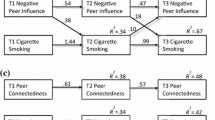
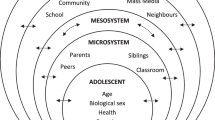
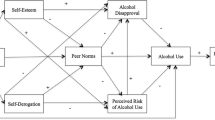
Using a probability sample of 4,230 adolescents from grades 7–12, we used negative binomial regression to estimate the effects of peer and six family variables on the risk of adolescent drug use. Peer drug use had relatively strong effects of adolescent drug use. Parental drug attitudes, sibling drug use, and adult drug use had significant direct effects net of peer influences. In addition, they had significant indirect effects that were mediated by peer drug use. The influences of parental monitoring, attachment to mother, and attachment to father were statistically significant but relatively small. The findings applied to alcohol, binge drinking, cigarettes, marijuana, and other illicit drugs.
Editors' Strategic Implications: The authors interpret their findings as being more consistent with social learning than social control theory. This research, although cross-sectional and limited to adolescents' self-reports, contributes to a growing literature on the direct and indirect influences of parents on their teens' substance use rates. It speaks to the need for school- and community-based prevention efforts to focus on families as well as peers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akers, R. L., & Sellers, C. S. (2004). Criminological theories: Introduction, evaluation, and application (4th ed.). Los Angeles: Roxbury.
Allison, P. D. (1999). Logistic regression using the SAS system: Theory and application. Cary, NC: SAS Institute.
Allision, P. D. (2002). Missing data. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Andrews, J. A., Hops, H., Ary, D., Tildesley, E., & Harris, J. (1993). Parental influence on early adolescent substance use: Specific and nonspecific effects. Journal of Early Adolescence, 13, 285–310.
Aseltine, R. H. (1995). A reconsideration of parental and peer influences on adolescent deviance. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 36, 103–121.
Bahr, S. J., Marcos, A. C., & Maughan, S. L. (1995). Family, educational and peer influences on the alcohol use of female and male adolescents. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 56, 457–469.
Bahr, S. J., Maughan, S. L., Marcos, A. C., & Li, B. (1998). Family, religion, and the risk of adolescent drug use. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 60, 979–992.
Barber, B. K. (1997). Adolescent socialization in context: The role of connection, regulation, and autonomy in the family. Journal of Adolescent Research, 12, 5–11.
Barnes, G. M., & Welte, J. W. (1986). Patterns and predictors of alcohol use among 7–12th grade students in New York State. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 47, 53–62.
Bauman, K. E., & Ennett, S. T. (1996). On the importance of peer influence for adolescent drug use: Commonly neglected considerations. Addiction, 91, 185–198.
Brook, J. S., Brook, D. W., & Richter, L. (2001). Risk factors for adolescent marijuana use across cultures and across time. Journal of Genetic Psychology, 162, 357–374.
Brook, J. S., Brook, D. W., & Whiteman, M. (1999). Older sibling correlates of younger sibling drug use in the context of parent-child relations. Genetic, Social, and General Psychology Monographs, 125, 451–468.
Brook, J. S., Whiteman, M., Gordon, A. S., & Brook, D. W. (1990). The role of older brothers in younger brothers' drug use viewed in the context of parent and peer influences. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 151, 59–75.
Brook, J. S., Whiteman, M., Gordon, A. S., & Cohen, P. (1986). Some models and mechanisms for explaining the impact of maternal and adolescent characteristics on adolescent stage of drug use. Developmental Psychology, 22, 460–467.
Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Haggerty, K., Hawkins, J. D., & Spoth, R. L. (1998). A universal intervention for the prevention of substance abuse: Preparing for the drug free years. In R. S. Ashery, E. B. Robertson, & K. L. Kumpfer (Eds.), Drug abuse prevention through family interventions (pp. 130–159). NIDA Research Monograph 1777. Rockville, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Newcomb, M., & Abbott, R. D. (1996). Modeling the etiology of adolescent substance use: A test of the social development model. Journal of Drug Issues, 26, 429–455.
Dorius, C. J., Bahr, S. J., Hoffmann, J. P., & Harmon, E. L. (2004). Parenting practices as moderators of the relationship between peers and adolescent marijuana use. Journal of Marriage and Family, 66, 163–178.
