Abstract
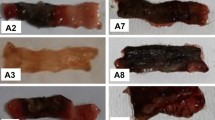
The aim of this study was to assess the efficienchyperbaric oxygen alone and in combination with 5-aminosalicylic acid in THE acetic acid–induced colitis model, a well-known experimental model of inflammatory bowel disease in rats. Rats were randomly divided into FIVE groups. In the noncolitis control group, rats were given isotonic saline, while in the other groups rats were treated by intracolonic administration of 4% acetic acid. In group 2, the untreated control group, no additional therapy was applied. In groups 3, 4, and 5 hyperbaric oxygen, 5-aminosalicylic acid. and 5-aminosalicylic acid + hyperbaric oxygen therapies were applied, respectively. Administration of acetic acid caused an inflammatory response in all animals. Histopathologic score was significantly higher in group 2 than in any other group. 5-Aminosalicylic acid and hyperbaric oxygen significantly decreased the histopathologic score (P < 0.05). Myeloperoxidase activity was also reduced significantly by 5-aminosalicylic acid (P < 0.05) but not by hyperbaric oxygen. The most prominent ameliorative effect, however, was seen in group 5 and the histopathologic score and myeloperoxidase activity were significantly lower than in groups 3 (P < 0.05) and 4 (P < 0.001). Hydroxyproline level also increased significantly in group 5, but not in groups 3 and 4 (P < 0.001). These findings indicate that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is effective in reducing the extent of colitis induced by acetic acid, although it is not as potent as 5-aminosalicylic acid. The combination of hyperbaric oxygen and 5-aminosalicylic acid, however, led to a much more prominent reduction in the severitcolitis. Hyperbaric oxygen may have a promising place in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanauer S: Medical therapy of ulcerative colitis. Lancet 342:412–417, 1993
Buchman AL, Fife C, Torres C, Smith L, Aristizibal J: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for severe ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 33(4):337–339, 2001
Grisham MB: Oxidants and free radicals in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet 24;344(8926):859–861, 1994
Lih-Brody L, Powell SR, Collier KP, Reddy GM, Cerchia R, Kahn E, Weissman GS, Katz S, Floyd RA, McKinley MJ, Fisher S, Mullin GE: Increased oxidative stress and decreased antioxidant defenses in mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 41:2078–2086, 1996
Nassif A, Longo WE, Mazuski JE, Vernava AM, Kaminski DL. Role of cytokines and platelet-activating factor in inflammatory bowel disease. Implications for therapy: Dis Colon Rectum 39:217–223, 1996
Pavlick KP, Laroux FS, Fuseler J, Wolf RE, Gray L, Hoffman J, Grisham MB: Role of reactive metabolites of oxygen and nitrogen in inflammatory bowel disease. Free Radic Biol Med 33(3):311–322, 2002
Rachmilewitz D, Karmeli F, Okon E, Rubenstein I, Better OS: Hyperbaric oxygen: a novel modality to ameliorate experimental colitis. Gut 43:512–518, 1998
Shirley PJ, Ross JAS: Hyperbaric medicine part I: theory and practice. Curr Anesth Crit Care 12:114–120, 2001
LaVan FB, Hunt TK: Oxygen and wound healing. Clin Plast Surg 17:463–472, 1990
Buras J: Basic mechanisms of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int Anesthesiol Clin 38(1):91–109, 2000
Buras JA, Stahl GL, Svoboda KK, Reenstra WR: Hyperbaric oxygen downregulates ICAM-1 expression induced by hypoxia and hypoglycemia: the role of NOS. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278(2):C292–C302, 2000
Sharon P, Stenson WP: Metabolism of arachidonic acid in acetic colitis in rats: similarity to human inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 88:55–63, 1995
Krawisz JE, Sharon P, Stenson WF: Quantitative assay for intestinal inflammation based on myeloperoxidase activity. Assessment of inflammation in rat and hamster models. Gastroenterology 87:1344–1350, 1984
Jamall IS, Finelli VN, Que Hee SS: A simple method to determine nanogram levels of 4-hydroxyproline in biological tissues. Anal Biochem 112:70–75, 1981
MacPherson BR, Pfeiffer C: Experimental production of diffuse colitis in rats. Digestion 17:135–150, 1978
Yamada T, Zimmerman BJ, Specian R, Grisham MB: Role of neutrophils in acetic acid induced colitis in rats. Inflammation 15:399–411, 1991
Strober W: Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease–an overview. Dig Dis Sci 12:3S–10S, 1985
Dong WG, Liu SP, Yu BP, Wu DF, Luo HS, Yu JP: Ameliorative effects of sodium ferulate on experimental colitis and their mechanisms in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 9(11):2533–2538, 2003
Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS, Riddell RH: Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 109(4):1344–1367, 1995
Hawkey CJ, Rampton DS: Prostaglandins and the gastrointestinal mucosa: Are they important in its function, disease, or treatment? Gastroenterology 89:1162–1188, 1985
Sharon P, Stenson WF: Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 86:453–460, 1984
Harris DW, Smith PR, Swan CH: Determination of prostaglandin synthetase activity in rectal biopsy material and its significance in colonic disease. Gut 19:875–877, 1978
