Abstract
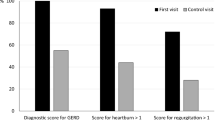
Questionnaires are widely used instruments to monitor gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. However, few of these questionnaires have been formally evaluated. We sought to evaluate our GI symptoms questionnaire in terms of clarity and reproducibility. Primary care patients referred for open access Helicobacter pylori urea breath testing reported GI symptoms (type+severity) and demographic information by written questionnaire. In an interview, patients gave a personal description of the meaning of the GI symptoms on the questionnaire. Patients’ descriptions of GI symptoms were compared with current definitions. Symptom severity scores were compared before and after, interview versus questionnaire. Of the 45 patients included, 19 (42%) described all symptoms correctly, whereas 17 (38%) described one symptom incorrectly. None of the patients made more than three mistakes. Regurgitation was the most common incorrectly described symptom (16 patients [36%]), whereas the other individual symptoms were well explained. Symptom severities before the interview, after the interview and reported by questionnaire (mean value±SEM) were 2.1 ± 0.2, 2.1 ± 0.2, and 1.5 ± 0.2 points on a 7-point Likert scale (0–6), respectively. Mean severity reported by interview (95% CI) was 1.4 (1.3–1.5) times higher than reported by questionnaire (P < .05). In conclusion, the GI symptom questionnaire is understandable and has good reproducibility for measuring the presence of GI symptoms, although symptom severity is consistently rated higher when reported by interview.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knill-Jones RP: Geographical differences in the prevalence of dyspepsia. Scand J Gastroenterol 26 (Suppl 182):17–24 1991
Garatt AM, Ruta DA, Russell I, MacLeod K, Brunt P, McKinlay A, Mowat A, Sinclair T: Developing a condition-specific measure of health for patients with dyspepsia and ulcer-related symptoms. J Clin Epidemiol 49:565–571 1996
Malfertheiner P: Current concepts in dyspepsia: a world perspective. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11 (Suppl 1):S25–29 1999
Guillemot F, Ducrotte P, Bueno L: Prevalence of functional gastrointestinal disorders in a population of subjects consulting for gastroesophageal reflux disease in general practice. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 29:243–246 2005
Wiklund I, Glise H, Jerndal P, Carlsson J, Talley NJ: Does endoscopy have a positive impact on quality of life in dyspepsia? Gastrointest Endosc 47:449–454 1998
Dimenäs E, Glise H, Hallerbäck B, Hernqvist H, Svedlund J, Wiklund I: Well-being and gastrointestinal symptoms among patients referred to endoscopy owing to suspected duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol 30:1046–1052 1995
Thomson AB, Barkun AN, Armstrong D, Chiba N, White RJ, Daniels A, Escobedo S, Chakraborty B, Sinclair P, Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJO: The prevalence of clinically significant endoscopic findings in primary care patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia: the Canadian adult dyspepsia empiric treatment—prompt endoscopy (CADET-PE) study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 17:1481–1491 2003
Ofman JJ, Shaw M, Sadik K, Grogg A, Emery K, Lee J, Reyes E, Fullerton S: Identifying patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: validation of a practical screening tool. Dig Dis Sci 47:1863–1869 2002
Bardhan KD, Stanghellini V, Armstrong D, Berghöfer P, Gatz G, Mönnikes H: International validation of ReQuestTM in patients with endoscopy-negative gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20:891–898 2004
Bardhan KD, Stanghellini V, Armstrong D, Berghöfer P, Gatz G, Mönnikes H: Evaluation of GERD symptoms during therapy. Part I. Development of the new GERD questionnaire ReQuestTM. Digestion 69:229–237 2004
Kuykendall DH, Rabeneck L, Campbell JM, Wray NP: Dyspepsia: how should we measure it? J Clin Epidemiol 51:99–106 1998
Kennedy T, Jones R: Development of a postal health status questionnaire to identify people with dyspepsia in the general population. Scand J Prim Health Care 13:243–249 1995
Agréus L, Svärdsudd K, Nyrén O, Tibblin G: Reproducibility and validity of a postal questionnaire. The abdominal symptom study. Scand J Prim Health Care 11:252–262 1993
Österberg A, Graf W, Karlbom U, Pahlman L: Evaluation of a questionnaire in the assessment of patients with faecal incontinence and constipation. Scand J Gastroenterol 31:575–580 1996
Talley NJ, Phillips SF, Melton L3rd , Wiltgen C, Zinsmeister AR: A patient questionnaire to identify bowel disease. Ann Intern Med 111:671–674 1989
Ruth M, Finizia C, Lundell L: Occurrence and future history of oesophageal symptoms in an urban Swedish population: Results of a questionnaire-based, ten-year follow-up study. Scand J Gastroentrerol 40:629–635 2005
DiBaise JK: A randomized, double-blind comparison of two different coffee-roasting processes on development of heartburn and dyspepsia in coffee-sensitive individuals. Dig Dis Sci 48:652–656 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bovenschen, H.J., Janssen, M.J.R., van Oijen, M.G.H. et al. Evaluation of a Gastrointestinal Symptoms Questionnaire. Dig Dis Sci 51, 1509–1515 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9120-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9120-6