Abstract
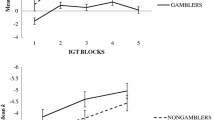
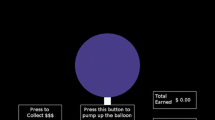
Previous research has demonstrated that adult pathological gamblers (compared to controls) show risk-proneness, foreshortened time horizon, and preference for immediate rewards. No study has ever examined the interplay of these factors in adolescent gambling. A total of 104 adolescents took part in the research. Two equal-number groups of adolescent non-problem and problem gamblers, defined using the South Oaks Gambling Screen-Revised for Adolescents, were administered the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART), the Consideration of Future Consequences (CFC-14) scale, and the Monetary Choice Questionnaire (MCQ). Adolescent problem gamblers were found to be more risk-prone, more oriented to the present, and to discount delay rewards more steeply than adolescent non-problem gamblers. Results of logistic regression analysis revealed that BART, MCQ, and CFC scores predicted gambling severity. These novel finding provides the first evidence of an association among problematic gambling, high risk-taking proneness, steep delay discounting, and foreshortened time horizon among adolescents. It may be that excessive gambling induces shortsighted behaviors that, in turn, facilitate gambling involvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, D., & Steinberg, L. (2011). Judgment and decision making in adolescence. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(1), 211–224.
Alessi, S. M., & Petry, N. M. (2003). Pathological gambling severity is associated with impulsivity in a delay discounting procedure. Behavioural Processes, 64, 345–354.
Anokhin, A. P., Golosheykin, S., & Mulligan, R. C. (2015). Long-term test–retest reliability of delayed reward discounting in adolescents. Behavioural Processes, 111, 55–59.
Banich, M. T., De La Vega, A., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Mackiewicz Seghete, K., Du, Y., & Claus, E. D. (2013). Developmental trends and individual differences in brain systems involved in intertemporal choice during adolescence. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 27(2), 416–430.
Billieux, J., Lagrange, G., Van der Linden, M., Lançon, C., Adida, M., & Jeanningros, R. (2012). Investigation of impulsivity in a sample of treatment-seeking pathological gamblers: A multidimensional perspective. Psychiatry Research, 198(2), 291–296.
Bjork, J. M., & Pardini, D. A. (2015). Who are those “risk-taking adolescents”? Individual differences in developmental neuroimaging research. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 11, 56–64.
Blakemore, S. J., & Robbins, T. W. (2012). Decision-making in the adolescent brain. Nature Neuroscience, 15(9), 1184–1191.
Blanco, C., Hasin, D. S., Petry, N., Stinson, F. S., & Grant, B. F. (2006). Sex differences in subclinical and DSM-IV pathological gambling: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Psychological Medicine, 36(7), 943–953.
Braams, B. R., van Duijvenvoorde, A. C., Peper, J. S., & Crone, E. A. (2015). Longitudinal changes in adolescent risk-taking: A comprehensive study of neural responses to rewards, pubertal development, and risk-taking behavior. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(18), 7226–7238.
Ciccarelli, M., Malinconico, R., Griffiths, M. D., Nigro, G., & Cosenza, M. (2016). Reward preferences of pathological gamblers under conditions of uncertainty: An experimental study. Journal of Gambling Studies,. doi:10.1007/s10899-016-9593-y. Epub ahead of print.
Clark, L. (2010). Decision-making during gambling: An integration of cognitive and psychobiological approaches. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 365(1538), 319–330.
Colasante, E., Gori, M., Bastiani, L., Scalese, M., Siciliano, V., & Molinaro, S. (2014). Italian adolescent gambling behaviour: Psychometric evaluation of the South Oaks Gambling Screen: Revised for Adolescents (SOGS-RA) among a sample of Italian students. Journal of Gambling Studies, 30(4), 789–801.
Cosenza, M., & Nigro, G. (2015). Wagering the future: Cognitive distortions, impulsivity, delay discounting, and time perspective in adolescent gambling. Journal of Adolescence, 45, 56–66.
Crone, E. A., Duijvenvoorde, A. C., & Peper, J. S. (2016). Annual research review: Neural contributions to risk-taking in adolescence–developmental changes and individual differences. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry,. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12502. Epub ahead of print.
