Abstract
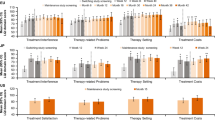
The lifelong IgG replacement therapy for patients with primary immunedeficiencies (PIDD) may be provided by intravenous (IVIG) or by subcutaneous IgG (SCIG) infusions. We investigated the impact of weekly SCIG self-infusions at home on the health-related quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and preferences in patients treated with IVIG at the hospital/doctor's office (Group A) or at home (Group B) before the study started. Forty-four adult North American PIDD patients were included in the study, 28 patients in Group A and 16 in Group B. Patients in Group A reported significantly less limitations with their work/daily activities, a significantly improved vitality, and better general health. Treatment satisfaction was significantly improved in Group A. The preference for the subcutaneous route and for home therapy was respectively 81% and 90% in Group A. In Group B, 69% preferred the subcutaneous route and 92% home therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Notarangelo L, Cassanova JL, Fischer A, Puck J, Rosen F, Seger R, Geha R: Primary immunodeficiency diseases: Un update. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:667–687, 2004
Stiehm ER, Ochs HD, Winkelstein JA: Immunologic disorders in infants and children. Philadelphia, Elesvier, 2004
Stiehm ER: Human intravenous immunoglobulin in primary and secondary antibody deficiencies. Pediatr Infect Dis 16:696–707, 1997
Eijkhout HW, van da Meer JWM, Kallenberg CGM, Weening RS, van Dissel JT, Sanders LAM, Strengers PFW, Nienhuis H, Schellekens PTH: The effect of two different doses of intravenous immunoglobulin on the incidence of recurrent infections in patients with primary hypoagammaglobulinemia. Ann Intern Med 135:165–174, 2001
Busse PJ, Razvi S, Cunningham-Rundles C: Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in the prevention of pneumonia in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 109:1001–1004, 2002
Roifman CH, Levison H, Gelfand EW: High-dose versus low-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in hypogammaglobulinaemia and chronic lung disease. Lancet 1:1075–1077, 1987
Schulmann, Ronca & Bucuvalas, Inc.: Treatment experiences and preferences of patients with primary immune deficiency diseases: First national survey; Immune Deficiency Foundation (IDF): June 20, 2003. (Accessed on June 10, 2005 at http:www. primaryimmune.org).
Ochs HD, Fischer SH, Lee ML, Delson ES, Kingdon HS, Wedgwood RJ: Intravenous immunoglobulin home treatment for patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases. Lancet 1:610–611, 1986
Ochs HD, Lee ML, Fischer SH, Delson ES, Chang BS, Wedgwood RJ: Self-infusions of intravenous immunoglobulin by immunodeficient patients at home. J Infect Dis 156:652–654, 1987
Ashida ER, Saxon A: Home intravenous immunoglobulin therapy by self-administration. J Clin Immunol 6:306–309, 1986
Soerensen RU, Kallick MD, Berger M: Home treatment of antibody deficiency syndromes with intravenous immune globulin. J Allergy Clin Immunol 80:810–815, 1987
Chapel H, Brennan V, Delson E: Immunoglobulin replacement therapy by self-infusion at home. Clin Exp Immunol 73:160–162, 1988
Kobayashi RH, Kobayashi AD, Lee N, Fischer S, Ochs HD: Home self-adminstration of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in children. Pediatrics 85:705–709, 1990
Brennan VM, Cochrane S, Fletcher C, Hendy D, Powell P: Surveillance of adverse reactions in patients self-infusing intravenous immunoglobulin at home. J Clin Immunol 15:116–119, 1995
Stiehm RE, Casillas AM, Finkelstein JZ, Gallagher KT, Groncy PM, Kobayashi RH, Oleske JM, Roberts RL, Sandberg ET, Wakim ME: Slow subcuateous human intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of antibody immunodeficiency: Use of an old method with a new product. J Allergy Clin Immunol 101:848–849, 1998
Gardulf A, Hammarström L, Smith CIE: Home treatment of hypogammaglobulinaemia with subcutaneous gammaglobulin by rapid infusion. Lancet 338:162–166, 1996
