Abstract
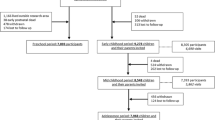
The Generation R Study is a population-based prospective cohort study from fetal life until young adulthood. The study is designed to identify early environmental and genetic causes of normal and abnormal growth, development and health from fetal life until young adulthood. The study focuses on four primary areas of research: (1) growth and physical development; (2) behavioural and cognitive development; (3) diseases in childhood; and (4) health and healthcare for pregnant women and children. In total, 9,778 mothers with a delivery date from April 2002 until January 2006 were enrolled in the study. Of all eligible children at birth, 61% participate in the study. In addition, more detailed assessments are conducted in a subgroup of 1,232 pregnant women and their children. Data collection in the prenatal phase and postnatal phase until the age of 4 years includes questionnaires, detailed physical and ultrasound examinations, behavioural observations and biological samples. This paper gives an update of the study design and cohort profile until the children’s age of 4 years. Eventually, results forthcoming from the Generation R Study have to contribute to the development of strategies for optimizing health and healthcare for pregnant women and children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Mackenbach JP, Moll HA, Snijders RF, Steegers EA, et al. Growth, development and health from early fetal life until young adulthood: the Generation R Study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2004;18:61–72. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2003.00521.x.
Jaddoe VW, Mackenbach JP, Moll HA, Steegers EA, Tiemeier H, Verhulst FC, et al. The Generation R Study: design and cohort profile. Eur J Epidemiol. 2006;21:475–84. doi:10.1007/s10654-006-9022-0.
Centre for Research and Statistics. Rotterdam (COS). 2005. http://www.cos.rotterdam.nl.
Troe EJ, Raat H, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Looman CW, Moll HA, et al. Explaining differences in birthweight between ethnic populations. The Generation R Study. BJOG. 2007;114:1557–65. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01508.x.
Statistics Netherlands. Standard Onderwijsindeling 2003. Voorburg/Heerlen: Statistics Netherlands; 2004.
Statistics Netherlands. Allochtonen in Nederland 2004. Voorburg/Heerlen: Statistics Netherlands; 2004.
Silva LM, Steegers EA, Burdorf A, Jaddoe VW, Arends LR, Hofman A, et al. No midpregnancy fall in diastolic blood pressure in women with a low educational level: the Generation R Study. Hypertension. 2008;52:645–51. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116632.
Verburg BO, Steegers EA, De Ridder M, Snijders RJ, Smith E, Hofman A, et al. New charts for ultrasound dating of pregnancy and assessment of fetal growth: longitudinal data from a population-based cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008;31:388–96. doi:10.1002/uog.5225.
Tunon K, Eik-Nes SH, Grottum P. A comparison between ultrasound and a reliable last menstrual period as predictors of the day of delivery in 15,000 examinations. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1996;8:178–85. doi:10.1046/j.1469-0705.1996.08030178.x.
Jaddoe VW, Verburg BO, de Ridder MA, Hofman A, Mackenbach JP, Moll HA, et al. Maternal smoking and fetal growth characteristics in different periods of pregnancy: the Generation R Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;165:1207–15. doi:10.1093/aje/kwm014.
Roza SJ, Verburg BO, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Mackenbach JP, Steegers EA, et al. Effects of maternal smoking in pregnancy on prenatal brain development. The Generation R Study. Eur J NeuroSci. 2007;25:611–7. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05393.x.
Verburg BO, Jaddoe VW, Wladimiroff JW, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Steegers EA. Fetal hemodynamic adaptive changes related to intrauterine growth: the Generation R Study. Circulation. 2008;117:649–59. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.709717.
Verburg BO, Geelhoed JJ, Steegers EA, Hofman A, Moll HA, Witteman JC, et al. Fetal kidney volume and its association with growth and blood flow in fetal life: the Generation R Study. Kidney Int. 2007;72:754–61. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5002420.