Dong WG, Liu SP, Yu BP, Wu DF, Luo HS, Yu JP: Ameliorative effects of sodium ferulate on experimental colitis and their mechanisms in rats. World J Gastroenterol 9(11):2533–2538, 2003
Wahl C, Liptay S, Adler G, Schmid MR: Sulfasalazine: a potent and specific inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B. J Clin Invest 101:1163–1174, 1998
Kane SV, Bjorkman DJ: The efficacy of oral 5–ASAs in the treatment of active ulcerative colitis: a systematic review. Rev Gastroenterol Disord 3:210–218, 2003
Baker DE, Kane S: The short and long-term safety of 5-aminosalicylate products in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Rev Gastroenterol Disord 4(2):86–91, 2004
Carlin G, Djursater R, Smedegard G: Inhibitory effects of sulfasalazine and related compounds on superoxide production by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Pharmacol Toxicol 65:121–127, 1989
Sheldon P, Webb C, Grindulis KA: Effect of sulphasalazine and its metabolites on mitogen induced transformation of lymphocytes–-Clues to its clinical action? Br J Rheumatol 27:344–349, 1988
Fujiwara M, Mitsui K, Yamamoto I: Inhibition of proliferative responses and interleukin 2 production by salazosulfapyridine and its metabolites. Jpn J Pharmacol 54:121–132, 1990
Gaginella TS, Walsh RE: Sulfasalazine: multiplicity of action Dig Dis Sci 37:801–812, 1992
Harris ML, Schiller HJ, Reilly PM, Donowitz M, Grisham MB, Bulkley GB: Free radicals and other reactive oxygen metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease: cause, consequence or epiphenomenon? Pharmacol Ther 53(3):375–408, 1992
Aruom OI, Wasil M, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J: The scavenging of oxidants by sulphasalazine and its metabolites. A possible contribution to their anti-inflammatory effects? Biochem Pharmacol 36:3739–3742, 1987
Gionchetti P, Guarnieri C, Campieri M, Bellusgi A, Brignola C, Tannone P, Miglioli M, Barbara C: Scavenger effect of sulfasalazine, 5-aminosalicylic acid, and osalazine on superoxide radical generation. Dig Dis Sci 36:174–178, 1991
Simmonds NJ, Millar AD, Blake DR, Rampton DS: Antioxidant effects of aminosalicylates and potential new drugs for inflammatory bowel disease: assessment in cell-free systems and inflamed human colorectal biopsies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 13(3):363–372, 1999
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K: Structure, regulation and function of NF-kB. Ann Rev Cell Biol 10:405–455, 1994
Weber CK, Liptay S, Wirth T, Adler G, Schmid RM: Suppression of NF-kappaB activity by sulfasalazine is mediated by direct inhibition of Ikappa B kinases alpha and beta. Gastroenterology 119(5):1209–1218, 2000
Isik AT, Mas MR, Comert B, Yasar M, Korkmaz A, Akay C, Deveci S, Tasci I, Mas N, Ates Y, Kocar IH: The effect of combination therapy of hyperbaric oxygen, meropenem, and selective nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in experimental acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 28(1):53–57, 2004
Korkmaz A, Oter S, Deveci S, Ozgurtas T, Topal T, Sadir S, Bilgic H: Involvement of nitric oxide and hyperbaric oxygen in the pathogenesis of cyclophosphamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. J Urol 170(6, Pt 1):2498–2502, 2003
Oztas E, Kilic A, Ozyurt M, Korkmaz A, Basustaoglu A: Effect of hyperbaric oxygen and penicillin in a murine model of streptococcal myositis. Undersea Hyperb Med. 28(4):181–186, 2001
Quirinia A, Viidik A: The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on different phases of healing of ischaemic flap wounds and incisional wounds in skin. Br J Plast Surg 48(8):583–589, 1995
Brady CE, Cooley BJ, Davis JC: Healing of severe perineal and cutaneous Crohn’s disease with hyperbaric oxygen. Gastroenterology 97:756–760, 1989
Colombel JF, Mathieu D, Bouault JM, Lesage X, Zavadil P, Quandelle P, Cortot A: Hyperbaric oxygenation in severe perineal Crohn’s disease. Dis Colon Rectum 38:609–614, 1995
Lavy A, Weisz G, Adir Y, Ramon Y, Eidelman S: Hyperbaric oxygen for perianal Crohn’s disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 19:202–205, 1994
Nelson EW JR, Bright DE, Villar LF: Closure of refractory perineal Crohn’s lesion: integration of hyperbaric oxygen into case management. Dig Dis Sci 35:1561–1565, 1990
Gulec B, Yasar M, Yildiz S, Oter S, Akay C, Deveci S, Sen D: Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on experimental acute distal colitis. Physiol Res 53:493–500, 2004
Weisz G, Lavy A, Adir Y, Melamed Y, Rubin D, Eidelman S, Pollack S: Modification of in vivo and in vitro TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-6 secretion by circulating monocytes during hyperbaric oxygen treatment in patients with perianal Crohn’s disease. J Clin Immunol 17(2):154–159, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorgulu, S., Yagci, G., Kaymakcioglu, N. et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Enhances the Efficiency of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid in Acetic Acid–Induced Colitis in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 51, 480–487 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3159-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3159-2