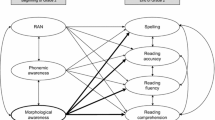
Abstract
Growth curve analyses showed that (a) word-level phonological and orthographic awareness show greatest growth during the primary grades but some additional growth thereafter, and (b) three kinds of morphological awareness show greatest growth in the first three or four grades but one—derivation—continues to show substantial growth after fourth grade. Implications of the findings for the role of three kinds of linguistic awareness—phonological, orthographic, and morphological—in learning to read and spell words are discussed. A case is made that phonological awareness, while necessary, is not sufficient for learning to read English—all three kinds of linguistic awareness that are growing during the primary grades need to be coordinated and applied to literacy learning. This finding and a review of the research on linguistic awareness support the conclusion that the recommendations of the National Reading Panel need to be amended so that the research evidence supporting the importance of both orthographic and morphological awareness, and not only phonological awareness, is acknowledged. Moreover, evidence-based strategies for teaching each of these kinds of linguistic awareness and their interrelationships need to be disseminated to educational practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M. J. (1990) Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about print. MIT Press, Cambridge, MD
Anglin J. (1993) Vocabulary development: A morphological analysis. Monographs for the Society for Research in Child Development 58: 1–66
Apel K., Masterson J. (2001) Theory-guided spelling assessment and intervention: A case study. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools 32: 182–195
Apel K., Wolter J., Masterson J. (2006) Effects of phonotactic and orthotactic probabilities during fast mapping on 5-year-olds’ learning to spell. Developmental Neuropsychology 29: 21–42
Arnback E., Elbro C. (2000) The effects of morphological awareness training on the reading and spelling skills of young dyslexics. Scandanavian Journal of Educational Research 44: 229–251
Bahr R. H., Silliman E. R., Berninger V. (2009) What spelling errors have to tell about vocabulary learning. In: Wood C., Connelly V. (eds) Reading and spelling: Contemporary perspectives. Routledge EARLi Writing Series, London
Barker T. A., Torgesen J. K., Wagner R. K. (1992) The role of orthographic processing skills on five different reading tasks. Reading Research Quarterly 27: 335–345
Bentler P. M. (2001) EQS structural equation modeling program manual. Multivariate Software, Encino, CA
Berko J. (1958) The child’s learning of English morphology. Word 14: 150–177
Berninger V. (1987) Global, component, and serial processing of printed words in beginning readers. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 43: 387–418
Berninger V. (2001) Process assessment of the learner (PAL) test battery for reading and writing. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Berninger V., Traweek D. (1991) Effects of two-phase reading intervention on three orthographic-phonological code connections. Learning and Individual Differences 3: 323–338
Berninger V., Abbott R., Brooksher R., Lemos Z., Ogier S., Zook D. et al (2000) A connectionist approach to making the predictability of English orthography explicit to at-risk beginning readers: Evidence for alternative, effective strategies. Developmental Neuropsychology 17: 241–271
Berninger V., Abbott R., Whitaker D., Sylvester L., Nolen S. (1995) Integrating low-level skills and high-level skills in treatment protocols for writing disabilities. Learning Disability Quarterly 18: 293–309
Berninger V., Cartwright A., Yates C., Swanson H., Abbott B. (1994) Developmental skills related to writing and reading acquisition in the intermediate grades. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 6: 161–196
Berninger V., Garcia N., Abbott R. (2009) Multiple processes that matter in writing instruction and assessment. In: Troia G. A. (eds) Instruction and assessment for struggling writers: Evidence based practices. Guilford, New York, pp 15–50
Berninger V., Nagy W., Carlisle J., Thomson J., Hoffer D., Abbott S. et al (2003) Effective treatment for dyslexics in grades 4–6: Behavioral and brain evidence. In: Foorman B. (eds) Preventing and remediating reading difficulties: Bringing science to scale. York Press, Timonium, MD, pp 275–308
Berninger V., Nagy W., Richards T., Raskind W. (2008a) Developmental dyslexia: A developmental neurolinguistic approach. In: Rickheit G., Strohner H. (eds) Handbook of communicative competence. Handbook of applied linguistics. Mouton de Gruyter, Germany, pp 397–440
Berninger V., Raskind W., Richards T., Abbott R., Stock P. (2008b) A multidisciplinary approach to understanding developmental dyslexia within working-memory architecture: Genotypes, phenotypes, brain, and instruction. Developmental Neuropsychology 33: 707–744
Berninger V., Winn W., Stock P., Abbott R., Eschen K., Lin C. et al (2008) Tier 3 specialized writing instruction for students with dyslexia. Reading and Writing. An Interdisciplinary Journal 21: 95–129
Berninger V., Yates C., Cartwright A., Rutberg J., Remy E., Abbott R. (1992) Lower-level developmental skills in beginning writing. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 4: 257–280
