Abstract
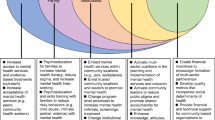
Promoting resilience prevents maladaptation among economically disadvantaged ethnic minority (EDEM) youth. EDEM youth need access to a variety of assets and promotive factors (i.e., resources) in the family, school, and community system to counter risks and promote positive adaptation. However, the field lacks a socio-ecological model of resilience for prevention targeted towards EDEM youth. We aim to review assets and promotive factors in the family, school, and community systems to present a socio-ecological model of resilience for the prevention of negative educational and health outcomes among EDEM youth. We reorient the social ecologies of EDEM youth from “at risk” to “at promise” focusing on family and community-centered prevention models. We discuss implications for the design of prevention strategies as well as their implementation and methodological challenges.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvord, S. H., Brown, L. D., & Letts, C. W. (2004). Social entrepreneurship and societal transformation: An exploratory study. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 40(3), 260–282. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/236252927?accountid=15070
American Psychological Association. (2008). Resilience in African American children and adolescents: A vision for optimal development. In Task Force on Resilience and Strength in Black Children and Adolescents. Washington, DC. Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/pi/cyf/resilience.html
Anderson, S. A., Sabatelli, R. M., & Kosutic, I. (2007). Families, urban neighborhood youth centers, and peers as contexts for development. Family Relations, 56(4), 346–357.
Berg, M., Coman, E., & Schensul, J. J. (2009). Youth action research for prevention: A multi-level intervention designed to increase efficacy and empowerment among urban youth. American Journal of Community Psychology, 43, 345–359. doi:10.1007/s10464-009-9231-2.
Brody, G. H., Dorsey, S., Forehand, R., & Armistead, L. (2002). Unique and protective contributions of parenting and classroom processes to the adjustment of African American children living in single-parent families. Child Development, 73(1), 274–286.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1977). Toward an experimental psychology of human development. American Psychologist, 32(7), 515–531.
Bronfenbrenner, U., & Evans, G. W. (2000). Developmental science in the 21st century: Emerging questions, theoretical models, research designs and empirical findings. Social Development, 9(1), 115–125. doi:10.1111/1467-9507.00114.
Brown, B. (2008). Key indicators of child and youth well-being: Completing the picture. New York: Taylor & Francis.
Burchinal, M. R., Peisner-Feinberg, E., Pianta, R., & Howes, C. (2002). Development of academic skills from preschool through second grade: Family and classroom predictors of developmental trajectories. Journal of School Psychology, 40(5), 415–436.
Caldwell, C., Horne, A., Davidson, B., & Quinn, W. (2007). Effectiveness of a multiple family group intervention for juvenile first offenders in reducing parent stress. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 16(3), 443–459.
Cameron, C. A., Lau, C., & Tapanya, S. (2009). Passing it on during a day in the life of resilient adolescents in diverse communities around the globe. Child & Youth Care Forum, 38(6), 305–325.
Campbell, R., Patterson, D., & Fehler-Cabral, G. (2010). Using ecological theory to evaluate the effectiveness of an indigenous community intervention: A study of sexual assault nurse examiner (SANE) programs. American Journal of Community Psychology, 46(3), 263–276.
Cauce, A. M., Domenech-Rodríguez, M., Paradise, M., Cochran, B. N., Shea, J. M., Srebnik, D., et al. (2002). Cultural and contextual influences in mental health help seeking: A focus on ethnic minority youth. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 70(1), 44–55.
Chand, A., & Thoburn, J. (2005). Child and family support services with minority ethnic families: What can we learn from research?. Child & Family Social Work, 10, 169–178. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2206.2005.00367.x.
Cleek, E., Wofsy, M., Boyd-Franklin, N., Mundy, B., & Howell, T. J. (2012). The Family Empowerment Program: An interdisciplinary approach to working with multi-stressed urban families. Family Process, 51(2), 207–217.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. P. (2011). Designing and conducting mixed methods research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Decker, D. M., Dona, D. P., & Christenson, S. L. (2007). Behaviorally at-risk African American students: The importance of student–teacher relationships for student outcomes. Journal of School Psychology, 45(1), 83–109.
DeCuir-Gunby, J. T., Martin, P., & Cooper, S. (2012). African American students in independent schools: Parents and school influences on racial identity development. Urban Review, 44(1), 113–132.
Diochon, M. (2013). Social entrepreneurship and effectiveness in poverty alleviation: A case study of a Canadian First Nations community. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship, 4(3), 302–330. doi:10.1080/19420676.2013.820779.
Dobbie, W., & Fryer, R. G., Jr. (2011). Are high-quality schools enough to increase achievement among the poor? Evidence from the Harlem Children’s Zone. American Economic Journal: Applied Economics, 3(3), 158–187. doi:10.1257/app.3.3.158.
