behavior, 17(1), 117–132.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Toomey, T., Komro, K., Anstine, P. S., McGovern, P., Finnegan, J. R., Forster, J. L., Wagenaar, A. C., and Wolfson, M. (1996). Outcomes of a community-wide alcohol use prevention program during early adolescence: Project Northland. Am Journal of Public Health, 86(7), 956–965.
Raudenbush, S. W. (2001). Comparing personal trajectories and drawing causal inferences from longitudinal data. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 501–25.
Raudenbush, S. W., and Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Resnicow, K., Royce, J., Vaughan, R., Orlandi, M. A., and Smith, M. (1997). Analysis of a multicomponent smoking cessation project: what worked and why. Preventive Medicine, 26, 373–381.
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., and Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Spoth, R., Redmond, C., and Lepper, H. (1999). Alcohol initiation outcomes of a universal family-focused prevention intervention: One- and two-year follow-ups of a controlled study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 13, 103–111.
Tobler, N. S., Roona, M. R., Ochshorn, P., Marshall, D. G., Streke, A. V., and Stackpole, K. M. (2000). School-based adolescent drug prevention programs: 1998 meta-analysis. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 20(4), 275–335.
Tobler, N. S., and Stratton, H. H. (1997). Effectiveness of school-based drug prevention programs: A meta-analysis of the research. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 18, 71–128.
Toomey, T. L., Williams, C. L., Perry, C. L., Murray, D. M., Dudovitz, B., and Veblen-Mortenson, S. (1996). An alcohol primary prevention program for parents of 7th graders: The Amazing Alternatives! home program. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse, 5(4), 35–53.
Turner, G., and Shepherd, J. (1999). A method in search of a theory: peer education and health promotion. Health Education Research: Theory and Practice, 14(2), 235–247.
Veblen-Mortenson, S., Rissel, C., Perry, C. L., Forster, J., Wolfson, M., and Finnegan, J. R. (1999). Lessons learned from Project Northland: Community organization in rural communities. In N. Bracht (Ed.), Health promotion at the community level: New advances (Vol. 2). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publica-tions.
Wagenaar, A. C., and Perry, C. L. (1994). Community strategies for the reduction of youth drinking: theory and application. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 4, 319–345.
West, S. G., and Aiken, L. S. (1997). Toward understanding individual effects in multicomponent prevention programs: Design and analysis strategies. In K. J. Bryant, M. Windle, and S. G. West (Eds.), The science of prevention: Methodological advances from alcohol and substance abuse research (pp. 167–210). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Williams, C. L., Perry, C. L., Dudovitz, B., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Anstine, P. S., Komro, K. A., and Toomey, T. L. (1995). A home-based prevention program for sixth-grade alcohol use: Results from Project Northland. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 16(2), 125–147.
Williams, C. L., Toomey, T. L., McGovern, P., Wagenaar, A. C., and Perry, C. L. (1995). Development, reliability, and validity of self-report alcohol use measures with young adolescents. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse, 4(3), 17–40
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by grants R01-AA08596 and R01-AA10791 (to Cheryl L. Perry and Carolyn L. Williams, Principal Investigators) from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism to the University of Minnesota (1990–99).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stigler, M.H., Perry, C.L., Komro, K.A. et al. Teasing Apart a Multiple Component Approach to Adolescent Alcohol Prevention: What Worked in Project Northland?. Prev Sci 7, 269–280 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-006-0040-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-006-0040-7