Dahne, J., Richards, J., Ernst, M., MacPherson, L., & Lejuez, C. W. (2013). Assessment of risk taking in addiction research. In J. MacKillop & H. de Wit (Eds.), The Wiley-Blackwell handbook of addiction psychopharmacology (pp. 209–231). New York: Wiley.
Daugherty, J. R., & Brase, G. L. (2010). Taking time to be healthy: Predicting health behaviors with delay discounting and time perspective. Personality and Individual Differences, 48(2), 202–207.
Defoe, I. N., Dubas, J. S., Figner, B., & van Aken, M. A. (2015). A meta-analysis on age differences in risky decision making: Adolescents versus children and adults. Psychological Bulletin, 141(1), 48–84.
Dixon, M. R., Marley, J., & Jacobs, E. A. (2003). Delay discounting by pathological gamblers. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 36(4), 449–458.
Dougherty, D. M., Lake, S. L., Mathias, C. W., Ryan, S. R., Bray, B. C., Charles, N. E., et al. (2015). Behavioral impulsivity and risk-taking trajectories across early adolescence in youths with and without family histories of alcohol and other drug use disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 39(8), 1501–1509.
Ernst, M., & Fudge, J. L. (2009). A developmental neurobiological model of motivated behavior: Anatomy, connectivity and ontogeny of the triadic nodes. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(3), 367–382.
Ernst, M., Pine, D. S., & Hardin, M. (2006). Triadic model of the neurobiology of motivated behavior in adolescence. Psychological Medicine, 36(03), 299–312.
Figner, B., Mackinlay, R. J., Wilkening, F., & Weber, E. U. (2009). Affective and deliberative processes in risky choice: Age differences in risk taking in the Columbia Card Task. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 35(3), 709–730.
Geier, C., & Luna, B. (2009). The maturation of incentive processing and cognitive control. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 93(3), 212–221.
Green, L., Fisher, E. B., Perlow, S., & Sherman, L. (1981). Preference reversal and self control: Choice as a function of reward amount and delay. Behaviour Analysis Letters, 1, 43–51.
Green, L., Fry, A. F., & Myerson, J. (1994). Discounting of delayed rewards: A life-span comparison. Psychological Science, 5(1), 33–36.
Harrison, G. W., Lau, M. I., & Williams, M. B. (2002). Estimating individual discount rates in Denmark: A field experiment. American Economic Review, 92(5), 1606–1617.
Hodgins, D. C., & Engel, A. (2002). Future time perspective in pathological gamblers. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 190, 775–780.
Holt, D. D., Green, L., & Myerson, J. (2003). Is discounting impulsive?: Evidence from temporal and probability discounting in gambling and non-gambling college students. Behavioural Processes, 64(3), 355–367.
Johnson, M. W., & Bickel, W. K. (2002). Within-subject comparison of real and hypothetical money rewards in delay discounting. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 77(2), 129–146.
Joireman, J., Balliet, D., Sprott, D., Spangenberg, E., & Schultz, J. (2008). Consideration of future consequences, ego-depletion, and self-control: Support for distinguishing between CFC-Immediate and CFC-Future sub-scales. Personality and Individual Differences, 45(1), 15–21.
Joireman, J., Shaffer, M. J., Balliet, D., & Strathman, A. (2012). Promotion orientation explains why future-oriented people exercise and eat healthy evidence from the two-factor consideration of future consequences-14 scale. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 38(10), 1272–1287.
Kirby, K. N. (2009). One-year temporal stability of delay-discount rates. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(3), 457–462.
Kirby, K. N., & Maraković, N. N. (1996). Delay-discounting probabilistic rewards: Rates decrease as amounts increase. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 3(1), 100–104.
Kirby, K. N., Petry, N. M., & Bickel, W. K. (1999). Heroin addicts have higher discount rates for delayed rewards than non-drug-using controls. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 128(1), 78–87.
Kräplin, A., Dshemuchadse, M., Behrendt, S., Scherbaum, S., Goschke, T., & Bühringer, G. (2014). Dysfunctional decision-making in pathological gambling: Pattern specificity and the role of impulsivity. Psychiatry Research, 215, 675–682.
Krmpotich, T., Mikulich-Gilbertson, S., Sakai, J., Thompson, L., Banich, M. T., & Tanabe, J. (2015). Impaired decision-making, higher impulsivity, and drug severity in substance dependence and pathological gambling. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 9(4), 273–280.