Emshoff, J., & Brounstein, P. (2002). Introduction to this series of papers in primary prevention: The setting for prevention programs. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 23(1), 43–47.
Fagan, A. A., Hanson, K., Briney, J. S., & Hawkins, J. D. (2012). Sustaining the utilization and high quality implementation of tested and effective prevention programs using the Communities That Care prevention system. American Journal of Community Psychology, 49, 365–377. doi:10.1007/s10464-011-9463-9.
Feinberg, M. E., Riggs, N. R., & Greenberg, M. T. (2005). Social networks and community prevention coalitions. Journal of Primary Prevention, 26(4), 279–298. doi:10.1007/s10935-005-5390-4.
Fisher, C., Wallace, S., & Fenton, R. (2000). Discrimination distress during adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 29(6), 679–695.
Gaines, S. O., Larbie, J., Patel, S., Pereira, L., & Sereke-Melake, Z. (2005). Cultural values among African-descended persons in the United Kingdom: Comparisons with European-descended and Asian-descended persons. Journal of Black Psychology, 31, 130–151. doi:10.1177/0095798405274720.
Galster, G., Marcotte, D. E., Mandell, M., Wolman, H., & Augustine, N. (2007). The influence of neighborhood poverty during childhood on fertility, education, and earning outcomes. Housing Studies, 22(5), 723–751.
Gardner, M., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2009). Adolescents’ exposure to community violence: Are neighborhood youth organizations promotive? Journal of Community Psychology, 37, 505–525. doi:10.1002/jcop.20310.
Ginwright, S. A. (2007). Black youth activism and the role of critical social capital in Black community organizations. American Behavioral Scientist, 51, 403–518. doi:10.1177/0002764207306068.
Ginwright, S. A., & Cammarota, J. (2007). Youth activism in the urban community: Learning critical civic praxis within community organizations. International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, 20(6), 693–710.
Guerra, N. G., & Knox, L. (2008). How culture impacts the dissemination and implementation of innovation: A case study of the families and schools together program (FAST) for preventing violence with immigrant Latino youth. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 304–313. doi:10.1007/s10464-008-9161-4.
Gunderson, L. H. (2000). Ecological resilience—In theory and application. Annual Review of Ecological Systems, 31(1), 425–439.
Haight, W. L., Bidwell, L. N., Marshall, J. M., & Khatiwoda, S. (2014). Implementing the crossover youth practice model in diverse contexts: Child welfare and juvenile justice professionals’ experiences of multisystem collaborations. Children and Youth Services Review, 39, 91–100. doi:10.1016/j.childyouth.2014.02.001.
Henderson, D. X., & Greene, J. (2014). Using mixed methods to explore resilience, social connectedness, and re-suspension among youth in a community-based alternative-to-suspension program. International Journal of Child, Youth, and Family Studies, 5(3), 423–446.
Holleran, L. K., & Waller, M. A. (2003). Sources of resilience among Chicano/a youth: Forging identities in the borderlands. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, 20(5), 335–350.
Hughes, D., Rodriguez, J., Smith, E. P., Johnson, D. J., Stevenson, H. J., & Spicer, P. (2006). Parents’ ethnic-racial socialization practices: A review of research and directions for future study. Developmental Psychology, 42(5), 747–770.
Jones, D. J., Zalot, A. A., Foster, S. E., Sterrett, E., & Chester, C. (2007). A review of childrearing in African American single mother families: The relevance of a coparenting framework. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 16, 671–683. doi:10.1007/s1026-006-9115-0.
Jonson-Reid, M., Davis, L., Saunders, J., Williams, T., & Williams, J. H. (2005). Academic self-efficacy among African American youth: Implications for school social work practice. Children and Schools, 27(1), 5–14.
Kahne, J., Nagaoka, J., Brown, A., O’Brien, J., Quinn, T., & Thiede, K. (2001). Assessing after-school programs as contexts for youth development. Youth & Society, 32(4), 421–446.
Kelly, J. G. (1986). Context and process: An ecological view of the interdependence of practice and research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 14(6), 581–589. doi:10.1007/BF00931335.
Knight, G. P., Roosa, M. W., & Umana-Taylor, A. J. (2009). Studying ethnic minority and economically disadvantaged populations: Methodological challenges and best practices. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Kuperminc, G. P., Darnell, A. J., & Alvarez-Jimenez, A. (2008). Parent involvement in the academic adjustment of Latino middle and high school youth: Teacher expectations and school belonging as mediators. Journal of Adolescence, 31, 469–483. doi:10.1016/j.adolescence.2007.09.003.