Jaddoe VW, Bakker R, van Duijn CM, van der Heijden AJ, Lindemans J, Mackenbach JP, et al. The Generation R Study biobank: a resource for epidemiological studies in children and their parents. Eur J Epidemiol. 2007;22:917–23. doi:10.1007/s10654-007-9209-z.
Ye X, Pierik FH, Hauser R, Duty S, Angerer J, Park MM, et al. Urinary metabolite concentrations of organophosphorous pesticides, bisphenol A, and phthalates among pregnant women in Rotterdam, The Netherlands: the Generation R study. Environ Res. 2008;108:260–7. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2008.07.014.
Rours GI, Verkooyen RP, Willemse HF, van der Zwaan EA, van Belkum A, de Groot R, et al. Use of pooled urine samples and a utomated DNA isolation to achieve improved sensitivity and cost-effectiveness of large-scale testing for Chlamydia trachomatis in pregnant women. R J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4684–90. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.9.4684-4690.2005.
Stichting Perinatale Registratie Nederland. 2008. (www.perinatreg.nl).
van Batenburg-Eddes T, de Groot L, Arends L, de Vries A, Moll HA, Steegers EA, et al. Does gestational duration within the normal range predict infant neuromotor development? Early Hum Dev. 2008;84:659–65. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2008.04.007.
Burgmeijer RJF, Merkx JAM. Pakket … En hoe pakt het uit: Ouder en Kindzorg tussen wetenschap en praktijk. Nederlands Congres Ouder en Kindzorg. Assen: van Gorcum; 1999.
Roza SJ, Steegers EA, Verburg BO, Jaddoe VW, Moll HA, Hofman A, et al. What is spared by fetal brain-sparing? Fetal circulatory redistribution and behavioral problems in the general population. Am J Epidemiol. 2008;168:1145–52. doi:10.1093/aje/kwn233.
Ay L, Hokken-Koelega AC, Mook-Kanamori DO, Hofman A, Moll HA, Mackenbach JP, et al. Tracking and determinants of subcutaneous fat mass in early childhood: the Generation R Study. Int J Obes. 2008;32:1050–9. doi:10.1038/ijo.2008.76.
Geelhoed JJ, Verburg BO, Nauta J, Lequin M, Hofman A, Moll HA, et al. Tracking and determinants of kidney size from fetal life until the age of 2 years: the Generation R Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.07.030.
Gabriele C, Asgarali R, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Moll HA, Jongste JC. Smoke exposure, airway symptoms and exhaled nitric oxide in infants: the Generation R study. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:307–13. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132607.
Labout JA, Duijts L, Arends LR, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, de Groot R, et al. Factors associated with pneumococcal carriage in healthy dutch infants: the Generation R Study. J Pediatr. 2008;153:771–6. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.05.061.
Lebon A, Labout JA, Verbrugh HA, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, van Wamel W, et al. Dynamics and determinants of Staphylococcus aureus carriage in infancy: the Generation R Study. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:3517–21. doi:10.1128/JCM.00641-08.
Duijts L, Bakker-Jonges LE, Labout JA, Jaddoe VW, Hofman A, Steegers EA, et al. Perinatal stress influences lymphocyte subset counts in neonates. The generation R study. Pediatr Res. 2008;63:292–8.
Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF- 36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473–83. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002.
Carver DJ, Chapman CA, Thomas VS, Stadnyk KJ, Rockwood K. Validity and reliability of the medical outcomes study short form-20 questionnaire as a measure of quality of life in elderly people living at home. Age Ageing. 1999;28:169–74. doi:10.1093/ageing/28.2.169.
De Brock AJLL, Vermulst AA, Gerris JRM, Abidin RR. Nijmeegse Ouderlijke Stress Index. Lisse. Swets en Zeitlinger b.v.; 1992.
Gerris JR, Boxtel DA, Vermulst AA, Janssens JM, van Zuthpen RA, Felling AJ. Parenting in Dutch families. Nijmegen: University of Nijmegen, Institute of Family Studies; 1993.
Cox JL, Holden JM, Sagovsky R. Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh postnatal depression scale. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:782–6. doi:10.1192/bjp.150.6.782.