Ladouceur, R., Mayrand, M., & Tourigny, Y. (1987). Risk-taking behavior in gamblers and non-gamblers during prolonged exposure. Journal of Gambling Behavior, 3(2), 115–122.
Lagorio, C. H., & Madden, G. J. (2005). Delay discounting of real and hypothetical rewards III: Steady-state assessments, forced-choice trials, and all real rewards. Behavioural Processes, 69(2), 173–187.
Ledgerwood, D. M., Alessi, S. M., Phoenix, N., & Petry, N. M. (2009). Behavioral assessment of impulsivity in pathological gamblers with and without substance use disorder histories versus healthy controls. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 105(1), 89–96.
Lejuez, C. W., Read, J. P., Kahler, C. W., Richards, J. B., Ramsey, S. E., Stuart, G. L., et al. (2002). Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 8(2), 75–84.
MacKillop, J., Anderson, E. J., Castelda, B. A., Mattson, R. E., & Donovick, P. J. (2006). Divergent validity of measures of cognitive distortions, impulsivity, and time perspective in pathological gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 22, 339–354.
MacKillop, J., Miller, J. D., Fortune, E., Maples, J., Lance, C. E., Campbell, W. K., et al. (2014). Multidimensional examination of impulsivity in relation to disordered gambling. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 22, 176–185.
MacLaren, V. V., Fugelsang, J. A., Harrigan, K. A., & Dixon, M. J. (2012). Effects of impulsivity, reinforcement sensitivity, and cognitive style on pathological gambling symptoms among frequent slot machine players. Personality and Individual Differences, 52, 390–394.
MacPherson, L., Magidson, J. F., Reynolds, E. K., Kahler, C. W., & Lejuez, C. W. (2010). Changes in sensation seeking and risk-taking propensity predict increases in alcohol use among early adolescents. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 34(8), 1400–1408.
Madden, G. J., Begotka, A. M., Raiff, B. R., & Kastern, L. L. (2003). Delay discounting of real and hypothetical rewards. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 11(2), 139–145.
Martins, S. S., Tavares, H., da Silva Lobo, D. S., Galetti, A. M., & Gentil, V. (2004). Pathological gambling, gender, and risk-taking behaviors. Addictive Behaviors, 29, 1231–1235.
Mazur, J. E. (1984). Tests of an equivalence rule for fixed and variable reinforcer delays. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 10(4), 426–436.
Meyer, G., Hayer, T., & Griffiths, M. D. (2009). Problem gaming in Europe: Challenges, prevention, and interventions. New York: Springer.
Michalczuk, R., Bowden-Jones, H., Verdejo-Garcia, A., & Clark, L. (2011). Impulsivity and cognitive distortions in pathological gamblers attending the UK National Problem Gambling Clinic: A preliminary report. Psychological Medicine, 41, 2625–2635.
Miedl, S. F., Büchel, C., & Peters, J. (2014). Cue-induced craving increases impulsivity via changes in striatal value signals in problem gamblers. Journal of Neuroscience, 34, 4750–4755.
Mishra, S., Lalumière, M. L., & Williams, R. J. (2010). Gambling as a form of risk-taking: Individual differences in personality, risk-accepting attitudes, and behavioral preferences for risk. Personality and Individual Differences, 49(6), 616–621.
Nigro, G., & Cosenza, M. (2016). Living in the now: Decision-making and delay discounting in adolescent gamblers. Journal of Gambling Studies,. doi:10.1007/s10899-016-9595-9. Epub ahead of print.
Olson, E. A., Hooper, C. J., Collins, P., & Luciana, M. (2007). Adolescents’ performance on delay and probability discounting tasks: Contributions of age, intelligence, executive functioning, and self-reported externalizing behavior. Personality and Individual Differences, 43(7), 1886–1897.
Petry, N. M. (2001a). Pathological gamblers, with and without substance abuse disorders, discount delayed rewards at high rates. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110, 482–487.
Petry, N. M. (2001b). Substance abuse, pathological gambling, and impulsiveness. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 63, 29–38.
Petry, N. M., & Casarella, T. (1999). Excessive discounting of delayed rewards in substance abusers with gambling problems. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 56, 25–32.
