Abstract
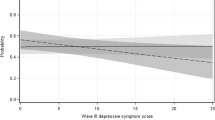
Young adulthood is a period renowned for engagement in impulsive and risky behaviors, including gambling. There are some indications that young adults exhibit higher gambling rates in comparison to older adults. Problem gambling has also been linked to ADHD. This longitudinal study examines the relationship between gambling and ADHD among an epidemiological sample of young adults (n = 235; males = 179, females = 56) aged 18-24. Results indicate that individuals who report childhood ADHD symptoms which persist into young adulthood experience greater gambling problem severity than participants with no ADHD or those with non-persistent ADHD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (text revision). Washington, DC: Author.
August, G. J., Realmuto, G. M., Crosby, R. D., & MacDonald, A. W., III (1995). Community-based multiple-gate screening of children at risk for conduct disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 23(4), 521–544.
August, G. J., Winters, K. C., Realmuto, G. M., Fahnhorst, T., Botzet, A., & Lee, S. (2006). Prospective study of adolescent drug use among community samples of ADHD and non-ADHD participants. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 45(7), 824–832.
Barkley, R. A., Fischer, M., Smallish, L., & Fletcher, K. (2004). Young adult follow-up of hyperactive children: Antisocial activities and drug use. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45(2), 195–211.
Barnes, G. M., Welte, J. W., Hoffman, J. H., & Dintcheff, B. A. (2005). Shared predictors of youthful gambling, substance use, and delinquency. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 19(2), 165–174.
Carlson, M. J., & Moore, T. L. (1998). Adolescent gambling in oregon: A report to the oregon gambling addiction treatment foundation. Retrieved May 28, 2008, from http://www.gamblingaddiction.org/adolescent/CHAPTER1.htm.
Carlton, P. L., & Manowitz, P. (1992). Behavioral restraint and symptoms of attention deficit disorder in alcoholics and pathological gamblers. Neuropsychobiology, 25, 44–48.
Carlton, P. L., Manowitz, P., McBride, H., Nora, R., Swartzburg, M., & Goldstein, L. (1987). Attention deficit disorder and pathological gambling. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 48(12), 487–488.
Derevensky, J., Pratt, L., Hardoon, K., & Gupta, R. (2007). Gambling problems and features of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder among children and adolescents. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 1(3), 165–172.
Derogatis, L. R. (1975). Brief symptom inventory. Baltimore, MD: Clinical Psychometric Research.
Elkins, I. J., McGue, M., & Iacono, W. G. (2007). Prospective effects of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, and sex on adolescent substance use and abuse. Archives of General Psychiatry, 64, 1145–1152.
Feigelman, W., Gorman, B. S., & Lesieur, H. (2006). Examining the relationship between at-risk gambling and suicidality in a national representative sample of young adults. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 36(4), 396–408.
Fuentes, D., Tavares, H., Artes, R., & Gorenstein, C. (2006). Self-reported and neuropsychological measures of impulsivity in pathological gambling. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12, 907–912.
Goudriaan, A. E., Oosterlaan, J., de Beurs, E., & van den Brink, W. (2006). Neurocognitive functions in pathological gambling: A comparison with alcohol dependence, Tourette syndrome, and normal controls. Addiction, 101, 534–547.
Goyette, C. H., Conners, C. K., & Ulrich, R. F. (1978). Normative data on revised conners parent and teacher rating scales. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 221–236.
Gupta, R., & Derevensky, J. (1998). Adolescent gambling behavior: A prevalence study and examination of the correlates associated with problem gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 14(4), 319–345.
Hansen, C., Weiss, D., & Last, C. G. (1999). ADHD boys in young adulthood: Psychosocial adjustment. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 38(2), 165–171.
Hardoon, K., & Derevensky, J. (2002). Child and adolescent gambling behavior: Our current knowledge. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 7(2), 263–281.
Henly, G. A., & Winters, K. C. (1989). Development of psychosocial scales for the assessment of adolescents involved with alcohol and drugs. International Journal of the Addictions, 24(10), 973–1001.
Hollingshead, A. B. (1975). Four factor index of social status. New Haven, CT: Yale University Department of Sociology.
Huang, J., Jacobs, D. F., Derevensky, J. L., Gupta, R., & Paskus, T. S. (2007). Gambling and health risk behaviors among U. S. college student athletes: Findings from a national study. Journal of Adolescent Health, 40, 390–397.
Kaminer, V., & Petry, N. (1999). Gambling behavior in youths: Why we should be concerned. Alcohol and Drug Abuse, 50(2), 167–168.
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (1990). Kaufman brief intelligence test manual. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Krain, A. L., & Castellanos, F. X. (2006). Brain development and ADHD. Clinical Psychology Review, 26, 433–444.
