Abstract
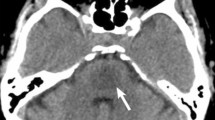
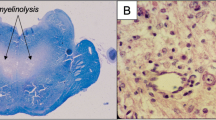
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) is a demyelinating condition affecting not only the pontine base, but also involving other brain areas. It usually occurs on a background of chronic systemic illness, and is commonly observed in individuals with alcoholism, malnutrition and liver disease. Studies carried out 25–30 years ago established that the principal etiological factor was the rapid correction of hyponatremia resulting in osmotic stress. This article reviews progress achieved since that time on its pathogenesis, focusing on the role of organic osmolytes, the blood–brain, barrier, endothelial cells, myelinotoxic factors triggered by osmotic stress, and the role of various factors that predispose to the development of CPM. These advances show great promise in providing novel therapeutic options for the management of patients afflicted with CPM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH (1962) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Jacob H (ed) IV International Congress of Neuropathology, vol 3. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 303–308
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiat 81:154–172
Adler S, Verbalis JG, Williams D (1995) Effect of rapid correction of hyponatremia on the blood–brain barrier of rats. Brain Res 679:135–143
Aleu FP, Terry RD (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Path 76:140–146
Alfieri RR, Cavazzoni A, Petronini PG, Bonelli MA, Caccamo AE, Borghetti AF, Wheeler KP (2002) Compatible osmolytes modulate the response of porcine endothelial cells to hypertonicity and protect them from apoptosis. J Physiol 540:499–508
Ashrafian H, Davey P (2001) A review of the causes of central pontine myelinosis: yet another apoptotic illness? Eur J Neurol 8:103–109
Ayus JC, Krothapalli RK, Armstrong DL (1985) Rapid correction of severe hyponatremia in the rat: histopathological changes in the brain. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 248:F711–F719
Baker EA, Tian Y, Adler S, Verbalis JG (2000) Blood–brain barrier disruption and complement activation in the brain following rapid correction of chronic hyponatremia. Exp Neurol 165:221–230
Bluml S, Zuckerman E, Tan J, Ross BD (1998) Proton-decoupled 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals osmotic and metabolic disturbances in human hepatic encephalopathy. J Neurochem 71:1564–1576
Bonham CA, Dominguez EA, Fukui MB, Paterson DL, Pankey GA, Wagener MM, Fung JJ, Singh N (1998) Central nervous system lesions in liver transplant recipients: prospective assessment of indications for biopsy and implications for management. Transplantation 66:1596–1604
Boon AP, Carey MP, Adams DH, Buckels J, McMaster P (1991) Central pontine myelinolysis in liver transplantation. J Clin Pathol 44:909–914
Brightman MW, Hori M, Rapoport SI, Reese TS, Westergaard E (1973) Osmotic opening of tight junctions in cerebral endothelium. J Comp Neurol 152:317–325
Brown WD (2000) Osmotic demyelination disorders: central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Curr Opin Neurol 13:691–697
Burcar PJ, Norenberg MD, Yarnell PR (1977) Hyponatremia and central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology 27:223–226
Burg MB, Ferraris JD (2008) Intracellular organic osmolytes: function and regulation. J Biol Chem 283:7309–7313
Burg MB, Ferraris JD, Dmitrieva NI (2007) Cellular response to hyperosmotic stresses. Physiol Rev 87:1441–1474
Cammer W, Bloom BR, Norton WT, Gordon S (1978) Degradation of basic protein in myelin by neutral proteases secreted by stimulated macrophages: a possible mechanism of inflammatory demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:1554–1558
Chason JL, Landers JW, Gonzalez JE (1964) Central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 27:317–325
Córdoba J, Gottstein J, Blei AT (1996) Glutamine, myo-inositol, and organic brain osmolytes after portacaval anastomosis in the rat: implications for ammonia-induced brain edema. Hepatology 24:919–923