Elliott, D. S., Huizinga, D., & Ageton, S. S. (1985). Explaining delinquency and drug use. Beverly Hills: Sage.
Etz, K. E., Robertson, E. M., & Ashery, R. S. (1998). Drug abuse prevention through family-based interventions: Future research. In R. S. Ashery, E. B. Robertson, & K. L. Kumpfer (Eds.), Drug abuse prevention through family interventions (pp. 1–11). NIDA Research Monograph 1777. Rockville, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Flannery, D. J., Williams, L. L., & Vazsonyi, A. T. (1999). Who are they with and what are they doing? Delinquent behavior, substance use, and early adolescents' after-school time. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 69, 247–253.
Gray, M. R., & Steinberg, L. (1999). Unpacking authoritative parenting: Reassessing a multidimensional construct. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 61, 574–587.
Gorman, D. M. (1996). Ethological theories and the primary prevention of drug use. Journal of Drug Issues, 26, 505–520.
Gorman, D. M. (1997). The failure of drug education. Public Interest, 129, 50–60.
Gorman, D. M. (1998). The irrelevance of evidence in the development of school-based drug prevention policy, 1986–1996. Evaluation Review, 22, 118–146.
Graham, N. (1996). The influence of predictors on adolescent drug use: An examination of individual effects. Youth and Society, 28, 215–235.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Miller, J. Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 64–105.
Hirschi, T. (1969). Causes of delinquency. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Hoffmann, J. P. (1993). Exploring the direct and indirect family effects on adolescent drug use. Journal of Drug Issues, 23, 535–557.
Hoffmann, J. P. (1995). The effects of family structure and family relations on adolescent marijuana use. International Journal of the Addictions, 30, 1207–1241.
Hoffmann, J. P. (2003). Generalized linear models: An applied approach. Boston: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon.
Hoffmann, J. P., & Johnson, R. A. (1998). A national portrait of family structure and adolescent drug use. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 60, 633–645.
Hoffmann, J. P., & Su, S. S. (1998). Parental substance use disorder, mediating variables and adolescent drug use: A non-recursive model. Addiction, 93, 1351–1364.
Huizinga, D., Loeber, R., & Thornberry, T. P. (1995). Urban delinquency and substance abuse (OJJDP Research Summary, NCJ 143454). Washington, DC: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, Office of Justice Programs.
Johnston, L. D., O'Malley, P. M., & Bachman, J. G. (1999). National survey results on drug use from the Monitoring the Future study, 1975–1998. Secondary school students (Vol. 1, NIH Publication No. 99-4660). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Johnston, L. D., O'Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2004). Monitoring the Future national results on adolescent drug abuse: Overview of key findings, 2003 (NIH publication no. 04-5506). Bethesda, Maryland: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Kandel, D. B. (1980). Drug and drinking behavior among youth. Annual Review of Sociology, 6, 235–285.
Kandel, D. B. (1996). The parental and peer contexts of adolescent deviance: An algebra of interpersonal influences. Journal of Drug Issues, 26, 289–315.
Kandel, D. B., & Andrews, K. (1987). Processes of adolescent socialization by parents and peers. The International Journal of the Addictions, 22, 319–342.
Kaplan, H. B., Martin, S. S., & Robbins, C. (1984). Pathways to adolescent drug use: Self-derogation, peer influence, weakening of social controls, and early substance use. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 25, 270–289.
Khavari, K. A. (1993). Interpersonal influences in college students' initial use of alcohol and drugs–the role of friends, self, parents, doctors, and dealers. International Journal of the Addictions, 28, 377–388.
Larzelere, R. E., & Patterson, G. R. (1990). Parental management: Mediator of the effect of socioeconomic status on early delinquency. Criminology, 28, 301–323.
McDermott, D. (1984). The relationship of parental drug use and parents' attitudes concerning adolescent drug use to adolescent drug use. Adolescence, 73, 89–97.
Miller, M. A., Alberts, J. K., Hecht, M. L., Trost, M. R., & Krizek, R. L. (2000). Adolescent relationships and drug use. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Moon, D. G., Hecht, M. L., Jackson, K. M., & Spellers, R. E. (1999). Ethnic and gender differences and similarities in adolescent drug use and refusals of drug offers. Substance Use and Misuse, 34, 1059–1083.
