Abstract
School connectedness has a significant impact on adolescent outcomes, including reducing risk-taking behavior. This paper critically examines the literature on school-based programs targeting increased connectedness for reductions in risk taking. Fourteen articles describing seven different school-based programs were reviewed. Programs drew on a range of theories to increase school connectedness, and evaluations conducted for the majority of programs demonstrated positive changes in school connectedness, risk behavior, or a combination of the two. Many of the reviewed programs involved widespread school system change, however, which is frequently a complex and time-consuming task. Future research is needed to examine the extent of intervention complexity required to result in change. This review also showed a lack of consistency in the definitions and measurement of connectedness as well as few mediation analyses testing assumptions of impact on risk-taking behavior through increases in school connectedness. Additionally, this review revealed very limited evaluation of the elements of multicomponent programs that are most effective in increasing school connectedness and reducing adolescent risk taking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. (2008). Injury among young Australians. Bulletin no. 66. Canberra: Australian Government.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A. (1997). Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Battistich, V., & Hom, A. (1997). The relationship between students’ sense of their school as a community and their involvement in problem behaviors. American Journal of Public Health, 87(12), 1997–2001.
Battistich, V., Schaps, E., Watson, M., Solomon, D., & Lewis, C. (2000). Effects of the Child Development Project on students’ drug use and other problem behaviors. Journal of Primary Prevention, 21(1), 75–99.
Battistich, V., Schaps, E., & Wilson, N. (2004). Effects of an elementary school intervention on students’ “connectedness” to school and social adjustment during middle school. Journal of Primary Prevention, 24(3), 243–262.
Battistich, V., Solomon, D., Watson, M., & Schaps, E. (1997). Caring school communities. Educational Psychologist, 32(3), 137–151.
Bergin, C., & Bergin, D. (2009). Attachment in the classroom. Educational Psychology Review, 21, 141–170.
Bond, L., Butler, H., Thomas, L., Carlin, J., Glover, S., Bowes, G., et al. (2007). Social and school connectedness in early secondary school as predictors of late teenage substance use, mental health, and academic outcomes. Journal of Adolescent Health, 40, 357.e359–357.e318.
Bond, L., Patton, G., Glover, S., Carlin, J., Butler, H., Thomas, L., et al. (2004). The Gatehouse Project: can a multilevel school intervention affect emotional wellbeing and health risk behaviours? Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 58, 997–1003.
Brown, E. C., Catalano, R. F., Fleming, C. B., Haggerty, K. P., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Adolescent substance use outcomes in the Raising Healthy Children project: a two-part latent growth curve analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(4), 699–710.
Catalano, R. F., & Hawkins, J. (1996). The social development model: a theory of antisocial behavior. In J. D. Hawkins (Ed.), Delinquency and crime: current theories (pp. 149–197). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Catalano, R. F., Haggerty, K. P., Oesterle, S., Fleming, C. B., & Hawkins, J. D. (2004). The importance of bonding to school for healthy development: findings from the Social Development Research Group. Journal of School Health, 74(7), 252–261.
Catalano, R. F., Mazza, J. J., Harachi, T. W., Abbott, R. D., Haggerty, K. P., & Fleming, C. B. (2003). Raising healthy children through enhancing social development in elementary school: results after 1.5 years. Journal of School Psychology, 41(2), 143–164.
Chapman, R. L., Buckley, L., Sheehan, M. C., Shochet, I. M., & Romaniuk, M. (2011). The impact of school connectedness on violent behavior, transport risk-taking behavior, and associated injuries in adolescence. Journal of School Psychology, 49(4), 399–410.
Dornbusch, S., Erickson, K., Laird, J., & Wong, C. (2001). The relation of family and school attachment to adolescent deviance in diverse groups and communities. Journal of Adolescent Research, 16, 396–422.
Eggert, L., & Kumpfer, K. L. (1997). Drug abuse prevention for at-risk individuals. Rockville, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Fagan, A. A., Hanson, K., Hawkins, J. D., & Arthur, M. W. (2008). Bridging science to practice: achieving prevention program implementation fidelity in the Community Youth Development Study. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 235–249.
Fagan, A. A., & Mihalic, S. (2003). Strategies for enhancing the adoption of school-based prevention programs: lessons learned from the Blueprints for Violence Prevention replications of the Life Skills Training Program. Journal of Community Psychology, 31(3), 235–253.
Flay, B. R., Allred, C. G., & Ordway, N. (2001). Effects of the Positive Action program on achievement and discipline: two matched-control comparisons. Prevention Science, 2(2), 71–89.
Furby, L., & Beyth-Marom, R. (1992). Risk-taking in adolescence: a decision-making perspective. Developmental Review, 12, 1–44.
Fredericks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74, 59–109.
Goodenow, C. (1993). The psychological sense of school membership among adolescents: scale development and educational correlates. Psychology in the Schools, 30, 79–90.
Gottfredson, M., & Hirschi, T. (1990). A general theory of crime. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Hawkins, J., Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Abbott, R., & Hill, K. (1999). Preventing adolescent health-risk behaviors by strengthening protection during childhood. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 153(3), 226–234.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., Morrison, D. M., O’Donnell, J., Abbott, R. D., & Day, L. E. (1992). The Seattle Social Development Project: effects of the first four years on protective factors and problem behaviors. In J. McCord & R. E. Tremblay (Eds.), Preventing antisocial behavior: interventions from birth through adolescence (pp. 139–161). New York: Guilford.