Cyong JC, Witkin SS, Rieger B, Barbarese E, Good RA, Day NK (1982) Antibody-independent complement activation by myelin via the classical complement pathway. J Exp Med 155:587–598
De Broucker T, Rueff B, Hammel P, Hadengue A (1989) Hypophosphoremia: a possible cause of central pontine myelinolysis. Presse Med 18:1166
DeLuca GC, Nagy Z, Esiri MM, Davey P (2002) Evidence for a role for apoptosis in central pontine myelinolysis. Acta Neuropathol 103:590–598
Estol CJ, Faris AA, Martinez AJ, Ahdab-Barmada M (1989) Central pontine myelinosis after liver transplantation. Neurology 39:493–498
Feigin I, Budzilovich GN (1978) The role of edema in diffuse sclerosis and other leukoencephalopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 37:326–357
Feigin I, Budzilovich G, Weinberg S, Ogata U (1973) Degeneration of white matter in hypoxia, acidosis and edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 32:125–143
Ferreiro JA, Robert MA, Townsend J, Vinters HV (1992) Neuropathologic findings after liver transplantation. Acta Neuropathol 84:1–14
Ghidoni P, Di Bella C, Masini T, Paone G, Matturri L (1994) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 26:3602–3603
Goebel HH, Zur PH (1972) Central pontine myelinolysis. A clinical and pathological study of 10 cases. Brain 95:495–504
Goebel HH, Zur PH (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 28. North Holland Publishing Co, Amsterdam, pp 285–316
Goldman JE, Horoupian DS (1981) Demyelination of the lateral geniculate nucleus in central pontine myelinolysis. Ann Neurol 9:185–189
Gupta RK, Saraswat VA, Poptani H, Dhiman RK, Kohli A, Gujral RB, Naik SR (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging and localized in vivo proton spectroscopy in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Amer J Gastroenterol 88:670–674
Häussinger D, Laubenberger J, Vom Dahl S, Ernst T, Bayer S, Langer M, Gerok W, Hennig J (1994) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies on human brain myo-inositol in hypo-osmolarity and hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 107:1475–1480
Hedley-Whyte E, Hsu DW (1986) Effect of dexamethasone on blood–brain barrier in the normal mouse. Ann Neurol 19:373–377
Heng AE, Vacher P, Aublet-Cuvelier B, Garcier JM, Sapin V, Deteix P, Souweine B (2007) Centropontine myelinolysis after correction of hyponatremia: role of associated hypokalemia. Clin Nephrol 67:345–351
Hoheisel D, Nitz T, Franke H, Wegener J, Hakvoort A, Tilling T, Galla HJ (1998) Hydrocortisone reinforces the blood–brain barrier properties in a serum free cell culture system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 244:312–316
Illowsky BP, Laureno R (1987) Encephalopathy and myelinolysis after rapid correction of hyponatraemia. Brain 110:855–867
Isaacks RE, Bender AS, Kim CY, Prieto NM, Norenberg MD (1994) Osmotic regulation of myo-inositol uptake in primary astrocyte cultures. Neurochem Res 19:331–338
Isaacks RE, Bender AS, Kim CY, Shi YF, Norenberg MD (1999a) Effect of ammonia and methionine sulfoximine on myo-inositol transport in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Res 24:51–59
Isaacks RE, Bender AS, Kim CY, Shi YF, Norenberg MD (1999b) Effect of osmolality and anion channel inhibitors on myo-inositol efflux in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 57:866–871
Karp BI, Laureno R (2000) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis after correction of hyponatremia. Neurologist 6:255–266
Ke QH, Liang TB, Yu J, Zheng SS (2006) A study of the pathogenesis and prevention of central pontine myelinolysis in a rat model. J Int Med Res 34:264–271
Kepes JJ, Reece CA, Oxley DK (1965) Central pontine myelinolysis in a 7-year-old boy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 28:39–47
Klavins JV (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:302–317
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Norenberg MD (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination: relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science 211:1068–1070