Needle, R., McCubbin, H., Wilson, M., Reineck, R., Lazar, A., & Mederer, H. (1986). Interpersonal influences on adolescent drug use—the role of older siblings, parents, and peers. International Journal of the Addictions, 21, 739–766.
Newcomb, M. D. (1992). Understanding the multidimensional nature of drug use and abuse: The role of consumption, risk factors, and protective factors. In M. Glantz & R. Pickens (Eds.), Vulnerability to drug abuse (pp. 255–297). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Osgood, D. W., Wilson, J. K., O'Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Johnston, L. D. (1996). Routine activities and deviant behavior. American Sociological Review, 61, 635–655.
Peiser, N. C., & Heaven, P. C. L. (1996). Family influences on self-reported delinquency among high school students. Journal of Adolescence, 19, 557–568
Penning, M., & Barnes, G. E. (1982). Adolescent marijuana use: A review. International Journal of the Addictions, 17, 749–791.
Petraitis, J., Flay, B. R., & Miller, T. Q. (1995). Reviewing theories of adolescent substance use: Organizing pieces in the puzzle. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 67–86.
Rankin, J. H., & Kern, R. (1994). Parental attachments and delinquency. Criminology, 32, 495–515.
Reed, M. D., & Rountree, P. W. (1997). Peer pressure and adolescent substance use. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 13, 143–180.
Rohde, P., Lewinsohn, P. M., Brown, R. A., Gau, J. M., & Kahler, C. W. (2003). Psychiatric disorders, familial factors and cigarette smoking. Nicotine and Tobacco Research, 5, 85–98.
Seydlitz, R. (1993). Complexity in the relationships among direct and indirect parental controls and delinquency. Youth and Society, 24, 243–275.
Simcha-Fagan, O., Gersten, J. C., & Langner, T. (1986). Early precursors and concurrent correlates of illicit drug use in adolescents. Journal of Drug Issues, 16, 7–28.
Sokol-Katz, J., Dunham, R., & Zimmerman, R. (1997). Family structure versus parental attachment in controlling adolescent deviant behavior: A social control model. Adolescence, 32, 199–215.
Stice, E., & Barrera, J. (1995). A longitudinal examination of the reciprocal relations between perceived parenting and adolescents substance use and externalizing behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 31, 322–423.
Stillwell, G., Hunt, N., Taylor, C., & Griffiths, P. (1999). The modeling of injecting behavior and initiation into injecting. Addiction Research, 7, 447–459.
Stormshak, E. A., Comeau, C. A., & Shepard, S. A. (2004). The relative contribution of sibling deviance and peer deviance in the prediction of substance use across middle childhood. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 32, 635–649.
Sutherland, E. H., Cressey, D. R., & Luckenbill, D. F. (1992). Principles of Criminology (11th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott.
Svensson, R. (2000). Risk factors for different dimensions of adolescent drug use. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse, 9, 67–90.
Thornberry, T. P., & Krohn, M. D. (1997). Peers, drug use, and delinquency. In D. M. Stoff, J. Breiling, & J. D. Maser (Eds.), Handbook of antisocial behavior (pp. 218–233). New York: John Wiley.
Trost, M. R., Langan, E. J., & Kellar-Guenther, Y. (1999). Not everyone listens when you “just say no”: Drug resistance in relational context. Journal of Applied Communication Research, 27, 120–138.
Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (2000). Influence of deviant friends on delinquency: Searching for moderator variables. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 313–325.
Wills, T. A., Mariani, J., & Filer, M. (1996). The role of family and peer relationships in adolescent substance use. In G. R. Pierce, B. R. Sarason, & I. G. Sarason (Eds.), Handbook of social support and the family (pp. 521–549). New York: Plenum Press.
Windle, M. (2000). Parental, sibling, and peer influences on adolescent substance use and alcohol problems. Applied Developmental Science, 4, 98–110
Wright, J. P., & Cullen, F. T. (2001). Parental efficacy and delinquent behavior: Do control and support matter? Criminology, 39, 677–705.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahr, S.J., Hoffmann, J.P. & Yang, X. Parental and Peer Influences on the Risk of Adolescent Drug Use. J Primary Prevent 26, 529–551 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-005-0014-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-005-0014-8