LaBrie, R. A., Shaffer, H. J., LaPlante, D. A., & Wechsler, H. (2003). Correlates of college student gambling in the United States. Journal of American College Health, 52(2), 53–62.
Langewisch, M. W. J., & Frisch, G. R. (1998). Gambling behavior and pathology in relation to impulsivity, sensation seeking, and risky behavior in male college students. Journal of Gambling Studies, 14(3), 245–262.
Lesieur, H. R., & Blume, S. B. (1987). South oaks gambling screen (SOGS): A new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. American Journal of Psychiatry, 144, 1184–1188.
Lightsey, O. R., Jr., & Hulsey, C. D. (2002). Impulsivity, coping, stress, and problem gambling among University students. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 49(2), 202–211.
Lynch, W. J., Maciejewski, P. K., & Potenza, M. N. (2004). Psychiatric correlates of gambling in adolescents and young adults grouped by age at gambling onset. Archives of General Psychiatry, 61, 1116–1122.
Messerlian, C., Derevensky, J., & Gupta, R. (2005). Youth gambling problems: A public health perspective. Health Promotion International, 20(1), 69–79.
Murphy, K. R. (1992). Evaluation interview for adult ADHD, ODD, and ASP. Unpublished manuscript, University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Boston.
National Research Council. (1999). Pathological gambling: A critical review. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Nower, L., Derevensky, J. L., & Gupta, R. (2004). The relationship of impulsivity, sensation seeking, coping, and substance use in youth gamblers. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18(1), 49–55.
Petry, N. M. (2001). Substance abuse, pathological gambling, and impulsiveness. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 63, 29–38.
Petry, N. M. (2005). Pathological gambling: Etiology, comorbidity, and treatment. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Petry, N. M., & Armentano, C. (1999). Prevalence, assessment, and treatment of pathological gambling: A review. Psychiatric Services, 50, 1021–1027.
Powell, J., Hardoon, K., Derevensky, J. L., & Gupta, R. (1999). Gambling and risk-taking behavior among University students. Substance Use & Misuse, 34(8), 1167–1184.
Reich, W., Shayla, J. J., & Taibelson, C. (1992). The diagnostic interview for children and adolescents–revised (DICA-R) (structured psychiatric interview). St. Louis: Washington University.
Reynolds, C., & Kamphaus, R. C. (1992). BASC: Behavioral assessment system for children and adolescents. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Services, Inc.
Rubia, K., Taylor, E., Smith, A. B., Oksannen, H., Overmeyer, S., & Newman, S. (2001). Neuropsychological analyses of impulsiveness in childhood hyperactivity. British Journal of Psychiatry, 179, 138–143.
Rugle, L., & Melamed, L. (1993). Neuropsychological assessment of attention problems in pathological gamblers. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 181(2), 107–112.
Shaffer, H. J., & Hall, M. N. (2001). Updating and refining prevalence estimates of disordered gambling behaviour in the United States and Canada. Canadian Journal of Public Health, 92(3), 168–172.
Slutske, W. S., Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., & Poulton, R. (2005). Personality and problem gambling: A prospective study of a birth cohort of young adults. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 769–775.
Specker, S. M., Carlson, G. A., Christenson, G. A., & Marcotte, M. (1995). Impulse control disorders and attention deficit disorder in pathological gamblers. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 7(4), 175–179.
Stinchfield, R. (2002). Reliability, validity, and classification accuracy of the South Oaks gambling screen (SOGS). Addictive Behaviors, 27(1), 1–19.
Volberg, R. A., & Banks, S. M. (1990). A review of two measures of pathological gambling in the United States. Journal of Gambling Studies, 6(2), 153–163.
Weinstock, J., Whelan, J. P., Meyers, A. W., & McCausland, C. (2007). The performance of two pathological gambling screens on college students. Assessment, 14(4), 399–407.
Winters, K. C., Bengston, P., Dorr, D., & Stinchfield, R. (1998). Prevalence and risk factors of problem gambling among college students. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 12(2), 127–135.
Winters, K. C., & Henly, G. A. (1993). Adolescent diagnostic interview (ADI) manual. Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Winters, K. C., Stinchfield, R., & Fulkerson, J. (1993). Toward the development of an adolescent gambling problem severity scale. Journal of Gambling Studies, 9, 371–386.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse grants DA12995 and DA14717 (Winters).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breyer, J.L., Botzet, A.M., Winters, K.C. et al. Young Adult Gambling Behaviors and their Relationship with the Persistence of ADHD. J Gambl Stud 25, 227–238 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-009-9126-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10899-009-9126-z