Derogatis LR, Melisaratos N. The brief symptom inventory: an introductory report. Psychol Med. 1983;13:595–605.
Wardle J, Guthrie CA, Sanderson S, Rapoport LJ. Development of the children’s eating behaviour questionnaire. Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001;42:963–70. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00792.
Raat H, Botterweck AM, Landgraf JM, Hoogeveen WC, Essink-Bot ML. Reliability and validity of the short form of the child health questionnaire for parents (CHQ-PF28) in large random school based and general population samples. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2005;59:75–82. doi:10.1136/jech.2003.012914.
Jenkins MA, Clarke JR. Validation of a questionnaire and bronchial hyper- responsiveness against respiratory physician assessment in the diagnosis of asthma. Int J Epidemiol. 1996;25:609–16. doi:10.1093/ije/25.3.609.
St James-Roberts I, Halil T. Infant crying patterns in the first year: normal community and clinical findings. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1991;32:951–68. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1991.tb01922.x.
van der Wal MF, van den Boom DC, Pauw-Plomp H, de Jonge GA. Mothers’ reports of infant crying and soothing in a multicultural population. Arch Dis Child. 1998;79:312–7.
Gartstein MA, Rothbart MK. Studying infant temperament via the revised infant behavior questionnaire. Infant Behav Dev. 2003;26:64–86. doi:10.1016/S0163-6383(02)00169-8.
Ireton H, Glascoe FP. Assessing children’s development using parents’ reports. The child development inventory. Clin Pediatr. 1995;34:248–55. doi:10.1177/000992289503400504.
St James-Roberts I, Wolke D. Differences between maternal and objective ratings of difficult neonatal behavioural style: implications for temperament research and clinical perspectives. J Reprod Infant Psychol. 1983;1:53–60. doi:10.1080/02646838308403151.
St James-Roberts I, Wolke D. Convergences and discrepancies, among mothers’ and professionals’ assessments of difficult neonatal behaviour. J Child Psychol Psych All Discipl. 1989;29:21–42. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1988.tb00686.x.
Achenbach TM. Manual for the child behavior checklist/4–18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry; 1991.
Verhulst FC, Van der Ende J, Koot HM. Manual for the CBCL/4–18. Rotterdam: Erasmus Universiteit/Dept of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Sophia Children’s Hospital; 1996.
Walker LS, Garber SJ, van Slyke DA. Development and validation of the pain response inventory for children. Psychol Assess. 1997;9:392–405. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.9.4.392.
Fenson L, Dale PS, Reznick JS, Thal D, Bates E, Hartung JP. MacArthur communicative development inventories; user’s guide and technical manual. San Diego: Singular Publishing Group, Inc; 1983.
Saudino KJ, Dale PS, Oliver B, Petrill SA, Richardson V, Rutter M, et al. The validity of parent-based assessment of cognitive abilities of 2-year-olds. Br J Dev Psychol. 1998;16:349–63.
Isquith PK, Gioia GA, Espy KA. Executive function in preschool children: examination through everyday behavior. Dev Neuropsychol. 2004;26:403–22. doi:10.1207/s15326942dn2601_3.
Acknowledgments
The Generation R Study is conducted by the Erasmus Medical Center in close collaboration with the School of Law and Faculty of Social Sciences of the Erasmus University Rotterdam, the Municipal Health Service Rotterdam area, Rotterdam, the Rotterdam Homecare Foundation, Rotterdam and the Stichting Trombosedienst and Artsenlaboratorium Rijnmond (STAR-MDC), Rotterdam. We gratefully acknowledge the contribution of children and parents, general practitioners, hospitals, midwives and pharmacies in Rotterdam. The authors thank Rachel Bakker and Claudia Kruithof for their assistance in data management. The first phase of the Generation R Study is made possible by financial support from the Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Erasmus University Rotterdam and The Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development (ZonMw).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaddoe, V.W.V., van Duijn, C.M., van der Heijden, A.J. et al. The Generation R Study: design and cohort update until the age of 4 years. Eur J Epidemiol 23, 801–811 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-008-9309-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-008-9309-4