Berninger V., Yates C., Lester K. (1991) Multiple orthographic codes in reading and writing. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 3: 115–149
Bourassa D., Treiman R., Kessler B. (2006) Use of morphology in spelling by children with dyslexia and typically developing children. Memory & Cognition 34: 703–714
Bradley L., Bryant P. (1983) Categorizing sounds and learning to read: A causal connection. Nature 303: 419–421
Bruce D. J. (1964) The analysis of word sounds. British Journal of Educational Psychology 34: 158–170
Bryant P., Nunes T., Bindman M. (1997) Children’s understanding of the connection between grammar and spelling. In: Blachman B. (eds) Foundations of reading acquisition and dyslexia. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ, pp 219–240
Carlisle J (1994) Morphological awareness, spelling, and story writing. Possible relationships for elementary-age children with and without learning disabilities. In: Jordan N. C., Goldsmith-Phillips J. (eds) Learning disabilities. New directions for assessment and intervention. Allyn Bacon, Boston, pp 123–145
Carlisle J. (1995) Morphological awareness and early reading achievement. In: Feldman L. B. (eds) Morphological aspects of language processing. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 189–209
Carlisle J. (2000) Awareness of the structure and meaning of morphologically complex words: Impact on reading. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 12: 169–190
Carlisle J., Nomanbhoy D. (1993) Phonological and morphological awareness in first graders. Applied Psycholinguistics 14: 177–195
Carlisle J., Rice M. (2002) Improving reading comprehension. Research-based principles and practices. York Press, Inc., Baltimore, MD
Casalis S., Louis-Alexandre M.-F. (2000) Morphological analysis, phonological analysis and learning to read French: A longitudinal study. Reading and Writing. An Interdisciplinary Journal 12: 303–335
Derwing B. L. (1976) Morpheme recognition and the learning of rules for derivational morphology. Canadian Journal of Linguistics 21: 38–66
Derwing B. L., Smith M. L., Wiebe G. E. (1995) On the role of spelling in morpheme recognition: Experimental studies with children and adults. In: Feldman L. (eds) Morphological aspects of language processing. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 3–27
Dixon R. C., Engelmann S. (2001) Spelling through morphographs: Teacher’s guide. SRA/McGraw-Hill, Columbus, OH
Ehri L. (1978) Beginning reading from a psycholinguistic perspective: Amalgamation of word identities. In: Murray F. B. (eds) The development of the reading process. International reading association monograph (No. 3). International Reading Association, Newark, pp 1–33
Ehri L. (1980) The development of orthographic images. In: Frith U. (eds) Cognitive processes in spelling. Academic Press, London, pp 311–338
Ehri L. C. (1992) Reconceptualizing the development of sight word reading and its relation to recoding. In: Gough P. B., Ehri L. C., Treiman R. (eds) Reading acquisition. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 107–143
Fayol M., Thévenin M.-G., Jarousse J.-P., Totereau C. (1995) From learning to teaching to learning French written morphology. In: Nunes T. (eds) Learning to read: An integrated view from research and practice. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherland, pp 43–64
Foulin J., Chanquoy L. (2006) Online study of word spelling production in children. In: Waes L., Leijten M., Neuwirth C. (eds) Writing and digital media. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 145–152
Fowler A., Liberman I. (1995) The role of phonology and orthography in morphological awareness. In: Feldman L. (eds) Morphological aspects of language processing. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, pp 157–188
Green L., McCutchen D., Schweibert C., Quinlan T., Eva-Wood A., Juelis J. (2003) Morphological development in children’s writing. Journal of Educational Psychology 95: 752–761
Henry M. (1989) Children’s word structure knowledge: Implications for decoding and spelling instruction. Reading and Writing. An Interdisciplinary Journal 1: 135–152
Henry M. (2003) Unlocking literacy. Effective decoding and spelling instruction. Paul H. Brookes Publishing, Baltimore
Jaffré J., Fayol M. (2006) Orthography and literacy in French. In: Joshi R. M., Aaron P. G. (eds) Handbook of orthography and literacy. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ, pp 3–20
Johnson N. (1978) Coding processes in memory. In: Estes W. K. (eds) Handbook of learning and cognitive processes. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 87–129
Johnson N. (1986) On looking at letters within words: Do we “see” them in memory? Journal of Memory and Language 25: 558–570
Kessler B., Treiman R. (1997) Syllable structure and the distribution of phonemes in English syllables. Journal of Memory and Language 37: 295–311
Ku Y., Anderson R. C. (2003) Development of morphological awareness in Chinese and English. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 16: 399–422
Largy P., Cousin M., Bryant P., Fayol M. (2007) When memorized instances compete with rules: The case of number-noun agreement in written French. Journal of Child Language 34: 425–437