LaFromboise, T. D., & Lewis, H. A. (2008). The Zuni life skills development program: A school/community-based suicide prevention intervention. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 38(3), 343–353.
Lee, S., Borden, L. M., Serido, J., & Perkins, D. F. (2009). Ethnic minority youth in youth programs: Feelings of safety, relationships with adult staff, and perceptions of learning social skills. Youth & Society, 41(2), 234–255.
Lichter, D. T., Qian, Z., & Crowley, M. L. (2005). Child poverty among racial minorities and immigrants: Explaining trends and differentials. Social Science Quarterly, 86, 1037–1059. doi:10.1111/j.0038-4941.2005.00335.x.
Luthar, S. S., Cicchetti, D., & Becker, B. (2000). The construct of resilience: A critical evaluation and guidelines for future work. Child Development, 71(3), 543–562.
Marek, L. I., Brock, D. J. P., & Sullivan, R. (2006). Cultural adaptations to a family life skills program: Implementation in rural Appalachia. Journal of Primary Prevention, 27(2), 113–133.
Masten, A. S. (2007). Resilience in developing systems: Progress and promise as the fourth wave rises. Development and Psychopathology, 19(3), 921–930.
Meehan, B. T., Hughes, J. N., & Cavell, T. A. (2003). Teacher-student relationships as compensatory resources for aggressive children. Child Development, 74, 1145–1157. doi:10.1111/1467-8624.00598.
Moore-Thomas, C., & Day-Vines, N. C. (2010). Culturally competent collaboration: School counselor collaboration with African American families and communities. Professional School Counseling, 14(1), 53–63.
Myers, L. J. (1988). Understanding an Afrocentric worldview: Introduction to an optimal psychology (2nd ed.). Dubuque: Kendall/Hunt Publishing.
National Center for Children in Poverty. (2014). Basic facts about low-income children: Children under 18 years, 2012. Retrieved from: http://www.nccp.org/publications/pub_1089.html
National Center for Education Statistics. (2011). Percentage of high school dropouts among persons 16 through 24 years old (status dropout rate), by income level, and percentage distribution of status dropouts, by labor force status and educational attainment: 1970 through 2009. Retrieved from U.S. Department of Education website: http://nces.ed.gov/programs/digest/d10/tables/dt10_116.asp
Ochoa, E. R., Jr., & Nash, C. (2009). Community engagement and its impact on child health disparities: Building blocks, examples, and resources. Pediatrics, 124, S237–S245. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-1100L.
Perkins-Dock, R. E. (2001). Family interventions with incarcerated youth: A review of the literature. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 45(5), 606–625.
Perry, J. C., DeWine, D. B., Duffy, R. D., & Vance, K. S. (2007). The academic self-efficacy of urban youth: A mixed-methods study of a school-to-work program. Journal of Career Development, 34(2), 103–126.
Powers, K. M. (2006). An exploratory study of cultural identity and culture-based educational programs for urban American Indian students. Urban Education, 41(1), 20–49. doi:10.1177/0042085905282249.
Prelow, H. M., Danoff-Burg, S., Swenson, R. R., & Pulgiano, D. (2004). The impact of ecological risk and perceived discrimination on the psychological adjustment of African American and European American youth. Journal of Community Psychology, 32, 375–389. doi:10.1002/jcop.20007.
Ripke, M., Huston, A. C., Eccles, J., & Templeton, J. (2008). The assessment of psychological, emotional, and social development indicators in middle childhood. In B. V. Brown (Ed.), Key indicators of child and youth well-being: Completing the picture (pp. 131–165). New York: Taylor & Francis Group.
Roeser, R. W., Eccles, J. S., & Sameroff, A. J. (2000). School as a context for early adolescent’s academic and socio-emotional development: A summary of findings. The Elementary School Journal, 100(5), 443–471.
Ryan, N., Head, B., Keast, R., & Brown, K. (2006). Engaging indigenous communities: Towards a policy framework for indigenous community justice programmes. Social Policy & Administration, 40(3), 304–321.
Sameroff, A. J., & Fiese, B. H. (2000). Transactional regulation: The developmental ecology of early intervention. Handbook of Early Childhood Intervention, 2, 135–159.
Sandefur, G. D., & Meier, A. (2008). The family environment: Structure, material, resources and child care. In B. V. Brown (Ed.), Key indicators of child and youth well-being: Completing the picture (pp. 237–259). New York: Taylor & Francis Group.
Scales, P. C., & Taccogna, J. (2001). Developmental assets for success in school and life. Retrieved from http://www.eddigest.com.
Schensul, J. J., & Trickett, E. (2009). Introduction to multi-level community based culturally situated interventions. American Journal of Community Psychology, 43, 232–240. doi:10.1007/s10464-009-9238-8.
