Abstract
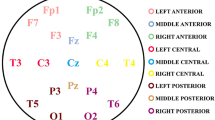
Quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG) has been used as a tool for neurophysiologic diagnostic. We used spectrogram and coherence values for evaluating qEEG in 17 children (13 boys and 4 girls aged between 6 and 11) with autism disorders (ASD) and 11 control children (7 boys and 4 girls with the same age range). Evaluation of qEEG with statistical analysis demonstrated that alpha frequency band (8–13 Hz) had the best distinction level of 96.4% in relaxed eye-opened condition using spectrogram criteria. The ASD group had significant lower spectrogram criteria values in left brain hemisphere, (p < 0.01) at F3 and T3 electrodes and (p < 0.05) at FP1, F7, C3, Cz and T5 electrodes. Coherence values at 171 pairs of EEG electrodes indicated that there are more abnormalities with higher values in the connectivity of temporal lobes with other lobes in gamma frequency band (36–44 Hz).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird, G., Charman, T., Cox, A., Baron-Cohen, S., Swettenham, J., Wheelwright, S., et al., Screening and Surveillance for autism and pervasive developmental disorders. Arch. Dis. Child. 84:468–475, 2001.
Charman, T., and Baird, G., Practitioner review: Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in 2- and 3-year-old children. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 43:289–305, 2002.
Rogers, S., Dignosis of autism before the age of 3. International Review of Mental Retardation 23:1–31, 2001.
Akhondzadeh, S., Erfani, S., Mohammadi, M. R., Taheri-Doost, M., Amini, H., Gudarzi, S. S., and Yasamyet, M. T., Cyproheptadine in the treatment of autistic disorder: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 29:145–150, 2004.
Blaxill, M. F., What’s going on? The question of time trends in autism. Public Health Rep. 119:536–551, 2004.
Coben, R., Clarke, A. R., Hudspeth, W., and Barry, R. J., EEG power and coherence in autistic spectrum disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 119:1002–1009, 2008.
Fombonne, E., The epidemiology of autism: A review. Psychol. Med. 29:769–786, 1999.
Sarbadhikari, S. N., and Chakrabarty, K., Chaos in the brain: A short review alluding to epilepsy, depression, exercise and lateralization. Med. Eng. Phys. 23:447–457, 2001.
Jeong, J., Chase, J. H., Kim, S. Y., and Han, S. H., Nonlinear dynamics analysis of EEG in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 18:58–67, 2001.
Hudetz, A. G., Effects of volatile anesthetics on interhemisphemispheric EEG cross-approximate entropy in the rat. Brain Res. 954:123–131, 2002.
Tong, S., Bezerianos, A., Paul, J., Zhu, Y., and Thakor, N. V., Nonextensive entropy measure of EEG following brain injury from cardiac arrest. Physica, A 305:619–628, 2002.
Chez, M. G., Chang, M., Krasne, V., Coughlan, C., Kominsky, M., and Schwartz, A., Frequency of epileptiform EEG abnormalities in a sequential screening of autistic patients with no known clinical epilepsy from 1996 to 2005. Epilepsy Behav. 8:267–271, 2006.
Rossi, P. G., Parmeggiani, A., Bach, V., Santucci, M., and Visconti, P., EEG features and epilepsy in patients with autism. Brain Dev. 17:169–174, 1995.
Bashina, V. M., Gorbachevskaia, N. L., Simashkova, N. V., Iznak, A. F., Kozhushko, L. F., and Iakupova, L. P., The clinical, neurophysiologial and differential diagnostic aspects in a study of severe forms of early childhood autism. Zh Nevropatol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 94:68–71, 1994.
Orekhova, E. V., Stroganova, T. A., Nygren, G., Tsetlin, M. M., Posikera, I. N., Gillberg, C., and Elam, M., Excess of High Frequency Electroencephalogram oscillation in boys with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 62:1022–1029, 2007.
Dawson, G., Klinger, L. G., Panagiotides, H., Lewy, A., and Castello, P., Subgroups of autistic children based on social behavior display distinct patterns of brain activity. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 23:569–583, 1995.
Stroganova, T. A., Nygren, G., Tsetlin, M. M., Posikera, I. N., Gillberg, C., Elam, M., and Orekhova, E. V., Abnormal EEG lateralization in boys with autism. Clin. Neurophysiol. 118:1842–1854, 2007.
Oberman, L. M., Hubbard, E. M., McCleery, J. P., Altschuler, E. L., Ramachandran, V. S., and Pineda, J. A., EEG evidence for mirror neuron dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders. Cogn. Brain Res. 24(2):190–198, 2005.