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Rojiani AM, Filley CM (2006) Central and extrapontine myelinolysis: then...and now. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:1–11
Kreis R, Ross BD, Farrow NA, Ackerman Z (1992) Metabolic disorders of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy detected with H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 182:19–27
Lampl C, Yazdi K (2002) Central pontine myelinolysis. Eur Neurol 47:3–10
Laureno R (1980) Experimental pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Ann Neurol 8:117
Laureno R (1983) Central pontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Ann Neurol 13:232–242
Leslie KO, Robertson AS, Norenberg MD (1980) Central pontine myelinolysis: an osmotic gradient hypothesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:370
Lien Y-HH (1995) Role of organic osmolytes in myelinolysis. A topographic study in rats after rapid correction of hyponatremia. J Clin Invest 95:1579–1586
Lien Y-HH, Shapiro JI, Chan L (1991) Study of brain electrolytes and organic osmolytes during correction of chronic hyponatremia. Implications for the pathogenesis of central pontine myelinolysis. J Clin Invest 88:303–309
Liu JS, Zhao ML, Brosnan CF, Lee SC (2001) Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine in multiple sclerosis lesions. Am J Pathol 158:2057–2066
Lohr JW (1994) Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia: association with hypokalemia. Am J Med 96:408–413
Lubrich B, Spleiss O, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Van Calker D (2000) Differential expression, activity and regulation of the sodium/myo-inositol cotransporter in astrocyte cultures from different regions of the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 39:680–690
Ludwin SK (1997) The pathobiology of the oligodendrocyte. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:111–124
Martin RJ (2004) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: the osmotic demyelination syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 75(Suppl 3):iii22–iii28
McKee AC, Winkelman MD, Banker BQ (1988) Central pontine myelinolysis in severely burned patients: relationship to serum hyperosmolality. Neurology 38:1211–1217
Messert B, Orrison WW, Hawkins MJ, Quaglieri CE (1979) Central pontine myelinolysis. Considerations on etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurology 29:147–160
Michell AW, Burn DJ, Reading PJ (2003) Central pontine myelinolysis temporally related to hypophosphataemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 74:820
Monteiro L (1971) La myelinolyse du centre du pont dans cadre d’un nouveau syndrome histopathologique de topographie systematisee. J Neurol Sci 13:293–314
Murase T, Sugimura Y, Takefuji S, Oiso Y, Murata Y (2006) Mechanisms and therapy of osmotic demyelination. Am J Med 119:S69–S73
Neuwelt EA, Barnett PA, Bigner DD, Frenkel EP (1982) Effects of adrenal cortical steroids and osmotic blood–brain barrier opening on methotrexate delivery to gliomas in the rodent: the factor of the blood–brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4420–4423
Norenberg MD (1981) Ultrastructural observations in electrolyte-induced myelinolysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 40:319
Norenberg MD (1983) A hypothesis of osmotic endothelial injury. A pathogenetic mechanism in central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol 40:66–69
Norenberg MD (1984) Treatment of hyponatremia: the case for a more conservative approach. In: Narins RG (ed) Controversies in nephrology and hypertension. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 379–391
Norenberg MD, Bell KP (1982) Plasminogen activator and steroids in electrolyte-induced myelinolysis. Proc Int Cong Neuropathol 9:76
Norenberg MD, Papendick RE (1984) Chronicity of hyponatremia as a factor in experimental myelinolysis. Ann Neurol 15:544–547
Norenberg MD, Leslie KO, Robertson AS (1982) Association between rise in serum sodium and central pontine myelinolysis. Ann Neurol 11:128–135
Oh MS, Choi KC, Uribarri J, Sher J, Rao C, Carroll HJ (1990) Prevention of myelinolysis in rats by dexamethasone or colchicine. Amer J Nephrol 10:158–161