Liberman L., Shankweiler D., Fischer F., Carter B. (1974) Explicit syllable and phoneme segmentation in the young child. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 18: 201–212
Liberman I., Shankweiler D., Liberman A., Fowler C., Fischer F. (1977) Phonetic segmentation and recoding in the beginning reader. In: Reber A., Scarborough D. (eds) Toward a psychology of reading. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 207–225
Mahony D., Singson M., Mann V. (2000) Reading ability and sensitivity to morphological relations. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 12: 191–218
Manis F., Szeszulski P., Holt L., Graves K. (1990) Variation in component word recognition and spelling skills among dyslexic children and normal readers. In: Carr T. H., Levy B. A. (eds) Reading and its development: Component skills approaches. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 207–259
Martinet C., Valdois S., Fayol M. (2004) Lexical orthographic knowledge develops from the beginning of reading acquisition. Cognition 91: B11–B22
Mattingly I. (1972) Reading, the linguistic process, and linguistic awareness. In: Kavanagh J., Mattingly I. (eds) Language by ear and by eye: The relationship between speech and reading. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 133–147
Nagy W. (2007) Metalinguistic awareness and the vocabulary-comprehension connection. In: Wagner R. K., Muse A., Tannenbaum K. (eds) Vocabulary acquisition and its implications for reading comprehension. Guilford, New York, pp 52–77
Nagy W.E., Anderson R. (1984) How many words in printed school English? Reading Research Quarterly 19: 304–330
Nagy W. E., Anderson R. C., Schommer M., Scott J., Stallman A. (1989) Morphological families and word recognition. Reading Research Quarterly 24: 262–282
Nagy W., Berninger V., Abbott R. (2006) Contributions of morphology beyond phonology to literacy outcomes of upper elementary and middle school students. Journal of Educational Psychology 98: 134–147
Nagy W., Berninger V., Abbott R., Vaughan K., Vermeulen K. (2003) Relationship of morphology and other language skills to literacy skills in at-risk second graders and at-risk fourth grade writers. Journal of Educational Psychology 95: 730–742
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). (2000). Report of the national reading panel. Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction: Reports of the subgroups (NIH Publication No. 00–4754). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing.
Nunes T., Bryant P. (1995) The effect of morphological training on word reading and spelling. In: Nunes T. (eds) Learning to read: An integrated view from research and practice. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 43–64
Nunes T., Bryant P. (2006) Improving literacy by teaching morphemes (improving learning series). Routledge, New York
Nunes T., Bryant P., Bindman M. (1997) Morphological spelling strategies: Developmental stages and processes. Developmental Psychology 33(4): 637–649
Nunes T., Bryant P., Bindman M. (2006) The effects of learning to spell on children’s awareness of morphology. Reading and Writing 19: 767–787
Nunes T., Bryant P., Olsson J. (2003) Learning morphological and phonological spelling rules: An intervention study. Scientific Studies of Reading 7: 289–307
Olson R., Datta H., Gayan J., DeFries J. (1999) A behavioral-genetic analysis of reading disabilities and component processes. In: Klein R., McMullen P. (eds) Converging methods for understanding reading and dyslexia. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 133–151
Olson R., Forsberg H., Wise B. (1994) Genes, environment, and the development of orthographic skills. In: Berninger V. W. (eds) The varieties of orthographic knowledge I: Theoretical and developmental issues. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 27–71
Olson R., Forsberg H., Wise B., Rack J. (1994) Measurement of word recognition, orthographic, and phonological skills. In: Lyon G. R. (eds) Frames of reference for the assessment of learning disabilities. Brooks, Baltimore, pp 243–277
Pacton, S. & Deacon, S. H. (2009). The timing and mechanisms of children’s use of morphological information in spelling: Evidence from English and French. Cognitive Development.
Pacton S., Fayol M. (2004) Learning to spell in a deep orthography, The case of French. In: Berman R. A. (eds) Language development across childhood and adolescence. John Benjamin Pub. Company, Amsterdam
Pacton S., Fayol M., Perruchet P. (2005) Children’s implicit learning of graphotactic and morphological regularities. Child Development 76: 324–339
Pacton S., Perruchet P., Fayol M., Cleeremans A. (2001) Implicit learning out of the lab: The case of orthographic regularities. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 130: 401–426
Perfetti C. (1992) The representation problem in reading acquisition. In: Gough P. B., Ehri L. C., Treiman R. (eds) Reading acquisition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 145–174
Plaza M., Cohen H. (2004) Predictive influence of phonological processing, morphological/syntactic skill, and naming speed on spelling performance. Brain and Cognition 55: 368–373
Raudenbush, S. W., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods (2nd ed.) Sage.