Hawkins, J. D., Guo, J., Hill, K. G., Battin-Pearson, S., & Abbott, R. D. (2001). Long-term effects of the Seattle Social Development intervention on school bonding trajectories. Applied Developmental Science, 5(4), 225–236.
Hawkins, J. D., Kosterman, R., Catalano, R., Hill, K. G., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Promoting positive adult functioning through social development intervention in childhood. Archives of Pediatric Adolescent Medicine, 159, 25–31.
Hirschi, T. (1969). Causes of delinquency. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Igra, V., & Irwin, C. E. (1996). Theories of adolescent risk-taking behaviour. In R. J. DiClemente, W. B. Hansen, & L. E. Ponton (Eds.), Handbook of adolescent health risk behaviour (pp. 35–51). New York: Plenum.
Irwin, C. E., Jr. (1990). The theoretical concept of at-risk adolescents. Adolescent Medicine: State of the Art Reviews, 1, 1–14.
Jimerson, S. R., Campos, E., & Greif, J. L. (2003). Toward an understanding of definitions and measures of school engagement and related terms. The California School Psychologist, 8, 7–27.
Li, K., Washburn, I., DuBois, D. L., Vuchinich, S., Ji, P., Brechling, V., et al. (2011). Effects of the Positive Action programme on problem behaviours in elementary school students: a matched-pair randomised control trial in Chicago. Psychology and Health, 26(2), 187–204.
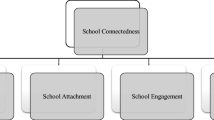
Libbey, H. (2004). Measuring student relationships to school: attachment, bonding, connectedness, and engagement. Journal of School Health, 74(7), 274–283.
Maddox, S., & Prinz, R. (2003). School bonding in children and adolescents: conceptualization, assessment, and associated variables. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 6(1), 31–49.
Matsueda, R. L. (1982). Testing control theory and differential association: a causal modeling approach. American Sociological Review, 47(4), 489–504.
Matsueda, R. L. (1988). The current state of differential association theory. Crime and Delinquency, 34(3), 277–306.
McLellan, L., Rissel, C., Donnelly, N., & Bauman, A. (1999). Health behaviour and the school environment in New South Wales, Australia. Social Science & Medicine, 49, 611–619.
McNeely, C., Nonnemaker, J., & Blum, R. (2002). Promoting school connectedness: Evidence from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Journal of School Health, 72(4), 138–146.
Monahan, K., Oesterle, S., & Hawkins, J. D. (2010). Predictors and consequences of school connectedness: the case for prevention. The Prevention Researcher, 17(3), 3–6.
Rimer, B., & Glanz, K. (2005). Theory at a glance: a guide for health promotion practice. Bethesda, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. NIH Publication No. 05-3896.
O’Farrell, S. L., & Morrison, G. M. (2003). A factor analysis exploring school bonding and related constructs among upper elementary students. The California School Psychologist, 8, 53–72.
Patton, G., Bond, L., Butler, H., & Glover, S. (2003). Changing schools, changing health? Design and implementation of the Gatehouse Project. Journal of Adolescent Health, 33, 231–239.
Pianta, R. C. (1999). Enhancing relationships between children and teachers. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Resnick, M., Harris, L., & Blum, R. (1993). The impact of caring and connectedness on adolescent health and well-being. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 29(Suppl 1), S3–S9.
Shochet, I. M., Smyth, T., & Homel, R. (2007). The impact of parental attachment on adolescent perception of the school environment and school connectedness. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Family Therapy, 28(2), 109–118.
Simons-Morton, B., Haynie, D., Saylor, K., Davis Crump, A., & Chen, R. (2005). Impact analysis and mediation of outcomes: the Going Places program. Health Education & Behavior, 32, 227–241.
Voisin, D., Salazar, L., Crosby, R., Diclemente, R., Yarber, W., & Staples-Horne, M. (2005). Teacher connectedness and health-related outcomes among detained adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 37, 337.e317–337.e323.
Wentzel, K. R. (1998). Social relationships and motivation in middle school: the role of parents, teachers, and peers. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(2), 202–209.
Wentzel, K. R., Battle, A., Russell, S. L., & Looney, L. B. (2010). Social supports from teachers and peers as predictors of academic and social motivation. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 35, 193–202.
Wentzel, K. R., & Wigfield, A. (2007). Motivational interventions that work: themes and remaining issues. Educational Psychologist, 42(4), 261–271.
Wenzel, V., Weichold, K., & Silbereisen, R. K. (2009). The life skills program IPSY: positive influences on school bonding and prevention of substance misuse. Journal of Adolescence, 32(6), 1391–1401.
Werner, E. E., & Smith, R. S. (1992). Overcoming the odds: high-risk children from birth to adulthood. New York: Cornell University Press.
Whitlock, J. (2004). Places to be and places to belong: youth connectedness in school and community. New York: ACT for Youth, Cornell University.
Whitlock, J. (2006). Youth perceptions of life at school: contextual correlates of school connectedness in adolescence. Developmental Science, 10(1), 13–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapman, R.L., Buckley, L., Sheehan, M. et al. School-Based Programs for Increasing Connectedness and Reducing Risk Behavior: A Systematic Review. Educ Psychol Rev 25, 95–114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-013-9216-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-013-9216-4