Gardulf A, Andersen V, Björkander J, Ericson D, Frøland SS, Gustafson R, Hammarström L, Jacobsen MB, Jonsson E, Möller G, Nyström T, Søeberg B, Smith CIE: Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement in patients with primary antibody deficiencies: Safety and costs. Lancet 345:365–369, 1995
Gardulf A, Björvell H, Andersen V, Björkander J, Ericson D, Froland SS, Gustafson R, Hammarström L, Nyström T, Soeberg B, Smeith CIE: Lifelong treatment with gammaglobulin for primary antibody deficiencies: The patients' experiences of subcutaneous self-infusions and home therapy. J Adv Nurs 21:917–927, 1995
Abrahamsen TG, Sandersen H, Bustnes A: Home therapy with subcutaneous immunoglobulin infusions in children with congenital immunodeficiencies. Pediatrics 98:1127–1131, 1996
Gaspar J, Gerritsen B, Jones A: Immunoglobulin replacement therapy by rapid subcutaneous infusions. Arch Dis Child 79:48–51, 1998
Chapel HM, Spickett GP, Ericson D, Engl W, Eibl M, Björkander J: The comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravenous versus subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy. J Clin Immunol 20:94–100, 2000
Thomas MJ, Brennan VM, Chapel HM: Rapid subcutaneous immunoglobulin infusions in children. Lancet 342:1432–1433, 1993
Hansen S, Gustafson R, Smith CIE, Gardulf A: Subcutaneous IgG infusions in patients with primary antibody deficiencies: Decreased time of delivery with maintained safety. Clin Immunol 104:237–241, 2002
Gardulf A, Nicolay U, Asensio O, Bernatowska E, Böck A, Costa-Carvalho B, Granert C, Haag S, Hernández D, Kiessling P, Kus J, Matamoros N, Niehues T, Schmidt S, Schulze I, Borte M: Children and adults with primary antibody deficiencies gain quality of life by subcutaneous IgG self-infusions at home. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:936–942, 2004
Berger M: Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement in primary immunodeficiencies. Clin Immunol 112:1–7, 2004
Daly PB, Evans JH, Kobayashi RH, Kobayashi AL, Ochs HD, Fischer SH, Pirofsky B, Sprouse C: Home-based immunoglobulin infusion therapy: Quality of life and patient health perceptions. Ann Allergy 67:504–510, 1991
Gardulf A, Björvell H, Gustafson R, Hammarström L, Smith CIE: The life situations of patients with primary antibody deficiency untreated or treated with subcutaneous gammaglobulin infusions. Clin Exp Immunol 92:200–204, 1993
Gardulf A, Möller G, Joonsson E: A comparison of the patient-borne costs of therapy with gamma globulin given at the hospital or at home. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 11:345–353, 1993
Ware JE, Snow KK, Kosinski M: SF-36® Health Survey: Manual and interpretation guide. Lincoln, RI, QualityMetric, 2000
Nicolay U, Haag S, Eichmann F, Herget S, Spruck D, Gardulf A: Measuring treatment satisfaction in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases receiving lifelong immunoglobulin replacement therapy. Quality Life Research 14:1683–1691, 2005
Hoybraten Sigstad HM, Stray-Pedersen A, Froland SS: Coping, quality of life, and hope in adults with primary antibody deficiencies. Health Qual Life Outcomes 3:31, 2005
Gardulf A, Björvell H, Andersen V, Björkander J, Ericson D, Frøland S, Gustafson R, Hammarström L, Nyström T, Søeberg B, Smith CIE: Lifelong treatment with gammaglobulin to patients with primary antibody deficiencies: The patients' experiences of subcutaneous self-infusions and home therapy. J Adv Nurs 21:917–927, 1995
Brown H, Prescott R: Applied Mixed Models in Medicine. New York, Wiley, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicolay, U., Kiessling, P., Berger, M. et al. Health-Related Quality of Life and Treatment Satisfaction in North American Patients with Primary Immunedeficiency Diseases Receiving Subcutaneous IgG Self-Infusions at Home. J Clin Immunol 26, 65–72 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-8905-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-8905-x