Raudenbush S. W., Chan W (1993) Application of hierarchical linear model to the study of adolescent deviance in an overlapping cohort design. Journal of Clinical and Consulting Psychology 61: 941–951
Raudenbush S. W., Bryk A. S., Congdon R. (2004) Hierarchical linear and nonlinear modeling (version 6). Scientific Software International, Lincolnwood
Richards T., Aylward E., Berninger V., Field K., Parsons A., Richards A., Nagy W. (2006a) Individual fMRI activation in orthographic mapping and morpheme mapping after orthographic or morphological spelling treatment in child dyslexics. Journal of Neurolinguistics 19: 56–86
Richards T., Aylward E., Raskind W., Abbott R., Field K., Parsons A. et al (2006) Converging evidence for triple word form theory in children with dyslexia. Developmental Neuropsychology 30: 547–589
Richards T., Berninger V., Aylward E., Richards A., Thomson J., Nagy W. et al (2002) Reproducibility of proton MR spectroscopic imaging PEPSI): Comparison of dyslexic and normal reading children and effects of treatment on brain lactate levels during language tasks. American Journal of Neuroradiology 23: 1678–1685
Richards, T., Berninger, V. & Fayol, M. (2009). FMRI activation differences between 11-year-old good and poor spellers’ access in working memory to temporary and long-term orthographic representations. Journal of Neurolinguistics. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroling.2008.11.002.
Richards T., Berninger V., Nagy W., Parsons A., Field K., Richards A. (2005) Brain activation during language task contrasts in children with and without dyslexia: Inferring mapping processes and assessing response to spelling instruction. Educational and Child Psychology 22(2): 62–80
Richards T., BerningerV. Winn W., Stock P., Wagner R., Muse A. et al (2007) fMRI activation in children with dyslexia during pseudoword aural repeat and visual decode: Before and after instruction. Neuropsychology 21: 732–747
Rosner J. (1974) Helping children overcome learning difficulties. Walker & Co, New York
Seymour P. (1997) Foundations of orthographic development. In: Perfetti C., Rieben L., Fayol M. (eds) Learning to spell. Research, theory, and practices across languages. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ, pp 319–337
Silliman E. R., Bahr R. H., Peters M. L. (2006) Spelling patterns in preadolescents with atypical language skills: Phonological, morphological, and orthographic factors. Developmental Neuropsychology 20: 93–123
Singson M., Mahoney D., Mann V. (2000) The relation between reading ability and morphological skills: Evidence from derivational suffixes. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 12: 219–252
Snowling M. (1980) The development of grapheme-phoneme correspondence in normal and dyslexic readers. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 29: 294–305
Stahl S., Nagy W. (2006) Teaching word meaning. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ
Templeton S. (1991) Teaching and learning the English spelling system: Reconceptualizing method and purpose. Elementary School Journal 92: 185–201
Templeton S., Bear D. (1992) Development of orthographic knowledge and the foundations of literacy: A memorial Feltschrift for Edmund Henderson. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ
Treiman R. (1985) Onsets and rimes as units of spoken syllables: Evidence from children. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 39: 161–181
Treiman R., Cassar M. (1997) Spelling acquisition in English. In: Perfetti C., Rieben L., Fayol M. (eds) Learning to spell. Research, theory, and practice. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ, pp 61–80
Tyler A., Nagy W. (1989) The acquisition of English derivational morphology. Journal of Memory and Language 28: 649–667
Tyler A., Nagy W. (1990) Use of derivational morphology during reading. Cognition 36: 17–34
Venezky R. (1970) The structure of English orthography. Mouton, The Hague
Venezky R. (1999) The American way of spelling. Guilford, New York
Wagner R. K., Torgesen J. K., Rashotte C. A. (1999) The comprehensive test of phonological processing. Pro-Ed, Austin, TX
Wechsler D. (1991) Wechsler intelligence scale for children (3rd ed.). Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Wagner R., Torgesen J. (1987) The nature of phonological processing and its causal role in the acquisition of reading skills. Psychological Bulletin 101: 192–212
Wagner R. K., Torgesen J. K., Rashotte C. A. (1999) The comprehensive test of phonological processing. Pro-Ed, Austin, TX
Walker J., Hauerwas L. (2006) Development of phonological, morphological, and orthographic knowledge in young spellers: The case of inflected verbs. Reading and Writing 19: 819–843
White T., Power M., White S. (1989) Morphological analysis: Implications for teaching and understanding vocabulary growth in diverse elementary schools: Decoding and word meaning. Journal of Educational Psychology 82: 283–304
Windsor J. (2000) The role of phonological opacity in reading achievement. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 43: 50–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grants HD25858 and P50 33812 from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) supported this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berninger, V.W., Abbott, R.D., Nagy, W. et al. Growth in Phonological, Orthographic, and Morphological Awareness in Grades 1 to 6. J Psycholinguist Res 39, 141–163 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-009-9130-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-009-9130-6