Okeda R (1974) Centrale pontine Myelinolyse. Pathogetische Aspekte aufgrund morphometrischer Untersuchungen des Brückenfusses. Acta Neuropathol 27:233–246
Powers JM, McKeever PE (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. An ultrastructural and elemental study. J Neurol Sci 29:65–81
Pujol J, Kulisevsky J, Moreno A, Deus J, Alonso J, Balanzó J, Martí-Vilalta JL, Capdevila A (1996) Neurospectroscopic alterations and globus pallidus hyperintensity as related magnetic resonance markers of reversible hepatic encephalopathy. Neurology 47:1526–1530
Qadir F, Hasan A, Masood M (2005) Extra pontine myelinolysis associated with hypophosphatemia. J Pakistan Med Assoc 55:254–256
Rapoport SI (1976) Blood–brain barrier in physiology and medicine. Raven, New York
Reynolds TB (1980) Water, electrolyte, and acid-base disorders in liver disease. In: Maxwell MH, Kleeman CR (eds) Clinical disorders of fluid and electrolyte metabolism. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1251–1261
Riggs JE, Schochet SS Jr (1989) Osmotic stress, osmotic myelinolysis, and oligodendrocyte topography. Arch Pathol Lab Med 113:1386–1388
Rojiani AM, Prineas JW, Cho ES (1987) Protective effect of steroids in electrolyte-induced demyelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:495–504
Rojiani AM, Prineas JW, Cho E-S (1994a) Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats—I. Role of the blood-barrier and edema. Acta Neuropathol 88:287–292
Rojiani AM, Cho E-S, Sharer L, Prineas JW (1994b) Electrolyte-induced demyelination in rats—II. Ultrastructural evolution. Acta Neuropathol 88:293–299
Rosenberg GA, Dencoff JE, Correa N Jr, Reiners M, Ford CC (1996) Effect of steroids on CSF matrix metalloproteinases in multiple sclerosis: relation to blood–brain barrier injury. Neurology 46:1626–1632
Rosman NP, Kakulas BA, Richardson EP Jr (1966) Central pontine myelinolysis in a child with leukemia. Arch Neurol 14:273–820
Schneck SA, Burks JS, Yarnell PR (1978) Antemortem diagnosis of central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology 28:389
Scolding NJ, Morgan BP, Houston A, Campbell AK, Linington C, Compston DA (1989) Normal rat serum cytotoxicity against syngeneic oligodendrocytes. Complement activation and attack in the absence of anti-myelin antibodies. J Neurol Sci 89:289–300
Shurtliff LF, Ajax ET, Englert E Jr, D’Agostino AN (1966) Central pontine myelinolysis and cirrhosis of the liver. A report of four cases. Am J Clin Pathol 46:239–244
Silver SM, Schroeder BM, Sterns RH, Rojiani AM (2006) Myoinositol administration improves survival and reduces myelinolysis after rapid correction of chronic hyponatremia in rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:37–44
Simka M (2009) Blood brain barrier compromise with endothelial inflammation may lead to autoimmune loss of myelin during multiple sclerosis. Curr Neurovasc Res 6:132–139
Singh N, Yu VL, Gayowski T (1994) Central nervous system lesions in adult liver transplant recipients: clinical review with implications for management. Medicine 73:110–118
Sinton CM, Fitch TE, Petty F, Haley RW (2000) Stressful manipulations that elevate corticosterone reduce blood–brain barrier permeability to pyridostigmine in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 165:99–105
Soupart A, Penninckx R, Stenuit A, Decaux G (2000) Azotemia (48 h) decreases the risk of brain damage in rats after correction of chronic hyponatremia. Brain Res 852:167–172
Soupart A, Silver S, Schroeder B, Sterns R, Decaux G (2002) Rapid (24-h) reaccumulation of brain organic osmolytes (particularly myo-inositol) in azotemic rats after correction of chronic hyponatremia. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1433–1441
Starzl TE, Schneck SA, Mazzoni G, Aldrete JA, Porter KA, Schroter GP, Koep LJ, Putnam CW (1978) Acute neurological complications after liver transplantation with particular reference to intraoperative cerebral air embolus. Ann Surg 187:236–240
Sterns RH, Silver S, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Rojiani AM (2007) Current perspectives in the management of hyponatremia: prevention of CPM. Expert Rev Neurotherap 7:1791–1797