American Psychiatric Association, Task force on DSM-IV Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, DSM-IV-IR 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC, 2000.
Wechsler, D., Whechsler Intelligence Scale for children-Third Edition (WISC-III). The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, 1991.
Oldfield, R. C., The assessment and analysis of handedness the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113, 1971.
Jasper, H. H., Report of committee on methods of clinical examination in electroencephalography. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 10:370–375, 1958.
Herbert, M. R., Ziegler, D. A., Makris, N., Filipek, P. A., Kemper, T. L., Normandin, J. J., et al., Localization of white matter volume increase in autism and developmental language disorder. Ann. Neurol. 55:530–540, 2004.
Nunez, P. L., and Srinvasan, R., Electric fields of the brain; The Neurophysics of EEG, 2nd edition. Oxford University Press, New York, 2006.
Tokmakei, M., and Erdogan, N., Investigation of the arterial stiffness on renal artery Doppler sonograms. J. Med. Syst. 33:101–106, 2009.
Diaz, M., Application of Fourier linear spectral analyses to the characterization of smooth muscle contractile signals. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 70:803–808, 2007.
Hardalac, F., Yildirin, H., and Serchatlioglu, S., Determination of carotid disease with the application of STFT and CWT methods. Comput. Biol. Med. 37:785–792, 2007.
Subha, D. P., Joseph, P. K., Acharya, U. R., and Lim, C. M., EEG signal analysis: A survey. J. Med. Syst. 34:195–212, 2010.
Tauscher, J., Fischer, P., Neumeister, A., Rappelsberger, P., and Kasper, S., Low frontal electroencephalographic coherence in neuroleptic-free schizophrenic patients. Biol. Psychiatry 44:438–447, 1998.
Weiss, S., and Rappelsberger, P., Long-range EEG synchronization during word encoding correlates with successful memory performance. Cogn. Brain Res. 9:299–312, 2000.
Tuncel, D., Dizibuyuk, A., Kiymik, M. K., Time frequency band coherence analysis between EEG and EMG activities in fatigue duration. J. Med. Syst. 34:131–138, 2010.
Metz, C. E., Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nuc. Med. 5:283–298, 1978.
Abasolo, D., Homero, R., Espino, P., Alvavez, D., and Poza, J., Entropy analysis of the EEG background activity in Alzheimer’s desease patients. Physiol. Meas. 27:241–253, 2006.
Lotte, F., Congedo, M., Lecuyer, A., Lamarche, F. and Arnaldi, B., A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. R1–R13, 2007.
Chandana, S. R., Behen, M. E., Juhasz, C., Muzik, O., Rothermel, R. D., and Manager, T. J., Significant of abnormalities trajectory and asymmetry of cortical serotonin synthesis in autism. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 23:171–182, 2005.
Lazarev, V. V., Pontes, A., and deAzevedo, L. C., Right hemisphere deficit in EEG photic driving reactivity in childhood autism. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 4:54–79, 2004.
Sheikhani, A., Behnam, H., Noroozian, M., Mohammadi, M. R., and Mohammadi, M., Abnormalities of quantitative electroencephalography in children with Asperger disorder in various conditions. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 3:538–546, 2009.
Klimesch, W., and Schack, B., The functional significance of theta and upper alpha oscillations. Exp. Psychol. 52:99–108, 2005.
Boddaert, N., and Zilbovicius, M., Temporal lobe dysfunction in childhood.autism. Brain 123:1838–1844, 2000.
Cherkassky, V. L., Kana, R. K., Keller, T. A., and Just, M. A., Functional connectivity in a baseline resting-state network in autism. NeuroReport 17:1687–1690, 2006.
Murias, M., Webb, S. J., Greenson, J., and Dawson, G., Resting state cortical connectivity reflected in EEG coherence in individuals with autism. Biol. Psychiatry 62:270–273, 2006.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Islamic Azad University, Science and Research branch-Tehran-Iran and Center of Research in Psychiatry and Psychology (Roozbeh Hospital) Tehran University of Medical science and Omid Iranian Children Association. We express our appreciation to Dr Gholam Reza Askarifar and Dr Kambiz Kamkari for the collection of children and review of statistical computations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhani, A., Behnam, H., Mohammadi, M.R. et al. Detection of Abnormalities for Diagnosing of Children with Autism Disorders Using of Quantitative Electroencephalography Analysis. J Med Syst 36, 957–963 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9560-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9560-6