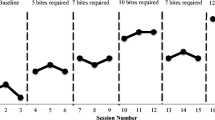
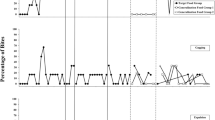
The feeding behaviors of a child diagnosed with failure to thrive were assessed using descriptive analysis methodology to identify the schedules of reinforcement provided by the child's parents. This analysis revealed that the child's appropriate feeding behaviors (i.e., bite acceptance, self-feeding) were on a lean schedule of positive reinforcement and that the child's refusal behaviors (e.g., non-acceptance, expulsion) were on a rich schedule of negative reinforcement. A treatment package consisting of differential positive reinforcement for bite acceptance with and without escape extinction was evaluated by manipulating the schedules of reinforcement that were identified to be used by the child's parents. The results showed a reduction of the child's inappropriate mealtime behaviors and increases in the child's acceptance of offered food items. The results also suggested that the differential reinforcement component appeared to be most responsible for ongoing effectiveness of the treatment. These results are discussed in terms of treating the food refusal behavior of children diagnosed with failure to thrive as a preventive measure for later development of developmental disabilities.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ahearn, W. H., Kerwin, M. E., Eicher, P. S., Shantz, J., & Swearingin, W. (1996). An alternating treatments comparison of two intensive interventions for food refusal. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 28, 321–332.
Budd, K. S., McGraw, T. E., Farbisz, R., Murphy, T. B., Hawkins, D., Heilman, N., et al. (1992). Psychosocial concomitants of children's feeding disorders. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 17, 81–94.
Cooper, L. J., Wacker, D. P., Brown, K., McComas, J. J., Peck, S. M., Drew, J., et al. (1999). Use of a concurrent operants paradigm to evaluate positive reinforcers during treatment of food refusal. Behavior Modification, 23, 3–40.
Cooper, L. J., Wacker, D. P., McComas, J. J., Brown, K., Peck, S. M., Richman, D., et al. (1995). Use of component analyses to identify active variables in treatment packages for children with feeding disorders. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 28, 139–153.
Iwata, B. A., Kahng, S., Wallace, M. D., & Lindberg, J. S. (2000). The functional analysis model of behavioral assessments. In J. Austin & J. E. Carr (Eds.), Handbook of Applied Behavior Analysis (pp. 61–90). Reno, NV: Context Press.
Kelleher, K. J., Casey, P. H., Bradley, R. H., Pope, S. K., Whiteside, L., Barrett, K. W., et al. (1993). Risk factors and outcomes for failure to thrive in low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatrics, 91, 941–948.
Kerwin, M. E., Ahearn, W. H., Eicher, P. S., & Burd, D. M. (1995). The cost of eating: A behavioral economic analysis of food refusal. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 28, 245–260.
Kristiansson, B., & Fallstrom, S. P. (1987). Growth at the age of 4 years subsequent to early failure to thrive. Child Abuse and Neglect, 11, 35–40.
Krugman, S. D., & Dubowitz, H. (2003). Failure to thrive. American Family Physician, 68, 879–884.
Lalli, J. S., & Goh, H. (1993). Naturalistic Observations in Community Settings. In J. Reichle & D. P. Wacker (Eds.), Communicative Alternatives to Challenging Behavior: Integrating functional assessment intervention strategies (pp. 11–39). Baltimore: Brooks.
Miles, A., & Reed, G. (2004). Feeding challenges in children with neurological impairment. Support Line, 26, 16–23.
Piazza, C. C., Fisher, W. W., Brown, K. A., Shore, B. A., Patel, M. R., Katz, R. M., et al. (2003). Functional analysis of inappropriate mealtime behaviors. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 36, 187–204.
Piazza, C. C., Patel, M. R., Gulotta, C. S., Sevin, B. M., & Layer, S. A. (2003). On the relative contributions of positive reinforcement and escape extinction in the treatment of food refusal. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 36, 309–324.
Reed, G. K., Piazza, C. C., Patel, M. R., Layer, S. A., Bachmeyer, M. H., Bethke, S. D., et al. (2004). On the relative contributions of noncontingent reinforcement and escape extinction in the treatment of food refusal. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 37, 27–42.
Shirley, M. J., Iwata, B. A., Kahng, S., Mazaleski, J. L., & Lerman, D. C. (1997). Does functional communication training compete with ongoing contingencies of reinforcement? An analysis during response acquisition and maintenance. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30, 93–104.
Thompson, R. H., & Iwata, B. A. (2001). A descriptive analysis of social consequences following problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 34, 169–178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casey, S.D., Cooper-Brown, L.J., Wacker, D.P. et al. The Use of Descriptive Analysis to Identify and Manipulate Schedules of Reinforcement in the Treatment of Food Refusal. J Behav Educ 15, 39–50 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-005-9001-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-005-9001-7