Abstract
Aims
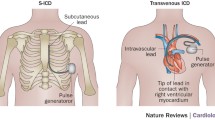
Complications of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) therapy are often linked to transvenous lead insertion, lead failure, or infections. An entirely subcutaneous ICD system (S-ICD) avoids the need for the placement of electrodes within the heart and can provide clinical advantages.
Methods and results
A 45-year-old patient with Brugada syndrome (spontaneous type 1 Brugada ECG, syncope during fever, family history of sudden death <45 years old) was implanted with an entirely S-ICD. A left lateral incision was made over the sixth rib in the anterior axillary line for pocket formation and pulse generator placement. The subcutaneous electrode was placed subcutaneously, parallel to and 2 cm to the left of the sternal midline, and was connected to the generator. The insertion of the system was guided only by anatomical landmarks, and no fluoroscopy was required. Ventricular fibrillation was induced and terminated by a 65-J shock (15-J safety margin). No complication occurred, and subsequent course was uneventful.
Conclusions
S-ICD is a new system for delivering lifesaving shock therapy in patients at risk of sudden cardiac death, without the need of intracardiac leads. Young patients with inherited arrhythmogenic syndromes could benefit the most from this system. This is the first case of Brugada syndrome implanted with a first-generation S-ICD in Italy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sacher, F., Probst, V., Iesaka, Y., et al. (2006). Outcome after implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with Brugada syndrome: a multicenter study. Circulation, 114, 2317–2324.
Rosso, R., Glick, A., Glikson, M., et al. (2008). Outcome after implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with Brugada syndrome: a multicenter Israeli study (ISRABRU). Israel Medical Association Journal, 10, 435–439.
Maytin, M., & Epstein, L. M. (2011). The challenge of transvenous lead extraction. Heart, 97, 425–434.
Wilkoff, B. L., Love, C. J., Byrd, C. L., et al. (2009). Transvenous lead extraction: Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus on facilities, training, indications and patients management: this document was endorsed by the American Heart Association (AHA). Heart Rhythm, 6, 1085–1104.
Bardy, G. H., et al. (2010). An entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. The New England Journal of Medicine, 363, 36–44.
Cappato, R., & Bardy, G. H. (2005). Sub-cutaneous electrical defibrillation in canines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 45(1), 106A. Abstract.
Bardy, G. H., Cappato, R., & Smith, Wm. (2002). The totally subcutaneous ICD system. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 25(II), 578. Abstract.
Neuzil, P., Petru, J., & Reddy, V. Y. (2011). Subcutaneous ICD implantation in the setting of an occluded superior vena cava. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22, 475–476.
Van Opstal, J., Geskes, G., & Debie, L. A completely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator system functioning simultaneously with an endocardial implantable cardioverter defibrillator programmed as a pacemaker. Europace 2010.
Baez-Escudero, J. L., Beshai, J. F., & Burke, M. C. (2010). Use of a primary prevention totally subcutaneous defibrillator in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 3, 560–561.
McLeod, K. A., & Mc Lean, A. (2010). Implantation of a fully subcutaneous ICD in children. PACE 1–4.
Sarkozy, A., Brugada, P., Mont, L., & Brugada, J. (2007). Optimizing the clinical use of implantable defibrillators in patients with Brugada syndrome. European Heart Journal Supplements, 9(I), 174–180.
Kalahasty, G., & Ellenbogen, K. A. (2011). Management of the patient with implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead failure. Circulation, 123, 1352–1354.
Grace, A. A., Smith, W. M., Hood, M., Connolly, D., Cappato, R., & Bardy, G. H. A prospective, randomized comparison in humans of defibrillation efficacy of a standard transvenous ICD system with a totally subcutaneous ICD system (The S-ICD® system). European Society of Cardiology Congress 2005, Stockholm. Website slide resource, session number FP3684.
Gold, M., Theuns, D. A., Knight, B. P., Sturdivant, J. L., Ellenbogen, K. A., Wood, M. A., et al. (2009). Arrhythmia detection by a totally subcutaneous S-ICD® system compared to a transvenous single-chamber ICD system with morphology discrimination. Heart Rhythm, 6, S34.
Gust Bardy answers questions about the entirely subcutaneous ICD. http://cardiobrief.org/2010/05/12. Accessed 12 May 2010.
Kleijn, S., & Van der Veldt, A. (2010). Correspondence to the editor. An entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. The New England Journal of Medicine, 363(16), 1577–1578.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Maria, E., Bonetti, L., Patrizi, G. et al. Implantation of a completely subcutaneous ICD system: case report of a patient with Brugada syndrome and state of the art. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 34, 105–113 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-011-9626-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-011-9626-5