Seidman, E., & Pederson, S. (2003). Holistic, contextual perspectives on risk, protection, and competence among low-income urban adolescents. In S. S. Luther (Ed.), Resilience and vulnerability: Adaptation in the context of childhood adversities (pp. 318–342). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sellers, R. M., Copeland-Linder, N., Martin, P. P., & Lewis, R. H. (2006). Racial identity matters: The relationship between racial discrimination and psychological functioning in African American adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 16(2), 187–216.
Slaton, A. E., Cecil, C. W., Lambert, L. E., King, T., & Pearson, M. M. (2012). What a difference family-driven makes: Stories of success and lessons learned. American Journal of Community Psychology, 49(3), 538–545.
Spielman, S. E., Golembeski, C. A., Northridge, M. E., Vaughan, R. D., Swaner, R., Jean-Louis, B., et al. (2006). Interdisciplinary planning for healthier communities: American Planning Association. Journal of the American Planning Association, 72(1), 100–108. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/229736498?accountid=15070
Springer, J. F., Sale, E., Hermann, J., Sambrano, S., Kasim, R., & Nistler, M. (2004). Characteristics of effective substance abuse prevention programs for high risk youth. Journal of Primary Prevention, 25(2), 171–194.
Tendulkar, S. A., Buka, S., Dunn, E. C., Subramanian, S. V., & Koenen, K. C. (2010). A multilevel investigation of neighborhood effects on parental warmth. Journal of Community Psychology, 38(5), 557–573.
Theron, L., Cameron, C., Didkowsky, N., Lau, C., Liebenberg, L., & Ungar, M. (2011). A ‘day in the lives’ of four resilient youths: A study of cultural roots of resilience. Youth and Society, 43, 799–818. doi:10.1177/0044118X11402853.
Trickett, E. J. (2009a). Multilevel community-based culturally situated interventions and community impact: An ecological perspective. American Journal of Community Psychology, 43, 257–266. doi:10.1007/s10464-009-9227-y.
Trickett, E. J. (2009b). Community psychology: Individuals and interventions in community context. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 395–419.
Ungar, M. (2011). The social ecology of resilience: Addressing contextual and cultural ambiguity of a nascent construct. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 81(1), 1–77.
Ungar, M., Brown, M., Liebenberg, L., Othman, R., Kwong, W. M., Armstrong, M., et al. (2007). Unique pathways to resilience across cultures. Adolescence, 42(166), 287–310.
United States Census Bureau. (2011). Child poverty in the United States 2009 and 2010: Selected race groups and Hispanic origin. Retrieved from U.S. Department of Commerce website: http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/poverty/data/
Velsor, P. V., & Orozco, G. L. (2007). Involving low-income parents in the schools: Community-centric strategies for school counselors. Professional School Counseling, 11(1), 17–24.
Village of Wisdom. (2015). Retrieved from http://www.villageofwisdom.org/
Wandersman, A., & Florin, P. (2003). Community interventions and effective prevention. American Psychologist, 58, 441–448. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.58.6-7.441.
Washington, K. (2010). Zulu traditional healing, Afrikan worldview and the practice of Ubuntu: Deep thought for African/Black Psychology. Journal of Pan African Studies, 3(8), 24–39.
Wenz-Gross, M., Irsfeld, T. D., Twomey, T., Perez, A., Thompson, J., Wally, M., et al. (2012). Changing the system by changing the workforce: Employing consumers to increase access, cultural diversity, and engagement. American Journal of Community Psychology, 49(3), 546–555.
Williams, J. L., Tolan, P. H., Durkee, M. I., Francois, A. G., & Anderson, R. Z. E. (2012). Integrating racial and ethnic identity research into developmental understanding of adolescents. Child Development Perspectives, 6, 304–311. doi:10.1111/j.1750-8606.2012.00235.x.
Windle, G., Bennett, K. M., & Noyes, J. (2011). A methodological review of resilience measurement scales. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 9, 1–18. Retrieved from http://www.hqlo.com/content/9/1/8
Yates, T. M., Egeland, B., & Sroufe, L. A. (2003). Rethinking resilience: A developmental process perspective. In S. S. Luther (Ed.), Resilience and vulnerability: Adaptation in the context of childhood adversities (pp. 243–266). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Zaff, J. F. (2011). A cease and desist order for school reform: It is time for educational transformation. Applied Developmental Science, 15(1), 1–7. doi:10.1080/10888691.2011.539099.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to report in the publication of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henderson, D.X., DeCuir-Gunby, J. & Gill, V. “It Really Takes a Village”: A Socio-Ecological Model of Resilience for Prevention Among Economically Disadvantaged Ethnic Minority Youth. J Primary Prevent 37, 469–485 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-016-0446-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-016-0446-3