Petry, N. M., & Madden, G. J. (2010). Discounting and pathological gambling. In G. J. Madden & W. K. Bickel (Eds.), Impulsivity: The behavioral and neurological science of discounting (pp. 273–294). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Potenza, M. N. (2013). Biological contributions to addictions in adolescents and adults: Prevention, treatment, and policy implications. Journal of Adolescent Health, 52(2), S22–S32.
Reynolds, B., Ortengren, A., Richards, J. B., & de Wit, H. (2006). Dimensions of impulsive behavior: Personality and behavioral measures. Personality and Individual Differences, 40, 305–315.
Romer, D. (2010). Adolescent risk taking, impulsivity, and brain development: Implications for prevention. Developmental Psychobiology, 52(3), 263–276.
Scheres, A., Dijkstra, M., Ainslie, E., Balkan, J., Reynolds, B., Sonuga-Barke, E., et al. (2006). Temporal and probabilistic discounting of rewards in children and adolescents: Effects of age and ADHD symptoms. Neuropsychologia, 44(11), 2092–2103.
Spear, L. P. (2000). Neurobehavioral changes in adolescence. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9(4), 111–114.
Spurrier, M., & Blaszczynski, A. (2014). Risk perception in gambling: A systematic review. Journal of Gambling Studies, 30(2), 253–276.
Steinberg, L. (2004). Risk taking in adolescence: What changes, and why? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1021(1), 51–58.
Steinberg, L. (2007). Risk taking in adolescence new perspectives from brain and behavioral science. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16(2), 55–59.
Steinberg, L. (2008). A social neuroscience perspective on adolescent risk-taking. Developmental Review, 28(1), 78–106.
Steinberg, L. (2010). A dual systems model of adolescent risk-taking. Developmental Psychobiology, 52(3), 216–224.
Steinberg, L., Graham, S., O’Brien, L., Woolard, J., Cauffman, E., & Banich, M. (2009). Age differences in future orientation and delay discounting. Child Development, 80(1), 28–44.
Strathman, A., Gleicher, F., Boninger, D. S., & Edwards, C. S. (1994). The consideration of future consequences: Weighing immediate and distant outcomes of behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 66(4), 742–752.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using multivariate statistics (6th ed.). Boston: Pearson.
Teuscher, U., & Mitchell, S. H. (2011). Relation between time perspective and delay discounting: A literature review. Psychological Record, 61(4), 613–632.
Toplak, M. E., Liu, E., MacPherson, R., Toneatto, T., & Stanovich, K. E. (2007). The reasoning skills and thinking dispositions of problem gamblers: A dual-process taxonomy. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 20(2), 103–124.
Van Brunschot, E. G. (2009). Gambling and risk behaviour: A literature review. Alberta: Gaming Research Institute.
Whiteside, S. P., Lynam, D. R., Miller, J. D., & Reynolds, S. K. (2005). Validation of the UPPS impulsive behaviour scale: A four-factor model of impulsivity. European Journal of Personality, 19(7), 559–574.
Wiehler, A., & Peters, J. (2015). Reward-based decision making in pathological gambling: The roles of risk and delay. Neuroscience Research, 90, 3–14.
Willoughby, T., Good, M., Adachi, P. J., Hamza, C., & Tavernier, R. (2013). Examining the link between adolescent brain development and risk taking from a social–developmental perspective. Brain and Cognition, 83(3), 315–323.
Winters, K. C., Stinchfield, R. D., & Fulkerson, J. (1993). Toward the development of an adolescent gambling problem severity scale. Journal of Gambling Studies, 9(1), 63–84.
Winters, K. C., Stinchfield, R. D., & Kim, L. G. (1995). Monitoring adolescent gambling in Minnesota. Journal of Gambling Studies, 11(2), 165–183.
Yoon, J. H., Higgins, S. T., Heil, S. H., Sugarbaker, R. J., Thomas, C. S., & Badger, G. J. (2007). Delay discounting predicts postpartum relapse to cigarette smoking among pregnant women. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 15(2), 176–186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosenza, M., Griffiths, M.D., Nigro, G. et al. Risk-Taking, Delay Discounting, and Time Perspective in Adolescent Gamblers: An Experimental Study. J Gambl Stud 33, 383–395 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-016-9623-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-016-9623-9