Strange K (1992) Regulation of solute and water balance and cell volume in the central nervous system. J Am Soc Nephrol 3:12–27
Strange K (1993) Maintenance of cell volume in the central nervous system. Pediatr Nephrol 7:689–697
Sugimura Y, Murase T, Takefuji S, Hayasaka S, Takagishi Y, Oiso Y, Murata Y (2005) Protective effect of dexamethasone on osmotic-induced demyelination in rats. Exp Neurol 192:178–183
Thurston JH, Hauhart RE, Nelson JS (1987) Adaptive decreases in amino acids (taurine in particular), creatine, and electrolytes prevent cerebral edema in chronically hyponatremic mice: rapid correction (experimental model of central pontine myelinolysis) causes dehydration and shrinkage of brain. Metab Brain Dis 2:223–241
Todd AS (1972) Endothelium and fibrinolysis. Atherosclerosis 15:137–140
Tomlinson BE, Pierides AM, Bradley WG (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. Two cases with associated electrolyte disturbance. Quart J Med 45:373–386
Vadeboncoeur N, Segura M, Al Numani D, Vanier G, Gottschalk M (2003) Pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine release by human brain microvascular endothelial cells stimulated by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 35:49–58
Vanguri P, Koski CL, Silverman B, Shin ML (1982) Complement activation by isolated myelin: activation of the classical pathway in the absence of myelin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:3290–3294
Verbalis JG, Gullans SR (1991) Hyponatremia causes large sustained reductions in brain content of multiple organic osmolytes in rats. Brain Res 567:274–282
Verbalis JG, Gullans SR (1993) Rapid correction of hyponatremia produces differential effects on brain osmolyte and electrolyte reaccumulation in rats. Brain Res 606:19–27
Verbalis JG, Martinez AJ (1991) Neurological and neuropathological sequelae of correction of chronic hyponatremia. Kidney Int 39:1274–1282
Verma S, Nakaoke R, Dohgu S, Banks WA (2006) Release of cytokines by brain endothelial cells: a polarized response to lipopolysaccharide. Brain Behavior Immun 20:449–455
Wing MG, Zajicek J, Seilly DJ, Compston DA, Lachmann PJ (1992) Oligodendrocytes lack glycolipid anchored proteins which protect them against complement lysis. Restoration of resistance to lysis by incorporation of CD59. Immunology 76:140–145
Wren DR, Noble M (1989) Oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte/type-2 astrocyte progenitor cells of adult rats are specifically susceptible to the lytic effects of complement in absence of antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9025–9029
Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M (1979) Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain 102:361–385
Wszolek ZK, McComb RD, Pfeiffer RF, Steg RE, Wood RP, Shaw BW Jr, Markin RS (1989) Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following liver transplantation: relationship to serum sodium. Transplantation 48:1006–1012
Acknowledgments
This article is dedicated to Bette Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, Kevin O. Leslie, Roger E. Riepe, Scott R. VandenBerg and Andrew S. Robertson, all terrific residents who spent uncountable hours analyzing human clinical and pathological data, performing animal experiments and providing ideas that ultimately led to the concept of CPM resulting as the consequence of a rapid rise in serum osmolarity—most commonly following the rapid correction of hyponatremia. All have gone on to achieve outstanding careers as neuropathologists, pathologists, and neurologists. I also would like to especially thank Professor Karin Weissenborn, Hannover Medical School, Germany, for encouraging me to write this article. This work was supported by a Merit Review from the Department of Veterans Affairs and NIH Grant No. DK063311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norenberg, M.D. Central pontine myelinolysis: historical and mechanistic considerations. Metab Brain Dis 25, 97–106 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9175-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9175-0